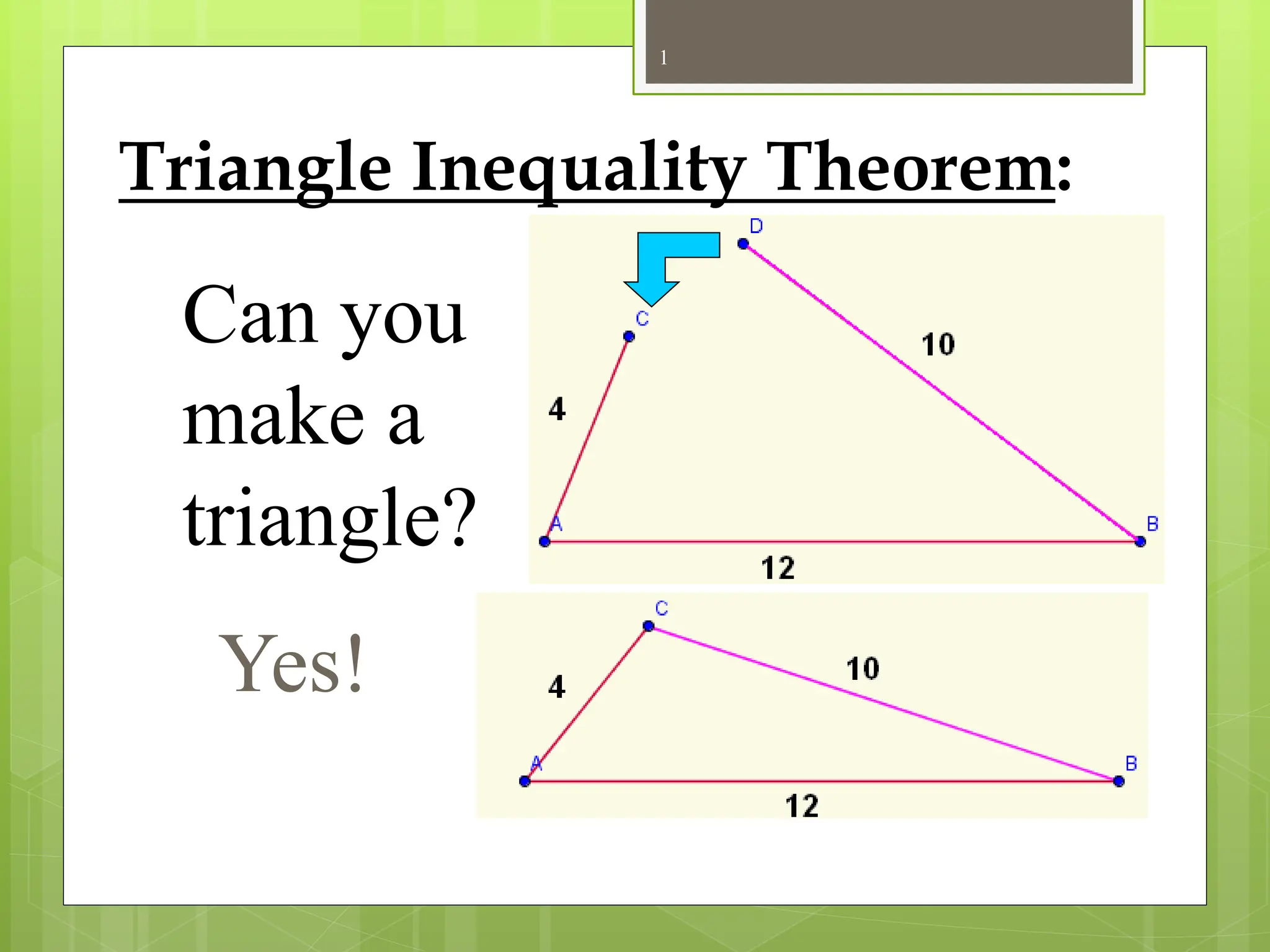
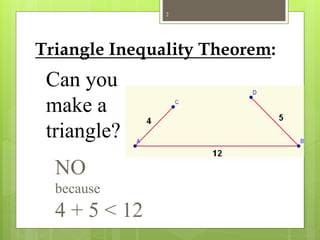
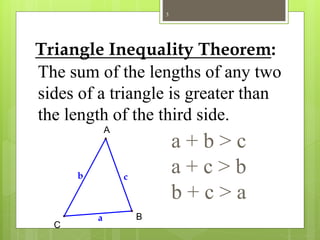
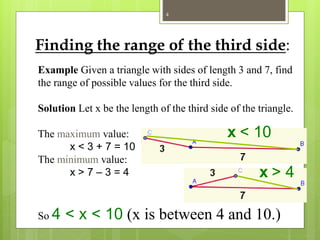
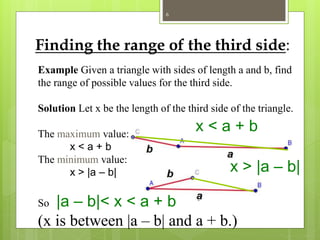
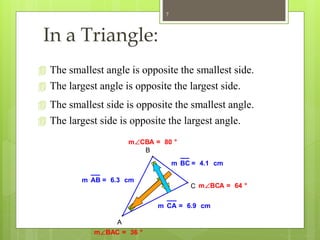
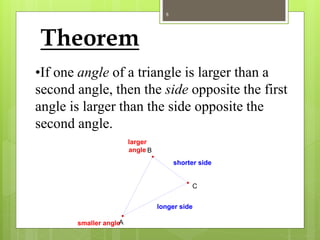
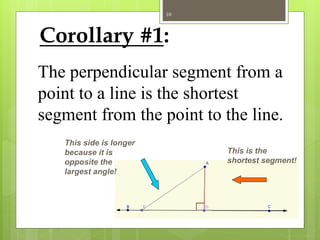
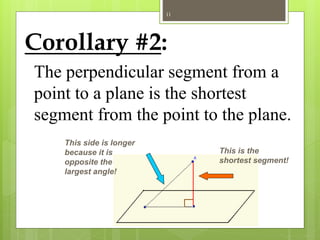
The document explains the triangle inequality theorem, which states that the sum of the lengths of any two sides of a triangle must be greater than the length of the third side. It also describes how to find the range of possible lengths for the third side when two sides are known, using the concepts of maximum and minimum values derived from the given side lengths. Additionally, it discusses relationships between angles and sides in a triangle and includes corollaries about the shortest segments from a point to a line or plane.