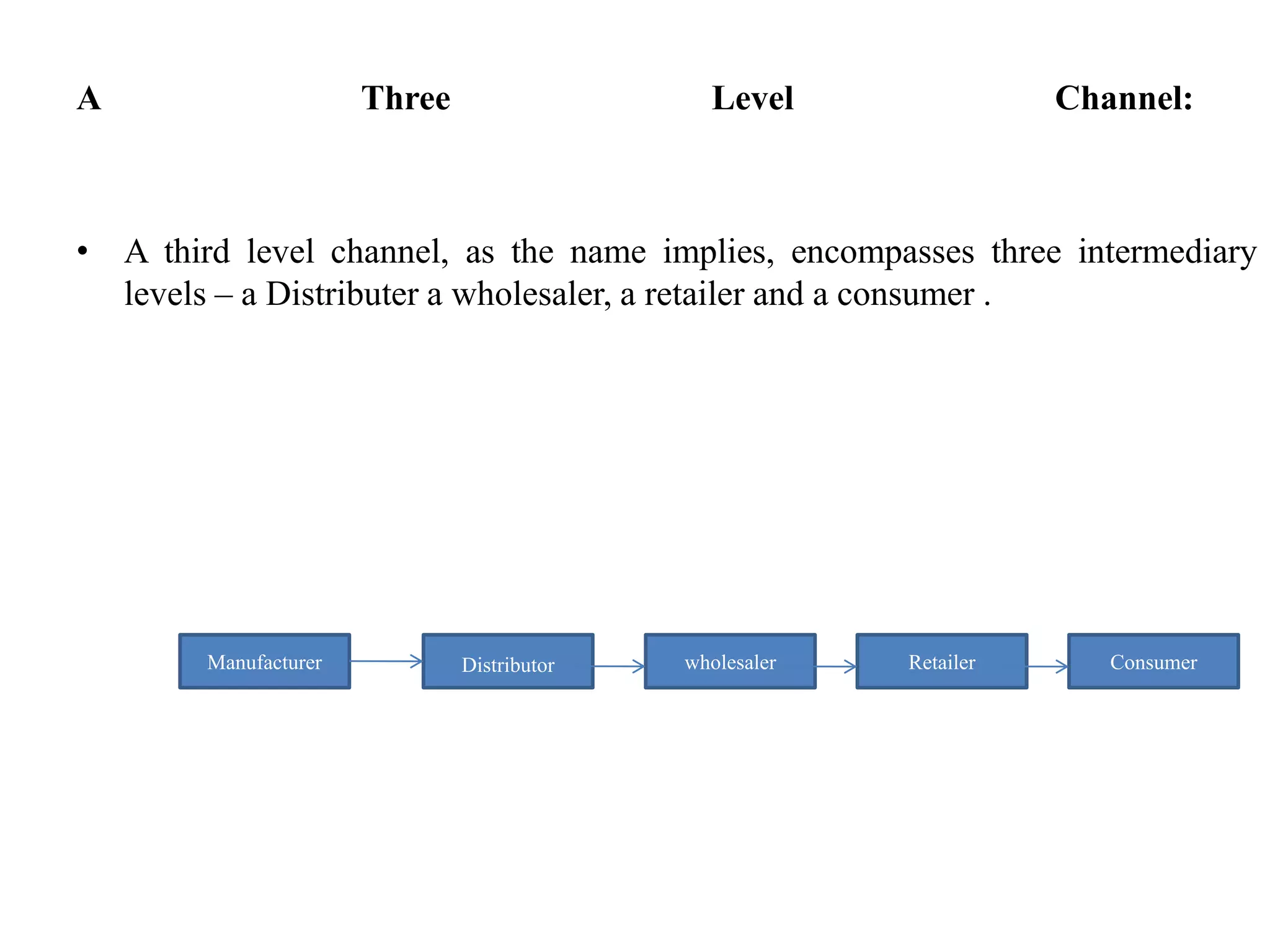
This document discusses marketing channels and distribution. It defines distribution channels as the flow of goods from production to the consumer. Traditional distribution involves manufacturers selling directly to consumers without intermediaries. The document outlines strategies for direct sales and notes advantages of introducing brokers, which include established retailer relationships but higher fees. E-commerce changes distribution by allowing direct sales and reducing intermediaries. The document also defines zero-level to three-level distribution channels involving varying numbers of intermediaries like distributors and wholesalers. Finally, it discusses types of channel conflicts like horizontal conflicts between same-level players and vertical conflicts between different channel members.