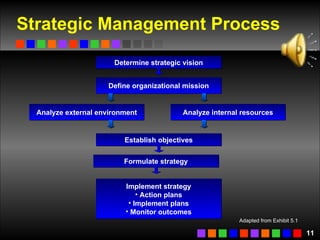
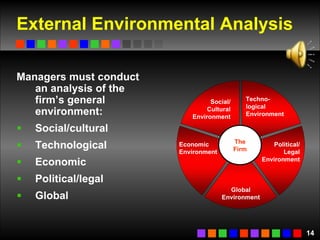
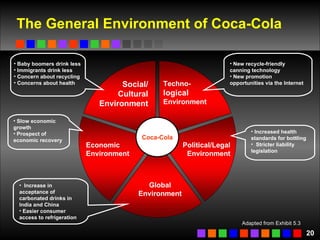
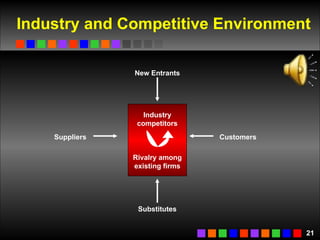
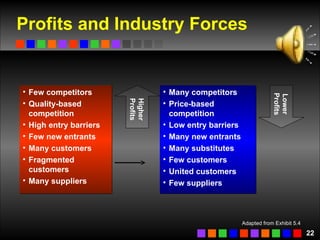
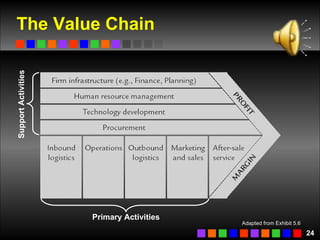
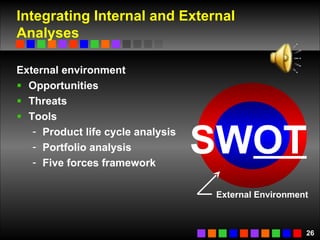
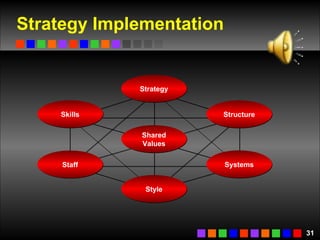
The document discusses strategic management concepts including competitive advantage, the strategic management process, environmental analysis, and strategy formulation and implementation. It defines competitive advantage as having superior value, rarity, difficulty to imitate, and non-substitutability. The strategic management process involves setting direction, analyzing internal/external environments, formulating strategy, implementing plans, and monitoring outcomes. Environmental analysis examines social, technological, economic, political, and global forces. Strategy is formulated using tools like SWOT analysis and value chain analysis.