This document discusses the effectiveness of fiscal policy using the IS-LM model. It shows how an increase in government spending shifts the IS curve to the right. The degree of effectiveness depends on the slope of the IS curve, with a steeper curve indicating lower interest rate elasticity of investment. A steeper IS curve means fiscal policy has a greater impact on output as less crowding out of investment occurs from rising interest rates. The document demonstrates this concept through three panels showing different IS curve slopes.
![PANEL A r
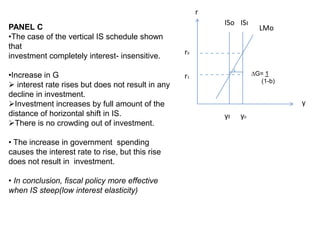
•The IS schedule is steep, investment is LMo
relatively
interest inelastic
r1
•Less sensitive the investment is to interest
rate, more effective fiscal policy.
r0 ∆G= 1
• The horizontal distance of the shift in the (1-b)
schedule ∆G [1/ (1-b) ] meaning that the size
of the policy action as well as the
autonomous expenditure multiplier that the
simple Keynesian model as equal. ISo ISı
y
• When G rises, Y rises
r must rises to keep the money market in y0 yı
equilibrium
The rise in r causes investment to fall,
partially offsetting the expansionary effect of
the increase in G.
Interest rate induced declined in I causes
income response given by the multiplier.
• Income rises by less than the horizontal
shift in IS](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/makroslide-121019112617-phpapp01/75/Makro-silide-1-2048.jpg)
![r
PANEL B
• Shows the effects of an increase in
government spending in the case of a LMo
relatively flat IS schedule.
• The increase in government spending shifts r1
∆G= 1
r0
the IS schedule from IS0 to IS1 (1-b)
• The horizontal distance of the shift in the
schedule ∆G [1/ (1-b) ] meaning that the size ISı
of the policy action as well as the autonomous ISo
y
expenditure multiplier that the simple y0 yı
Keynesian model as equal.
• This fiscal policy action is much less effective
in panel B, where the IS schedule is relatively
flat.
• Income in Panel B, increased less than
income Panel A because fiscal policy more
effective when IS steep(low interest elasticity).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/makroslide-121019112617-phpapp01/85/Makro-silide-2-320.jpg)