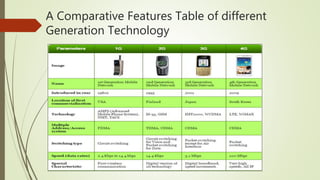
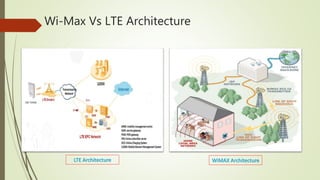
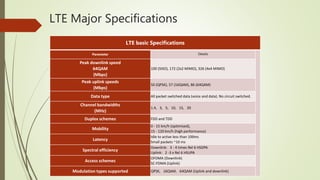
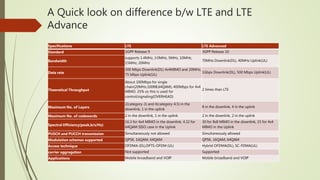
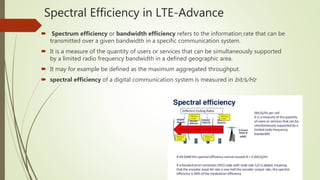
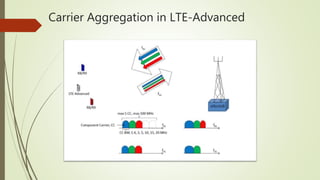
LTE is an IP-based broadband network technology developed by 3GPP as an evolution of 3G mobile networks. It provides higher data rates and an improved end-to-end solution for delivery of voice, data and multimedia to users. Key aspects of LTE include support for wider channel bandwidths up to 20MHz, OFDMA on the downlink and SC-FDMA on the uplink, peak data rates of 100Mbps downlink and 50Mbps uplink, and backward compatibility with 2G and 3G networks. LTE Advanced further enhances LTE through the use of carrier aggregation to bond multiple component carriers, support for higher order MIMO up to 8x8, and theoretical peak data rates