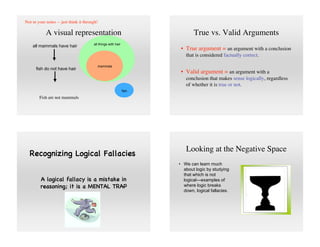
Socrates, Plato, and Aristotle are considered the founders of Western philosophy. Socrates developed the Socratic method of questioning beliefs and examining ideas. Plato was Socrates' student and founded The Academy. Aristotle was both Plato's student and the tutor of Alexander the Great. He made significant contributions to logic and established the basis of scientific reasoning. Aristotle defined logic as the study of correct reasoning and developed formal rules for deduction and induction. Syllogisms and the scientific method are two logical systems developed by Aristotle.