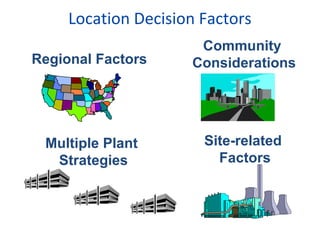
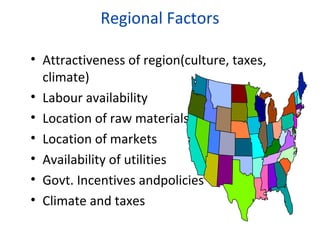
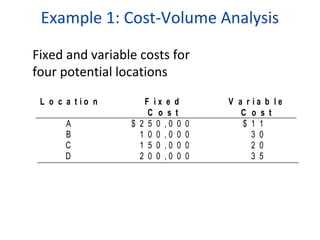
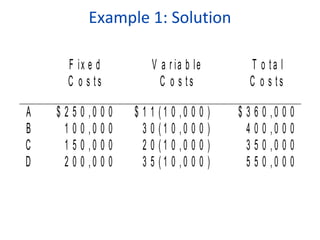
This document discusses various factors to consider when making location decisions for facilities. It identifies the strategic importance of location decisions and objectives like profit potential. Key factors include availability of infrastructure, resources, labor, transportation and costs. Methods for evaluating locations are described, such as cost-volume analysis to determine the location with the lowest total costs based on fixed and variable costs. The factor-rating method scores locations based on weights assigned to relevant factors. Location decisions require analyzing regional, community, site and multiple plant strategies. Manufacturing and service facilities have different location considerations.












![Factor-Rating Method
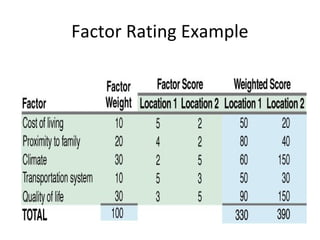
•
Six steps:
1. Develop a list of relevant factors.
2. Assign a weight to each factor reflecting its relative
importance to the firm.
3. Develop a rating scale for the factors.
4. Score each location on each factor based on the scale.
5. Multiply the scores by the weights for each factor and total
the weighted scores for each location.
6. Make a recommendation based on the maximum point
score, considering other [quantitative?] factors.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/locationdecision-140117103611-phpapp01/85/Location-decision-19-320.jpg)