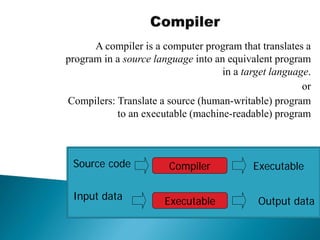
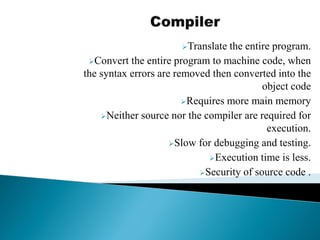
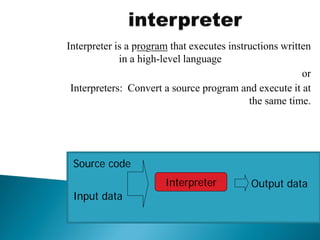
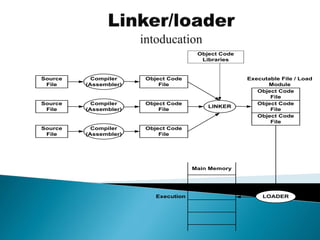
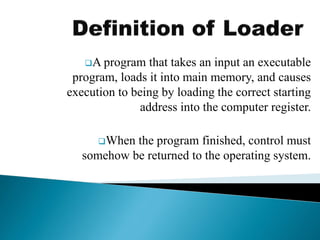
The document discusses different types of software used in the compilation and execution process of a computer program. It describes compilers, interpreters, linkers, and loaders.
Compilers translate source code into executable machine code, while interpreters convert and execute source code line-by-line. Linkers combine object files into a single executable file, resolving references between modules. Loaders load the executable into memory and start execution by setting the starting address. The document also discusses different types of system software, application software, and utility software.