This document defines and provides examples of different types of numeric sequences:
- Linear/arithmetic sequences have a constant difference between consecutive terms. Formulas use the first term and common difference.
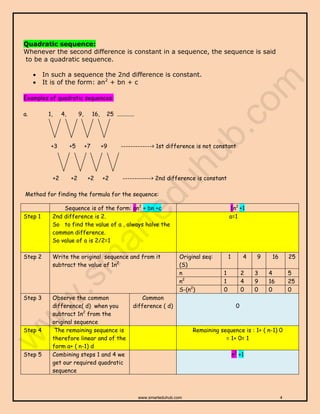
- Quadratic sequences have a constant second difference; their formulas are of the form an^2 + bn + c.
- Cubic sequences have a constant third difference; their formulas are of the form an^3 + bn^2 + cn + d.
Step-by-step methods are provided for determining the formulas for quadratic and cubic sequences based on analyzing differences between terms. Worked examples demonstrate finding common differences and deriving sequence formulas.


![Cubic sequences:
Sequences where the 3rd difference is constant are known as cubic sequences.
Cubic sequences are of the form:
an3
+ bn2
+ cn + d
Examples:
0 12 10 0 -12 -20
1st difference +12 -2 -10 -12
2nd difference -14 -8 -2
3rd difference +6 +6
3rd difference is constant so it is a cubic sequence .
It is of the form: an3
+ bn2
+ cn + d = n3
-13n2
Step 1: Value of a= 1/6 X( 3rd difference) = 1/6 X (6) = 1 . Hence a=1.
Step 2: Write original sequence and subtract an3
i.e. n3
from it as shown below.
S 0 12 10 0 -12 -20
1n3
1 8 27 64 125 216
s-1n3
= our new sequence -1 +4 -17 -64 -137 -236
1st Common difference
2nd common difference
+5 -21 -47 -73
-26 -26 -26
2nd common difference 2nd difference is constant so our new sequence is quadratic and of the
form bn2
+ cn +d; where b=-26/2 = -13
Performing this operation:
[S-( n3
-13n2
)];
leaves us with a linear
sequence and we get the
part cn+d
S 0 12 10 0 -12
n 1 2 3 4 5
( n3
-13n2
) (1-13)=
-12
8-52=
-44
27-117=
-90
64-208
=-144
125-325
=200
Finally the required
sequence is
s-( n3
-13n2
) 12 56 100 144 -212
Common difference is
44.Sequence is linear +44 +44 +44 +44
Formula for the linear
sequence is 12 + (n-1) 44 = 12 + 44n-44 = 44n+32
Ans: Cubic sequence is n3
- 13 n2
+ 44n +32
w
w
w
.sm
arteduhub.com
www.smarteduhub.com 5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/numbersequences-150920142433-lva1-app6891/85/Linear-Quadratic-and-Cubic-sequences-5-320.jpg)