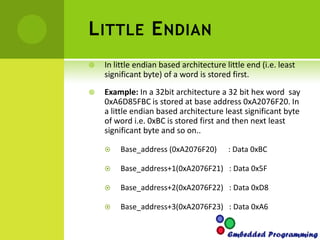
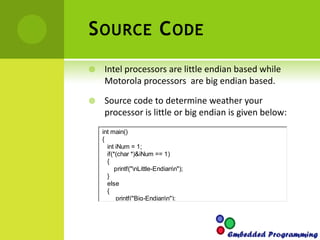
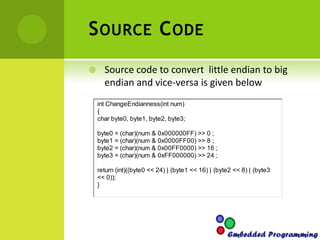
This document discusses endianness in computing. It defines endianness as the order in which bytes of a word are stored in computer memory. There are two types: little endian, where the least significant byte is stored first, and big endian, where the most significant byte is stored first. Intel processors use little endian format while Motorola processors use big endian. The document provides code samples to determine a processor's endianness and to convert between little and big endian formats.