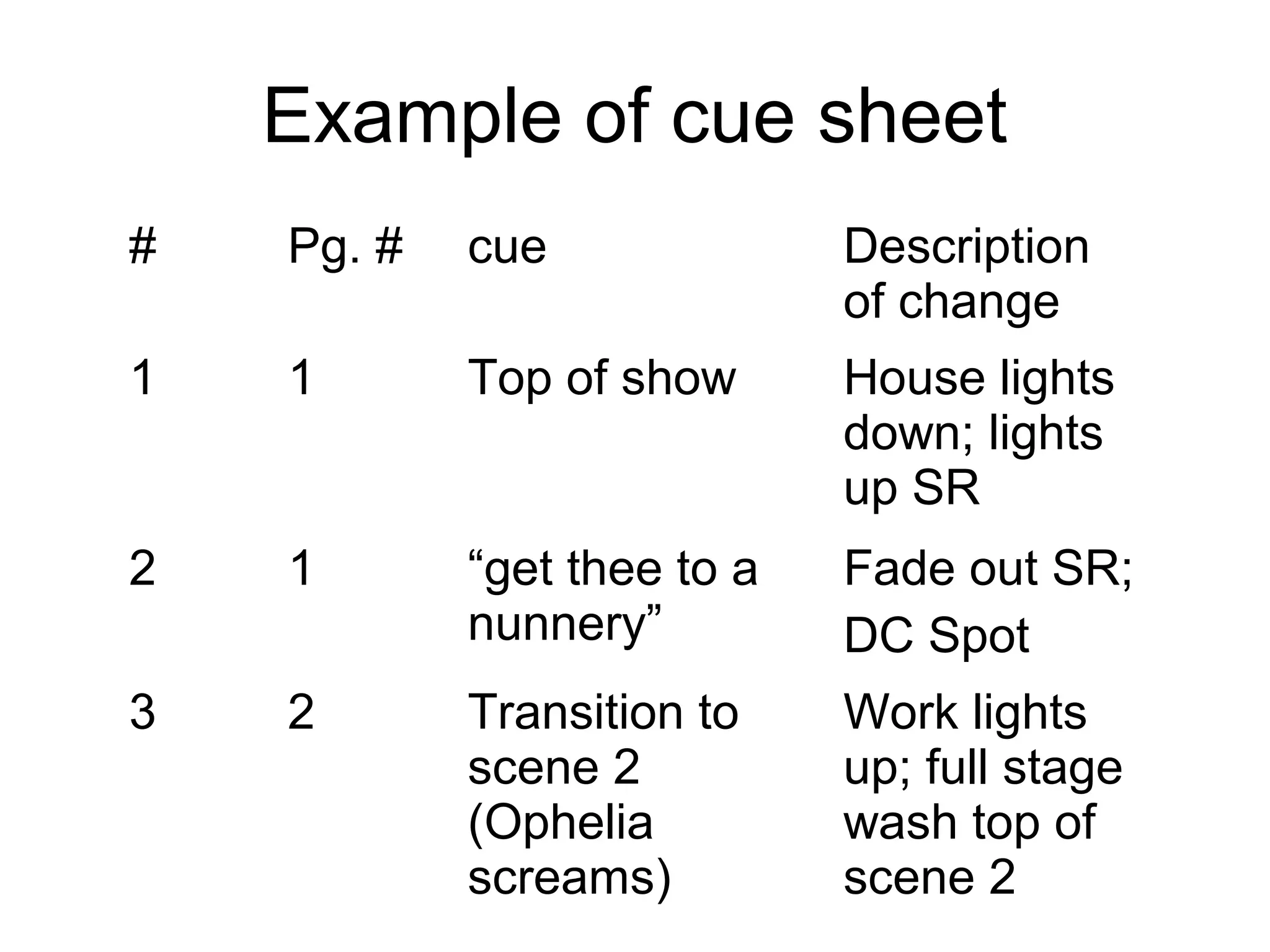
This document discusses the functions and processes of lighting and sound design for theatre. It explains that lights are used to see actors, focus audience attention, create mood, and establish interior/exterior sources. Specific lighting instruments like spots, washes and gels are discussed. The lighting design process involves reading the script, meeting with the director, creating a light plot and cue sheet. For sound design, the major functions are establishing mood, providing realistic sounds, and situating the audience. The document discusses using music and effects to set mood and provide realism. The sound design process is similar to lighting, involving script analysis and creating a cue sheet.