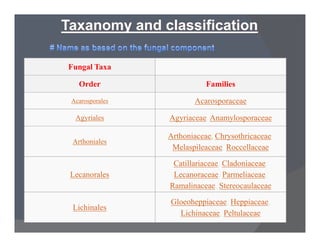
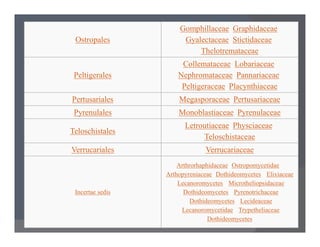
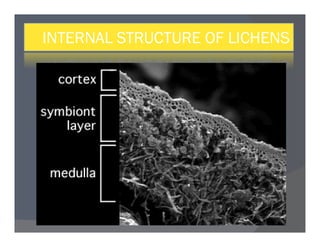
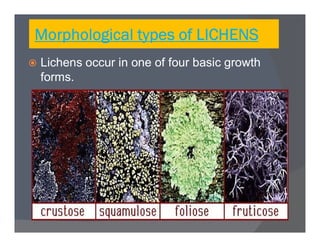
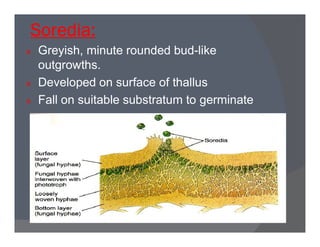
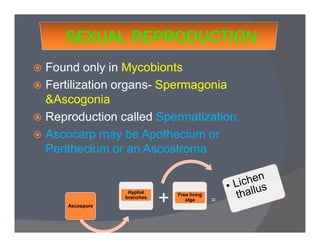
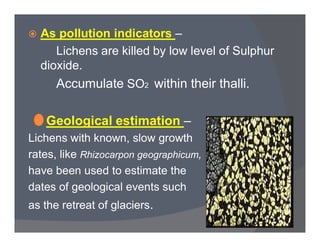
Lichens are a symbiotic partnership between a fungus and an alga or cyanobacterium. There are estimated to be 15,000-20,000 lichen species that can grow in crustose, foliose, or fruticose forms. Lichens reproduce asexually through structures like soredia, isidia, and soralia or sexually through spores. They have economic importance as food, medicine, dyes, indicators of pollution, and in geological estimations. A recently discovered lichen was named after Barack Obama.