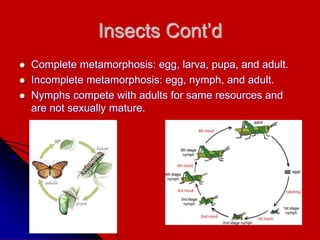
The document provides an overview of the phylum Arthropoda, which includes insects, arachnids, crustaceans, and others. It discusses their shared characteristics like jointed appendages and exoskeletons. It then describes some of the major classes within the phylum, including Insecta, Arachnida, Crustacea, Chilopoda, and Diplopoda. Key details are provided on traits and examples for each group.