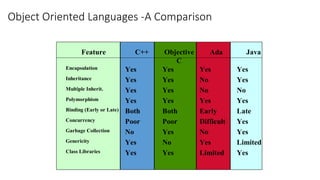
This document provides an introduction to Java programming concepts including:
1. Java was originally created by Sun Microsystems in 1991 for consumer electronics and later adapted for internet programming.
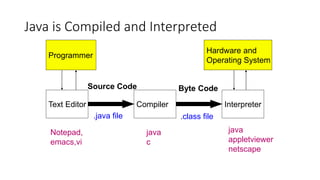
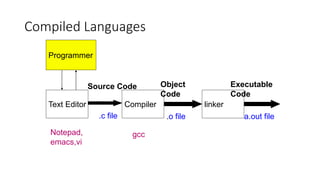
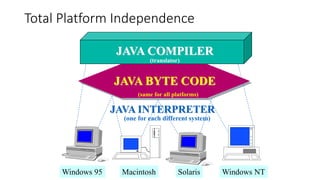
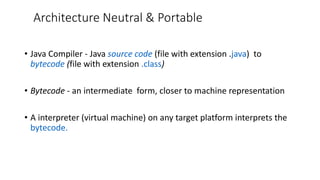
2. Java code is compiled to bytecode that can be run on any system with a Java Virtual Machine, making it platform independent.
3. Key characteristics of Java include being simple, object-oriented, distributed, interpreted, robust, secure, architecture-neutral, portable, multithreaded, and dynamic.