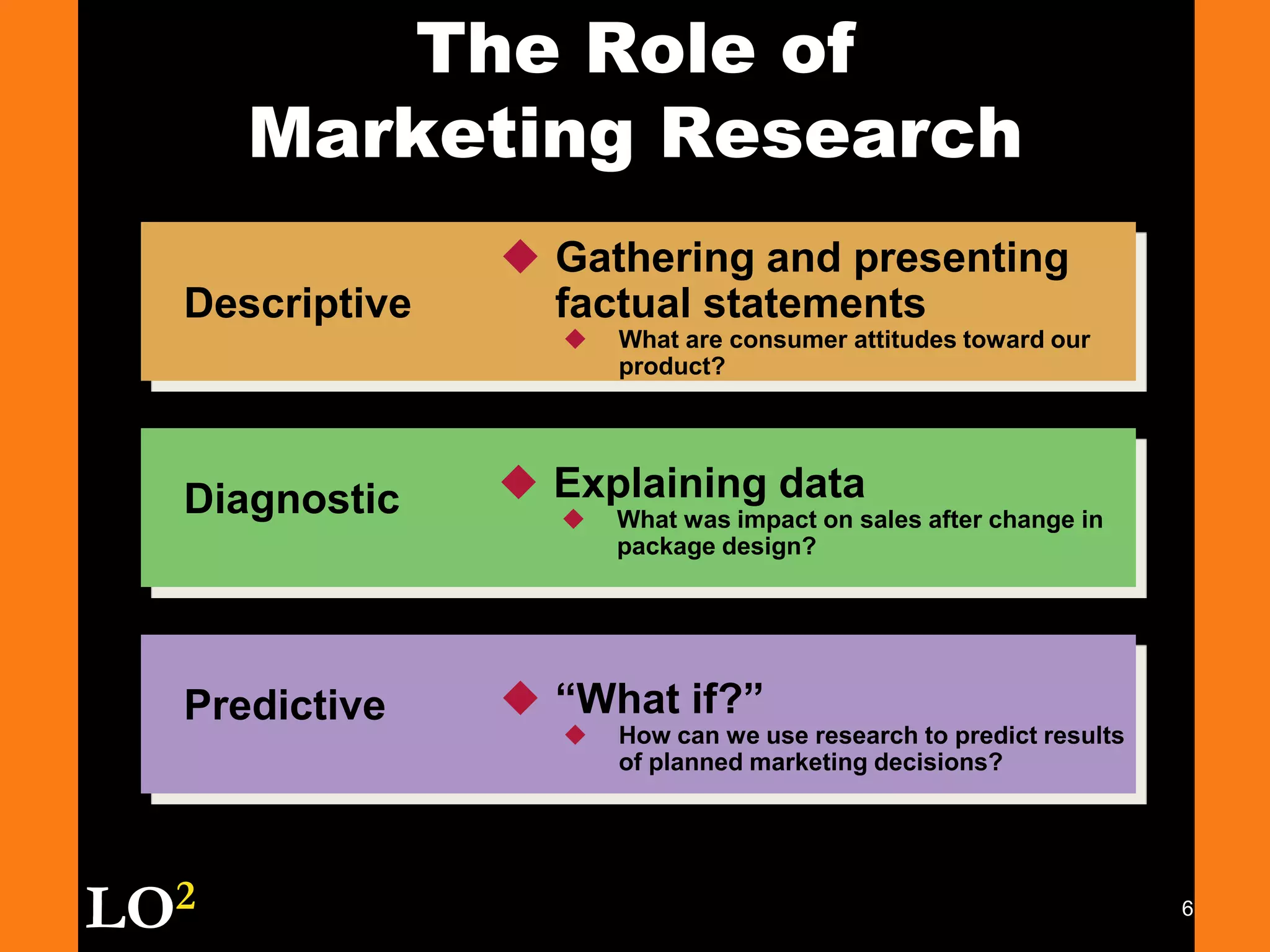
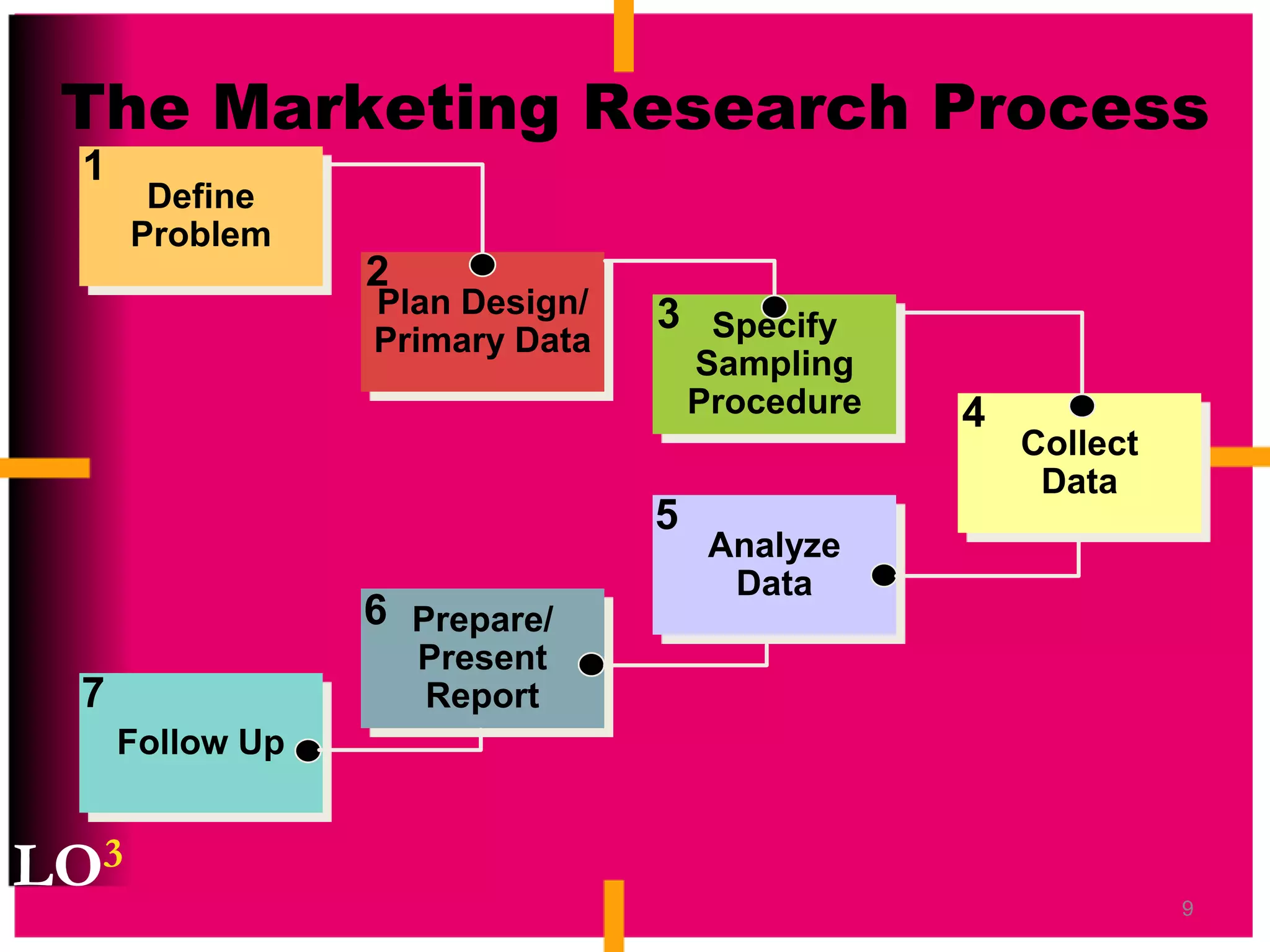
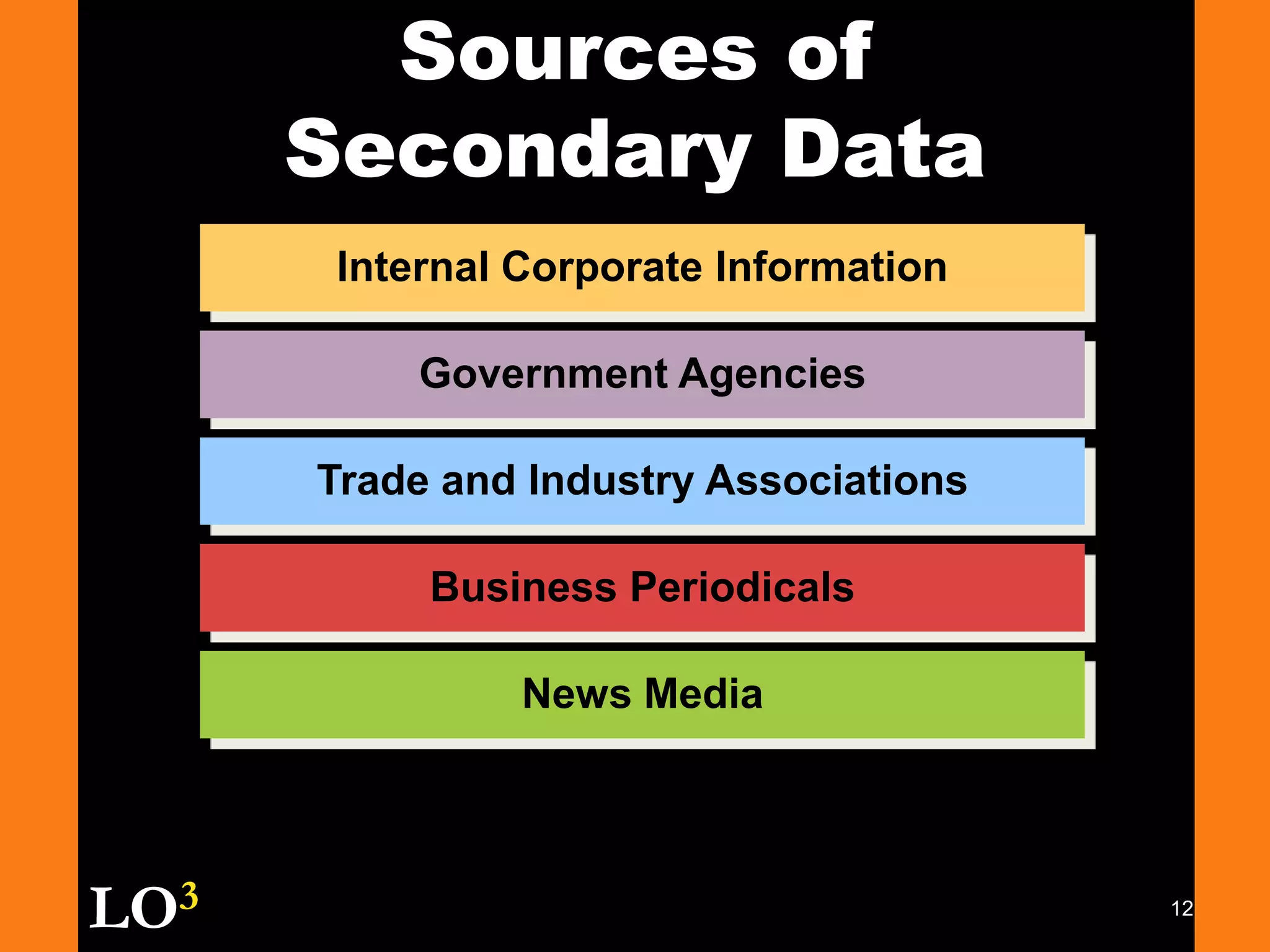
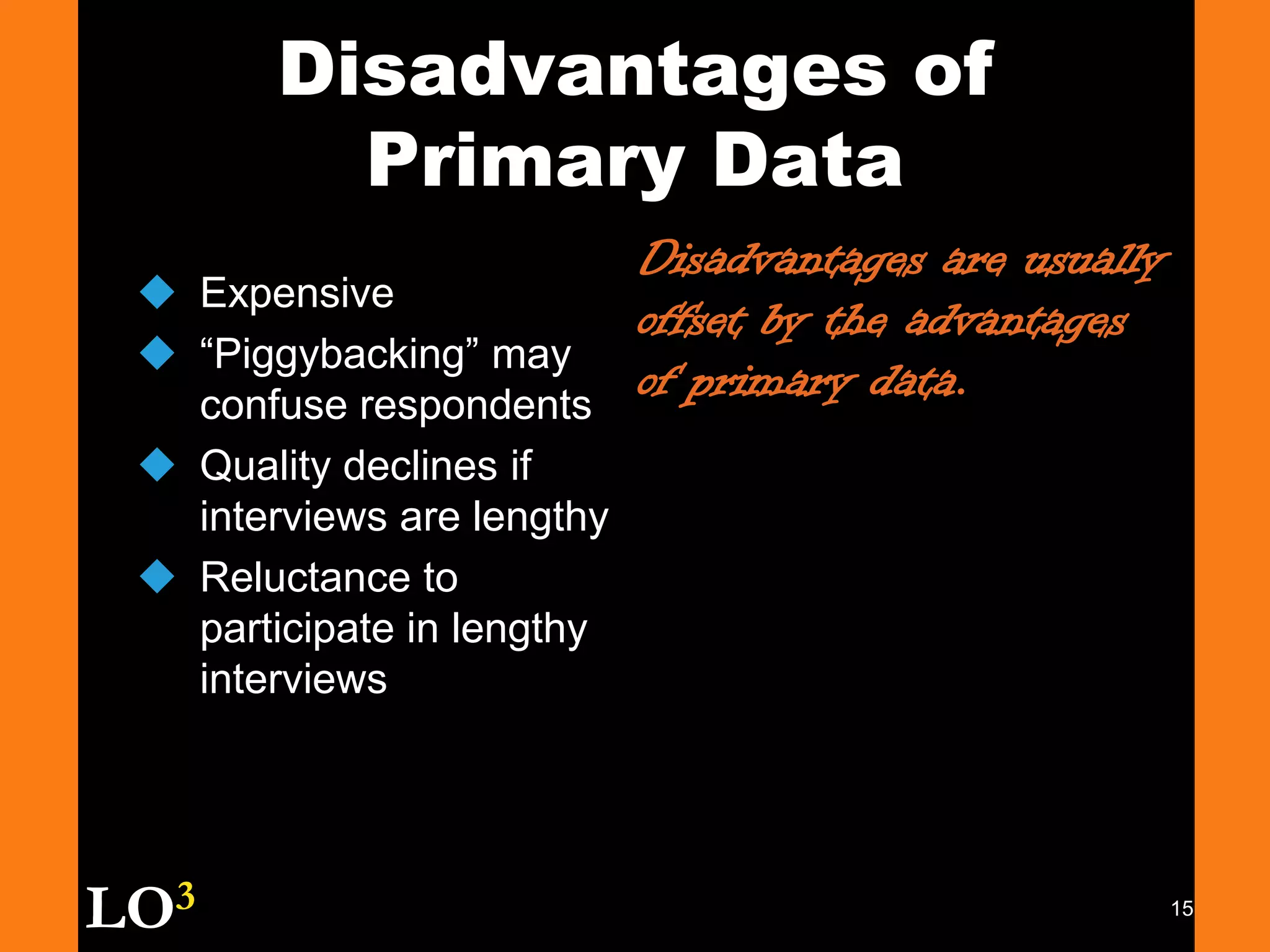
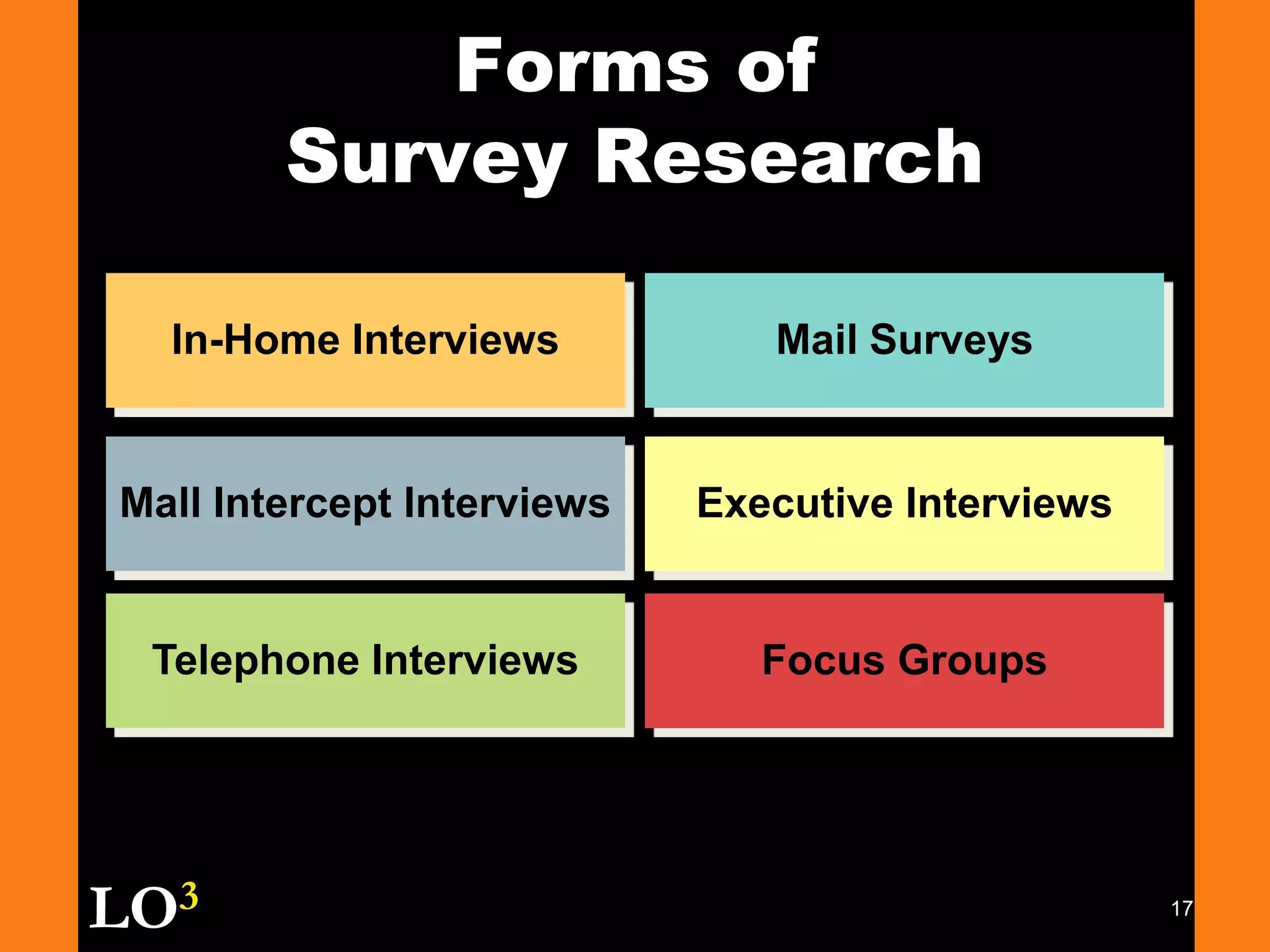
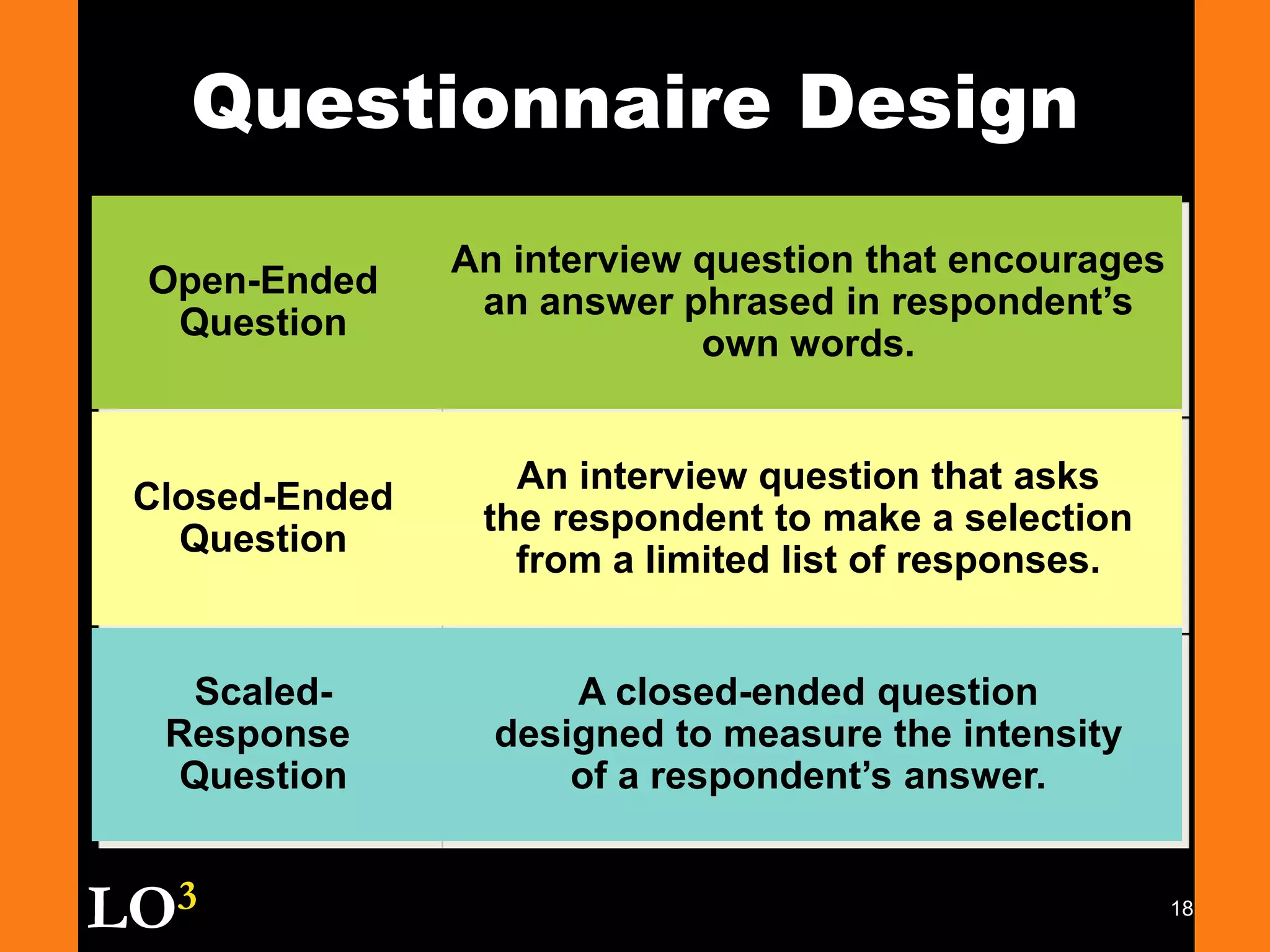
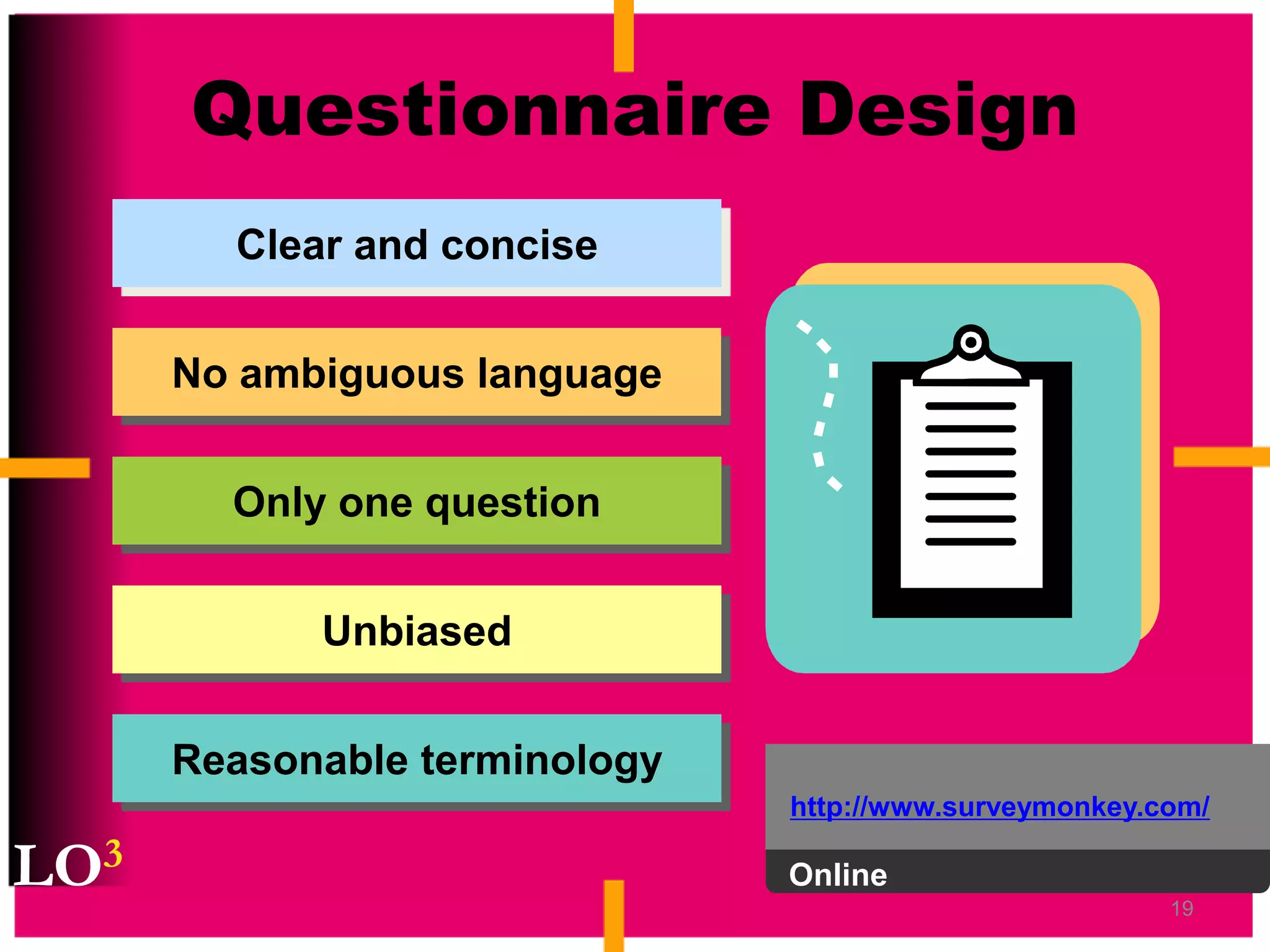
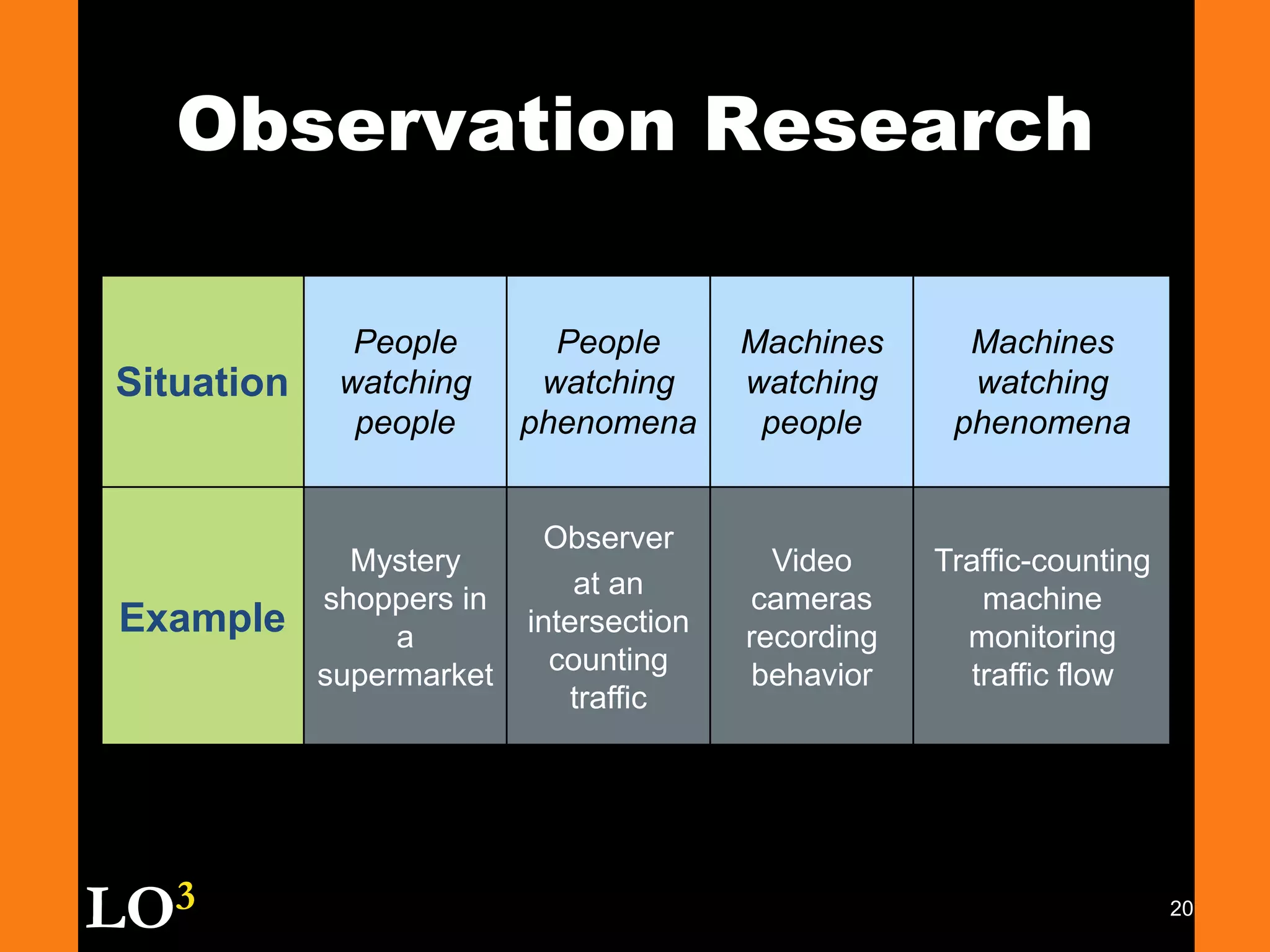
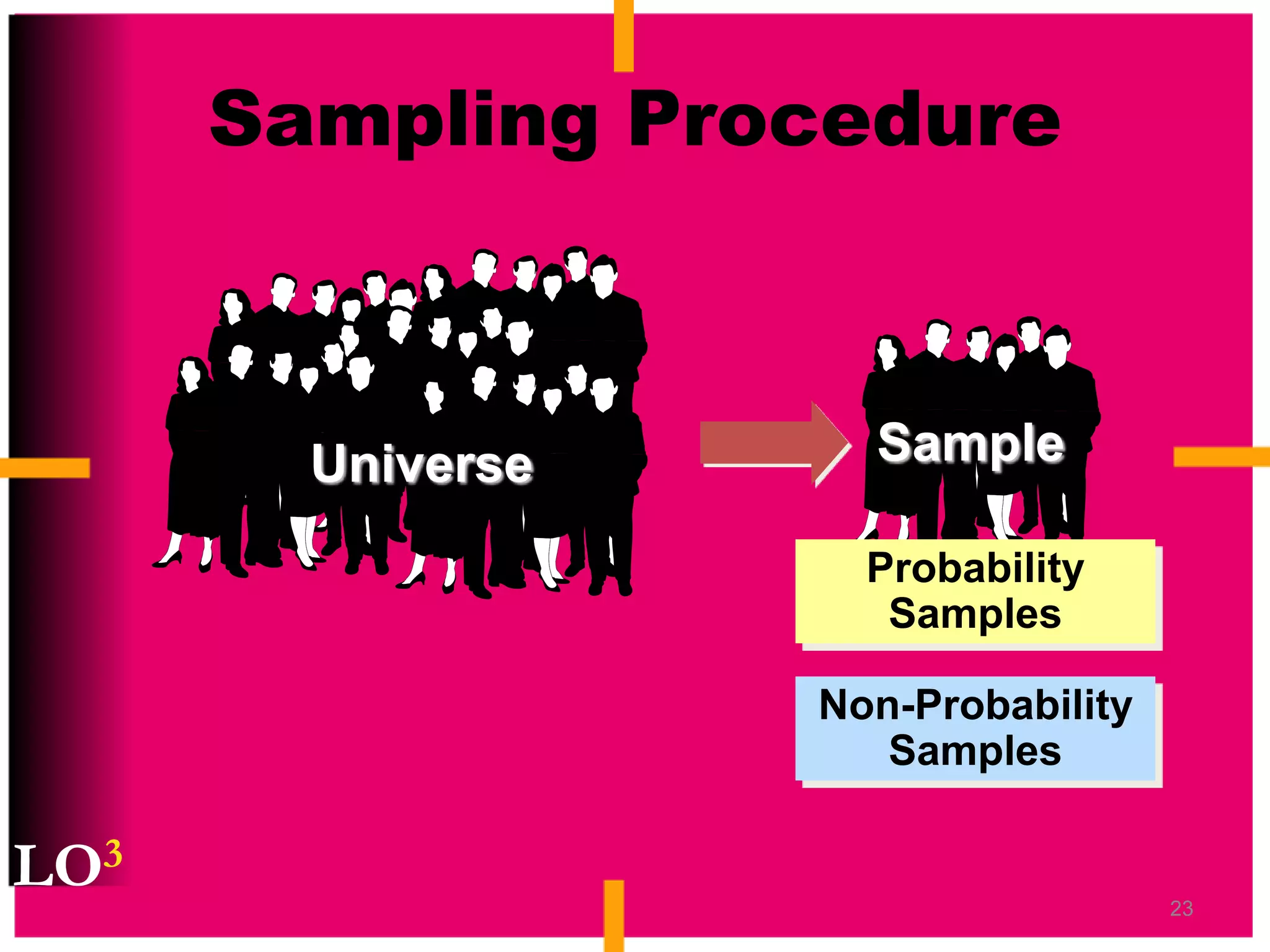
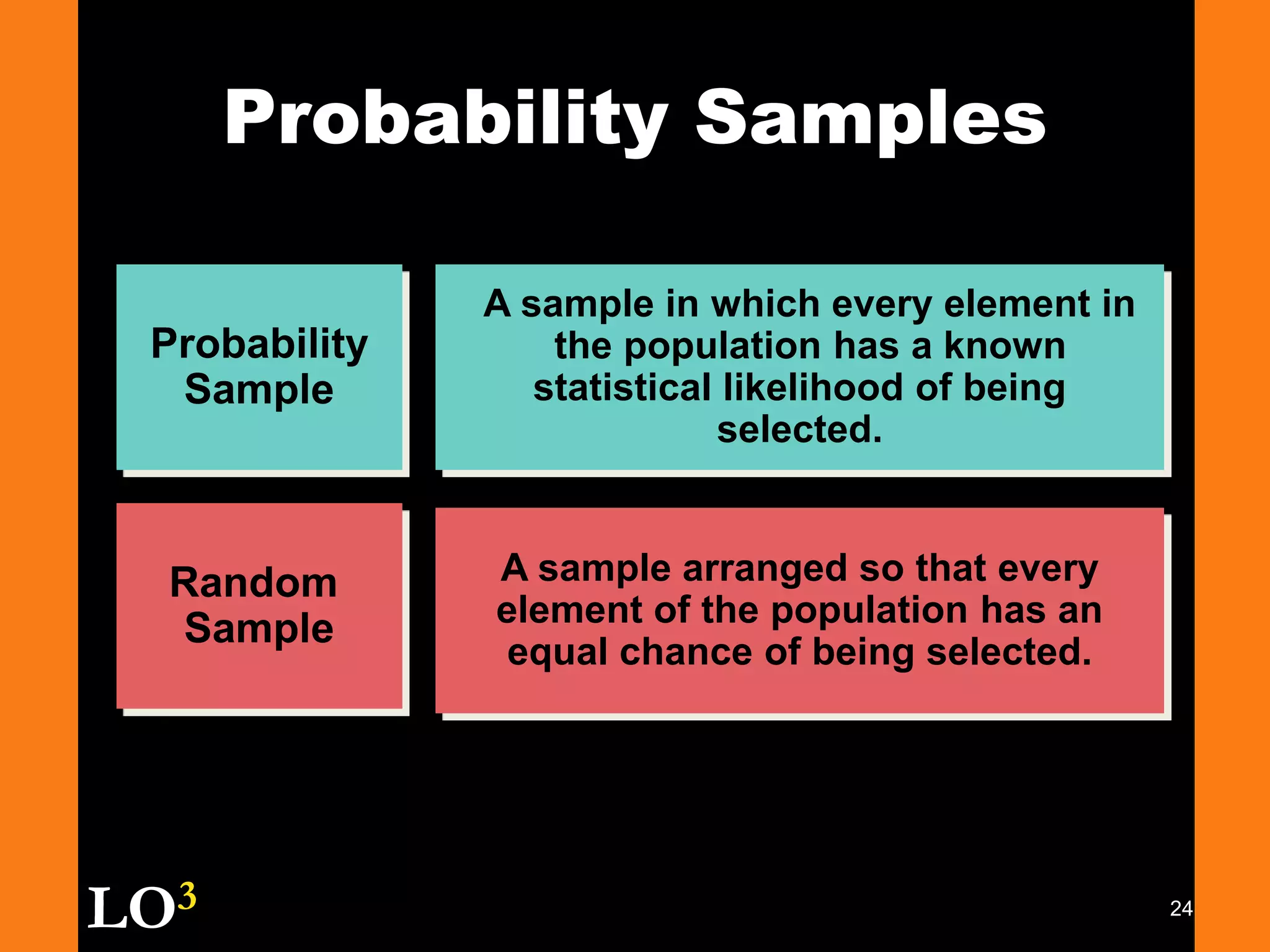
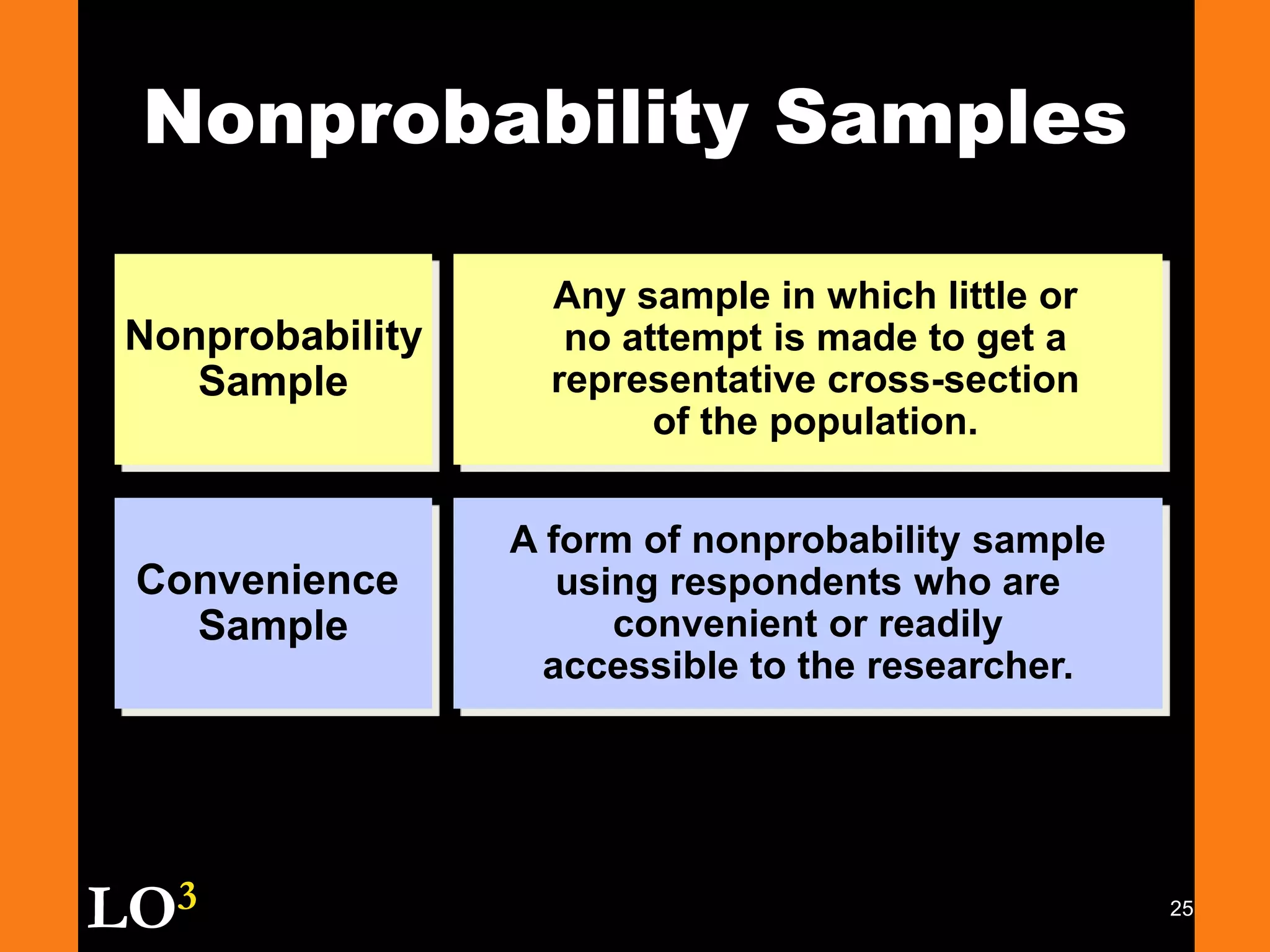
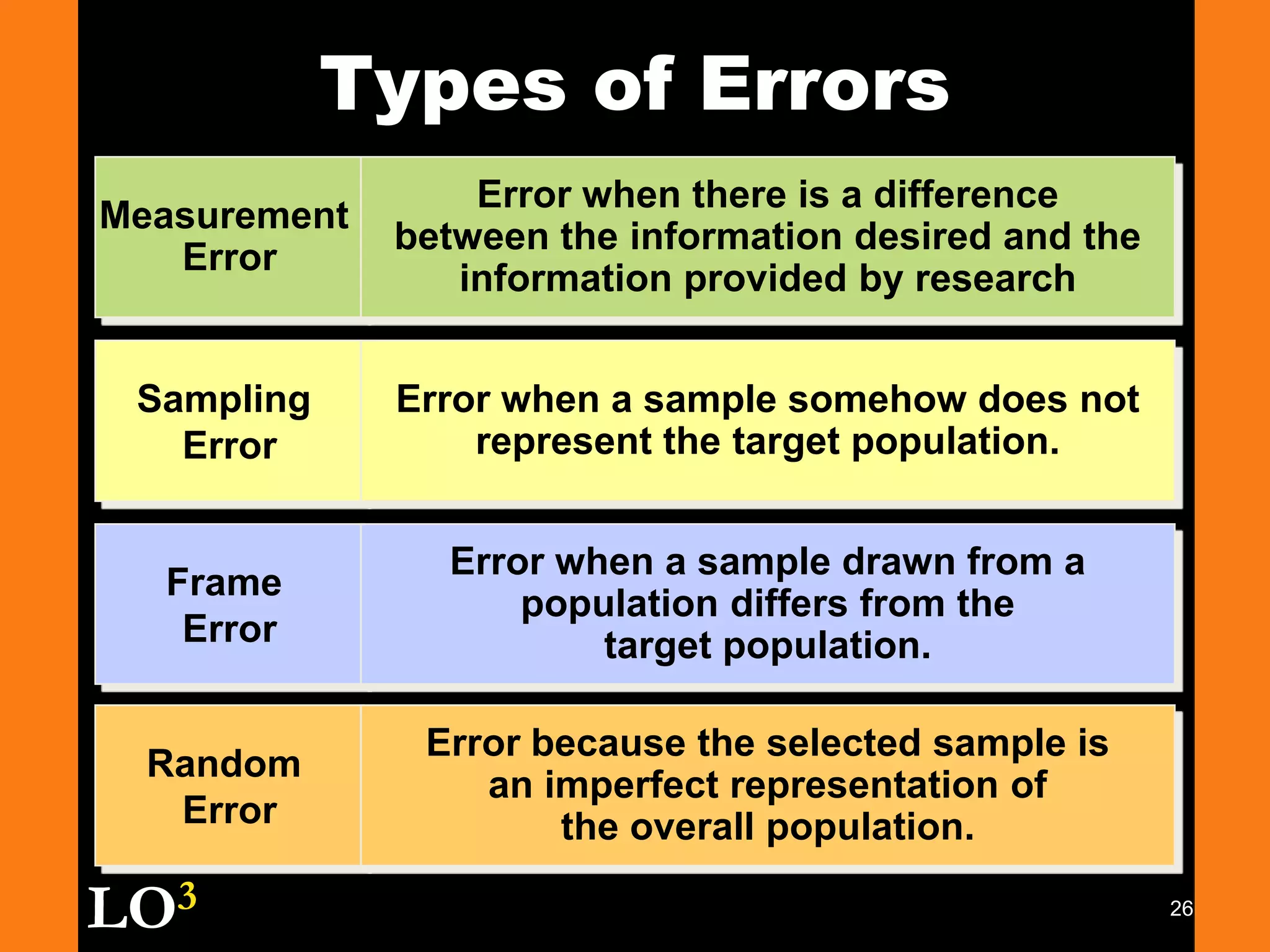
Marketing decision support systems use large databases of customer profiles and purchase patterns as a key tool for one-to-one marketing. Marketing research is the process of planning, collecting, and analyzing data relevant to marketing decisions and improves decision making by understanding markets and tracing problems. Marketing research projects generally follow steps of defining the problem, planning the research design, collecting and analyzing data, and presenting findings.