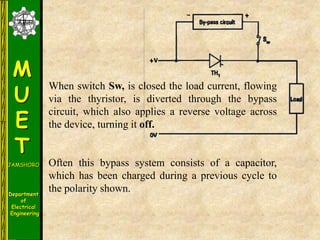
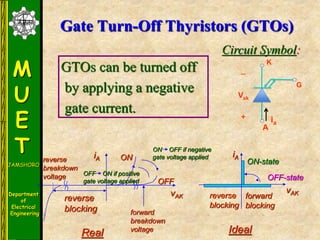
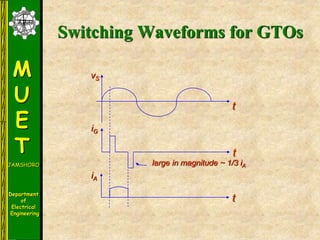
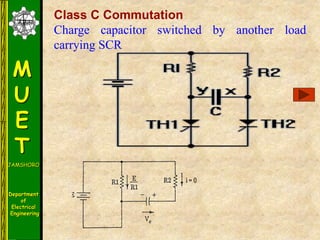
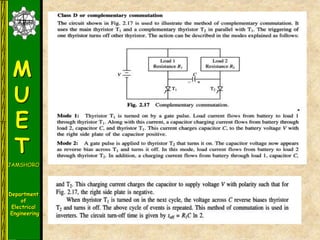
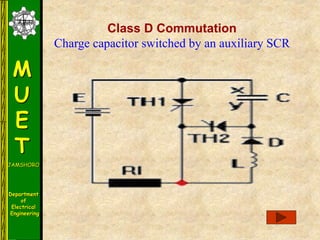
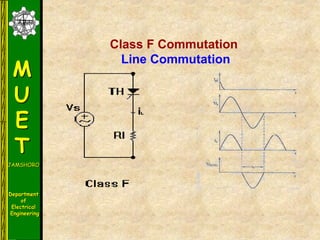
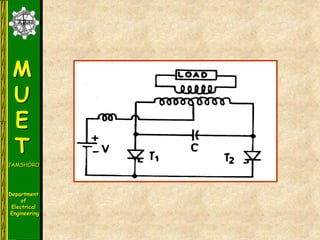
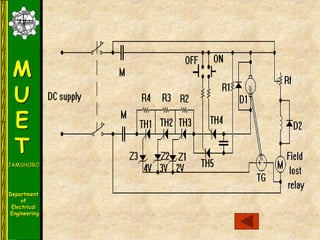
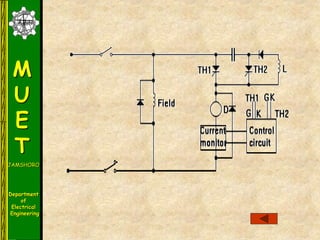
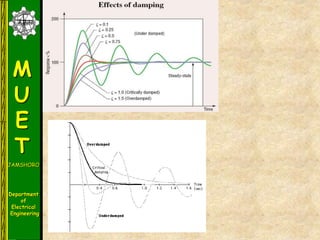
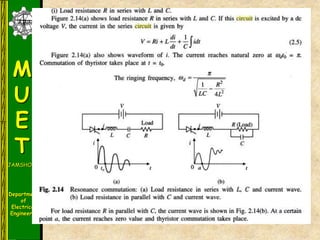
The document discusses various methods for turning off thyristors, including natural commutation, load commutation, forced commutation, and gate turn-off. It describes six classes of commutation circuits (A through F) that are used to force the current through a conducting thyristor to zero and subject it to reverse bias in order to turn it off. Class A commutation uses a resonant load circuit to naturally commutate the thyristor. Class C commutation uses another load-carrying thyristor to divert the current and charge a capacitor that reverse biases the first thyristor.