This document discusses conformal mapping, which maps curves and regions in such a way that preserves angles and their directions. It provides examples of conformal mappings:
1) The mapping w = ez maps a vertical line in the z-plane to a circle in the w-plane, with the phase angle increasing along the circle.
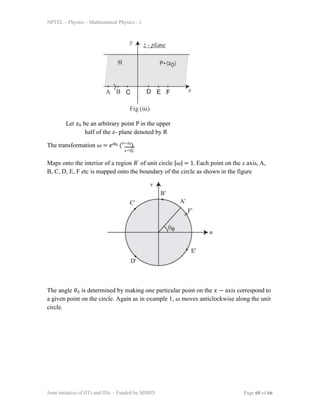
2) The mapping ω = eiθ0(z-z0)/(z-z0) maps an area in the upper half z-plane to the interior of a unit circle in the ω-plane. Points on the x-axis in z are mapped to the boundary of the circle.

![NPTEL – Physics – Mathematical Physics - 1
By transformation defined by Eq. (1) let a point (𝑥0, 𝑦0) in the 𝑥𝑦 plane is
mapped onto a point (𝑢0, 𝑣0) in the uv plane and further two curves 𝐶1 and 𝐶2 in 𝑥𝑦
plane map onto two other curves 𝐶̃1and 𝐶̃2 in the 𝑢𝑣 plane. Let us assume that the curves
meet at (𝑥0, 𝑦0) and (𝑢0, 𝑣0) and further the angles surrounded by the respective set
of curves are same in both magnitude and direction as shown in the figure.
In this case, the mapping is said to be conformal at (𝑥0, 𝑦0). In some other
mapping, where only the magnitude of the angle is preserved but not the direction
is called as isogonal mapping. The results can trivially be extended to the case of
complex variables, where it can be stated as in the following.
Let a curve 𝐶 be presented by a parametric equation,
𝑧 = 𝑧(𝑡) (𝑎 ≤ 𝑡 ≤ 𝑏)
And 𝑓(𝑧) be a function defined at all points z on 𝐶.
Then
(4)
𝑤 = 𝑓[𝑧(𝑡)] (5)
is the equation of the image 𝑐̃ of 𝐶 under the transformation 𝑤 = 𝑓(𝑧) (in the
same sense of Eq. (1)). This transformation is said to be conformal at a point 𝑧0 if
𝑓(𝑧) is analytic there and 𝑓′(𝑧) ≠ 0. Also this transformation is conformal
at each point in the neighborhood of 𝑧0.
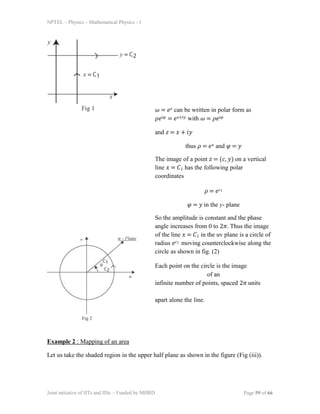
Example 1 : Mapping of a curve
The mapping 𝜔 = 𝑒𝑧 is conformal throughout the entire z plane since 𝑓′(𝑧) =
𝑒𝑧 ≠ 0 for all 𝑧. Now consider two lines 𝑥 = 𝐶1 and 𝑦 = 𝐶2 in the z plane as
shown in figure. The images of these curves 𝐶1 and 𝐶2 can be obtained as
follows.
Joint initiative of IITs and IISc – Funded by MHRD Page 58 of 66](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lec41-231023101044-e76eaefa/85/lec41-ppt-2-320.jpg)