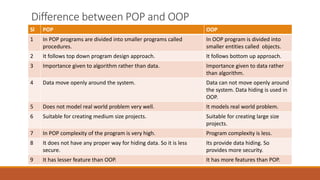
This document provides an overview of different types of programming languages, including procedural and object-oriented programming languages. It defines procedural languages as dividing programs into modules and procedures, with an emphasis on algorithms over data. Object-oriented languages are described as dividing programs into objects that bundle data and functions, allowing for data hiding and modeling real-world problems by encapsulating code and data. The key differences between the two paradigms are that procedural languages follow a top-down design, treat data and functions separately, and are less secure, while object-oriented languages follow a bottom-up design, encapsulate data within objects, and model the real world by protecting data integrity.