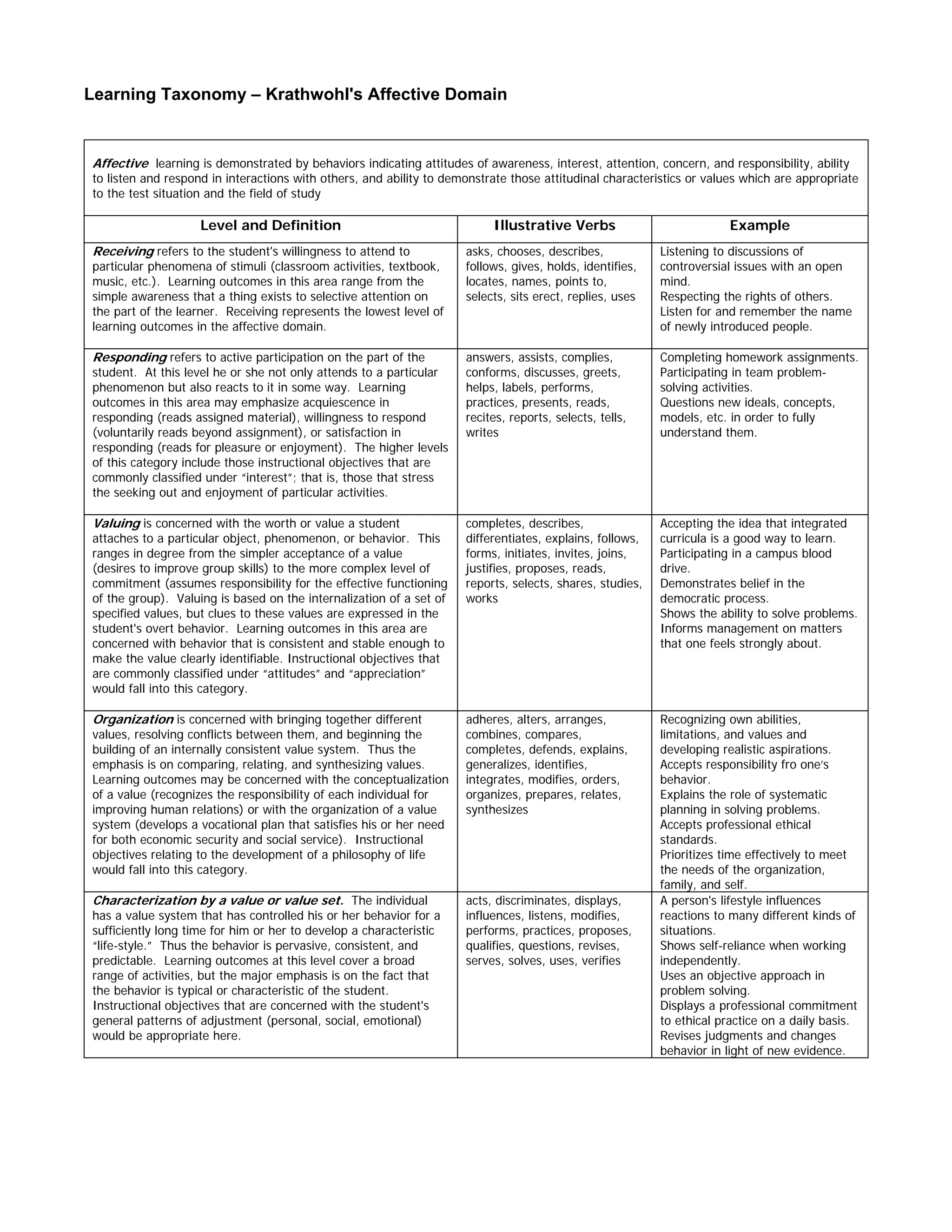
The document summarizes Krathwohl's Affective Domain taxonomy which describes the affective or attitudinal aspects of learning. The taxonomy includes 5 major levels - Receiving, Responding, Valuing, Organization, and Characterization. Each level builds upon the previous one as students progress from simply being aware of phenomena to having value systems and consistent behaviors characterized by internalized values. The levels provide a framework for formulating instructional objectives focused on attitudes, appreciation, values, adjustment, and responsible behaviors.