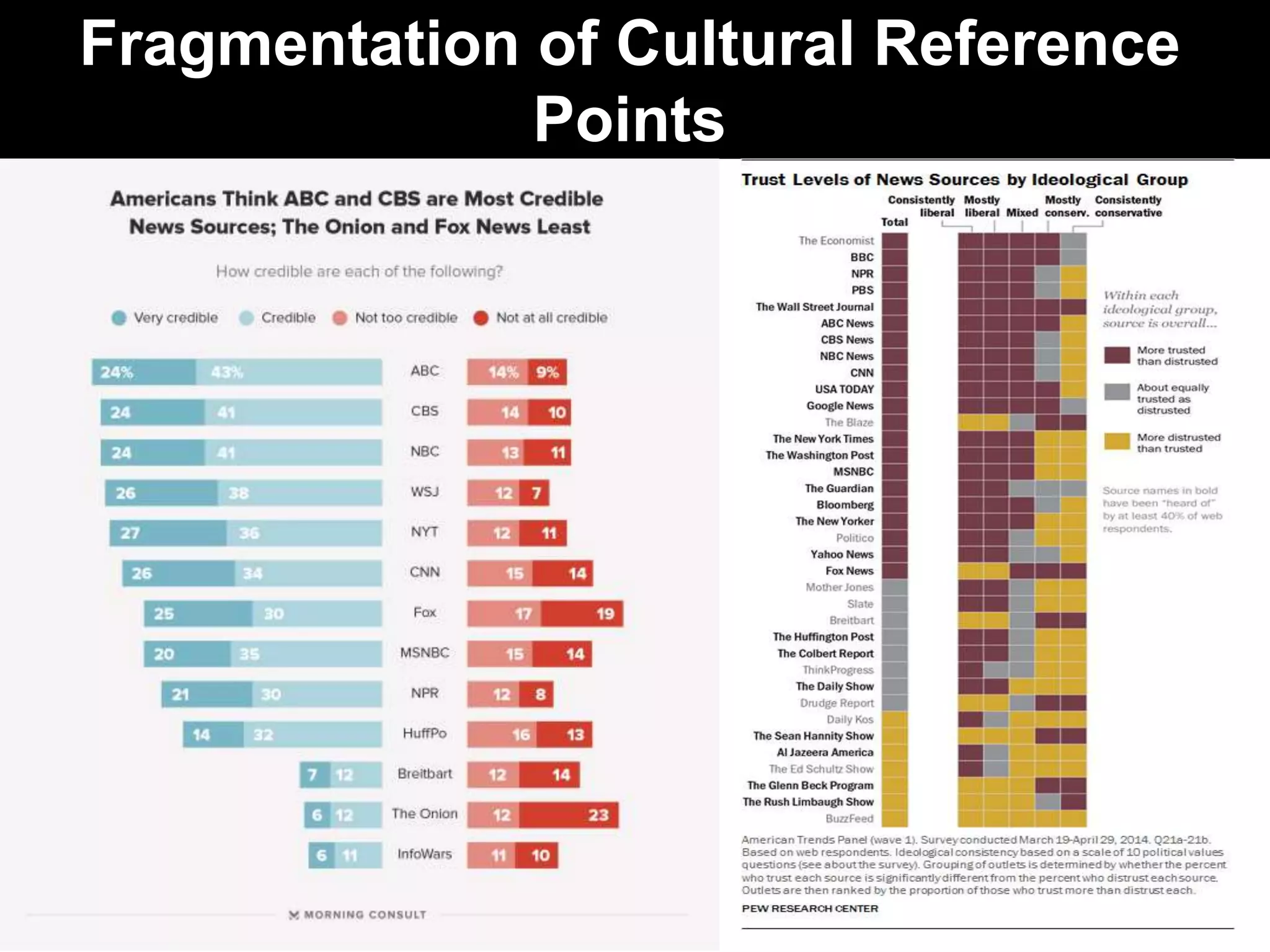
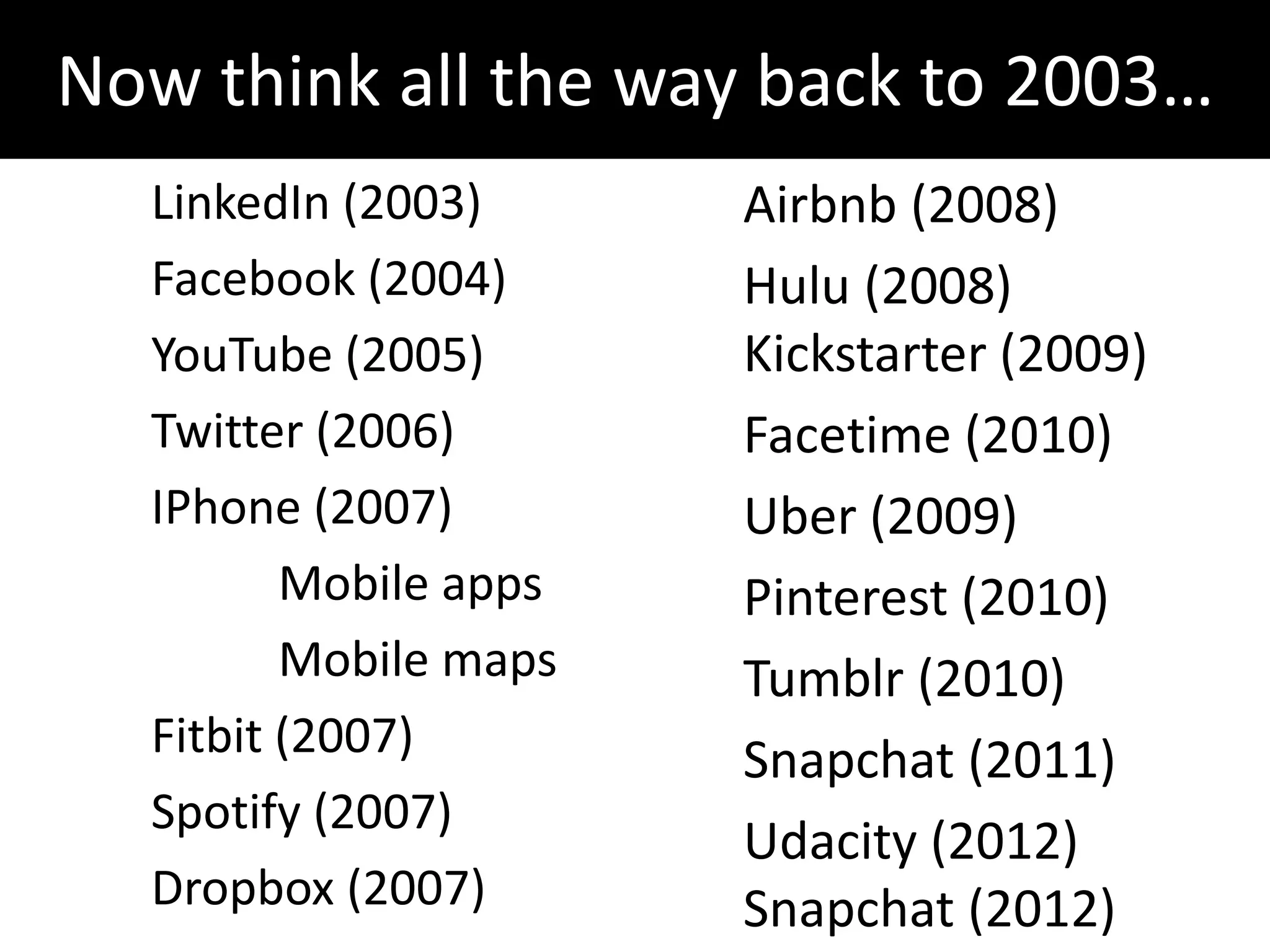
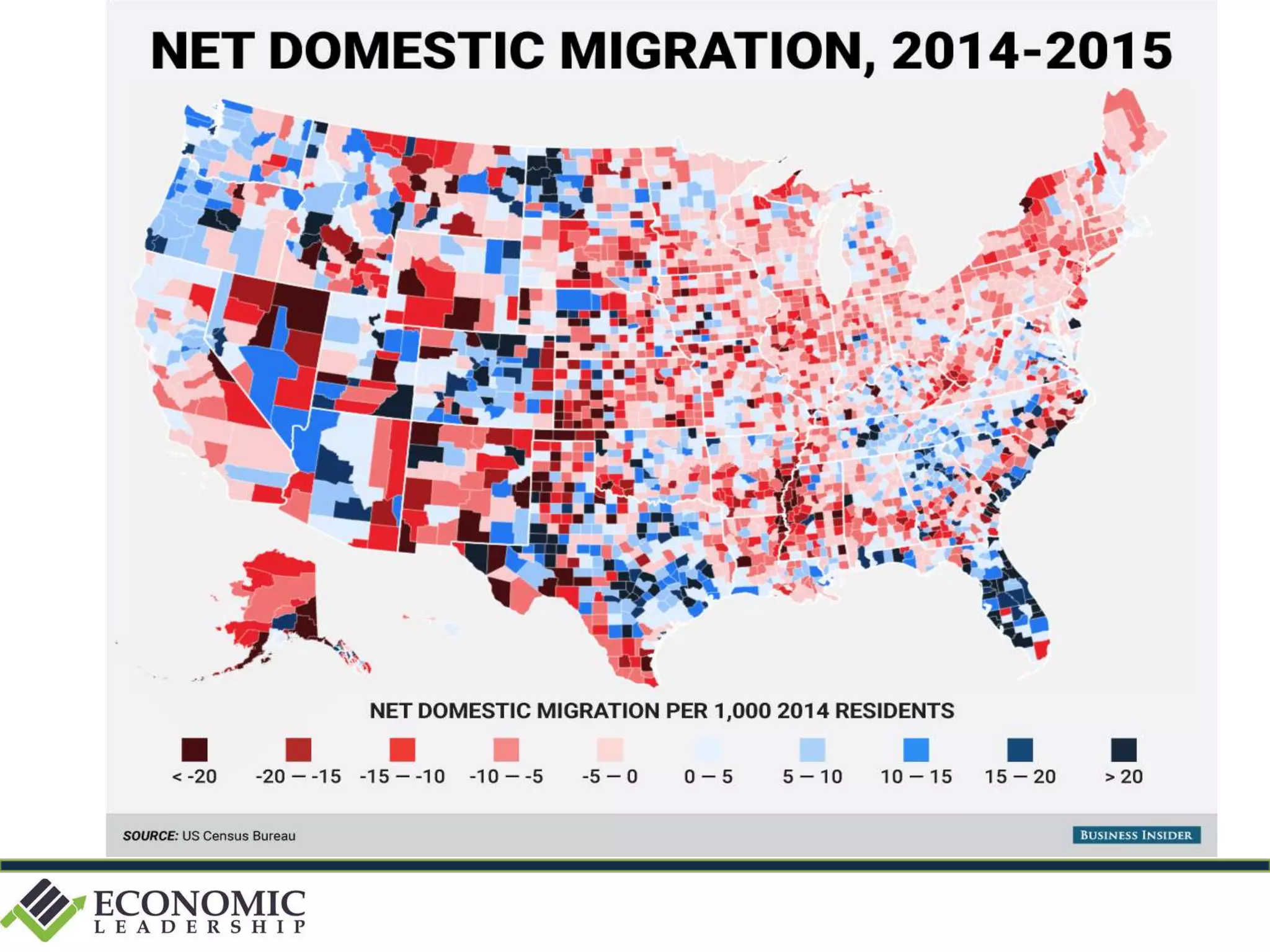
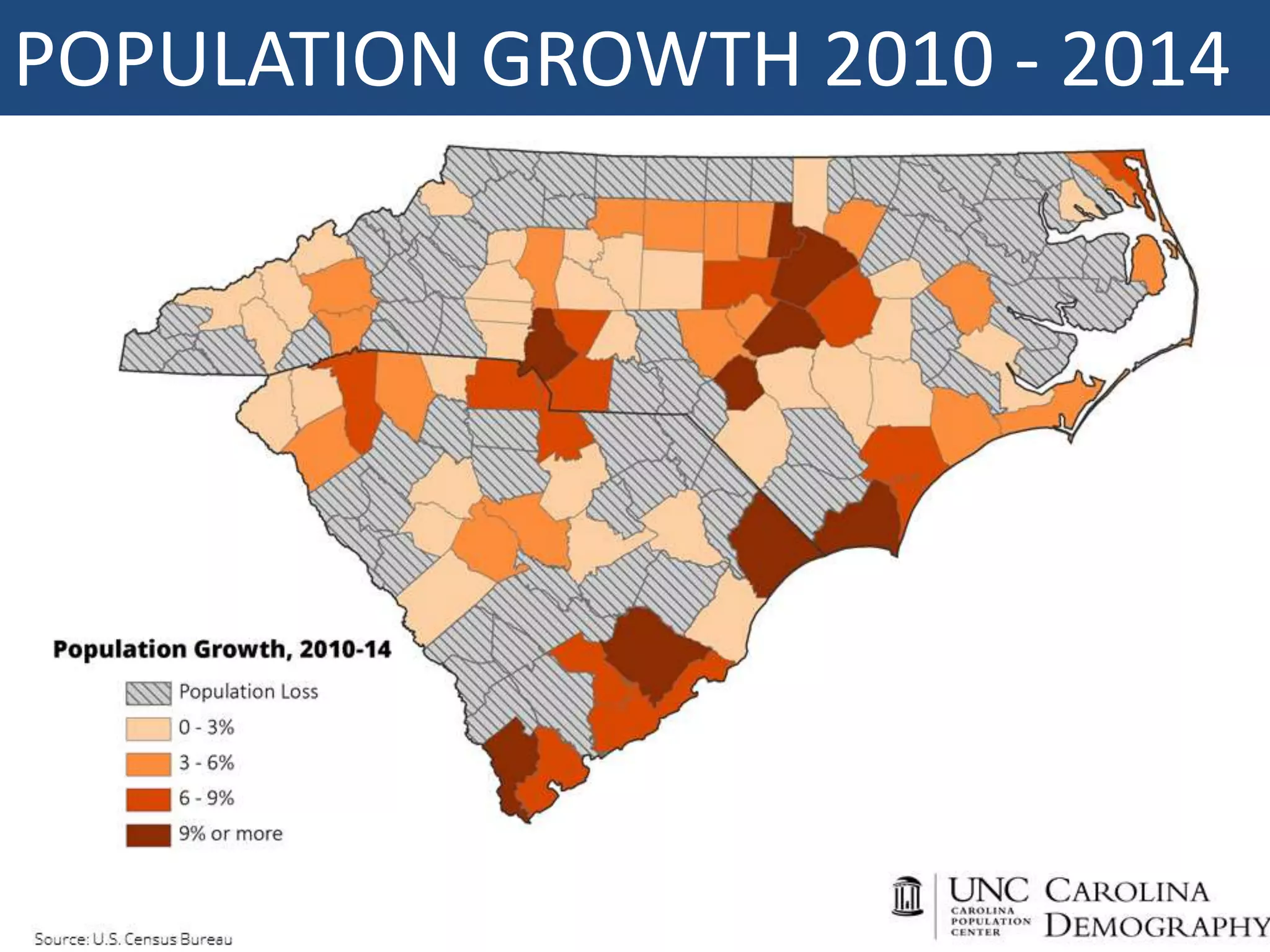
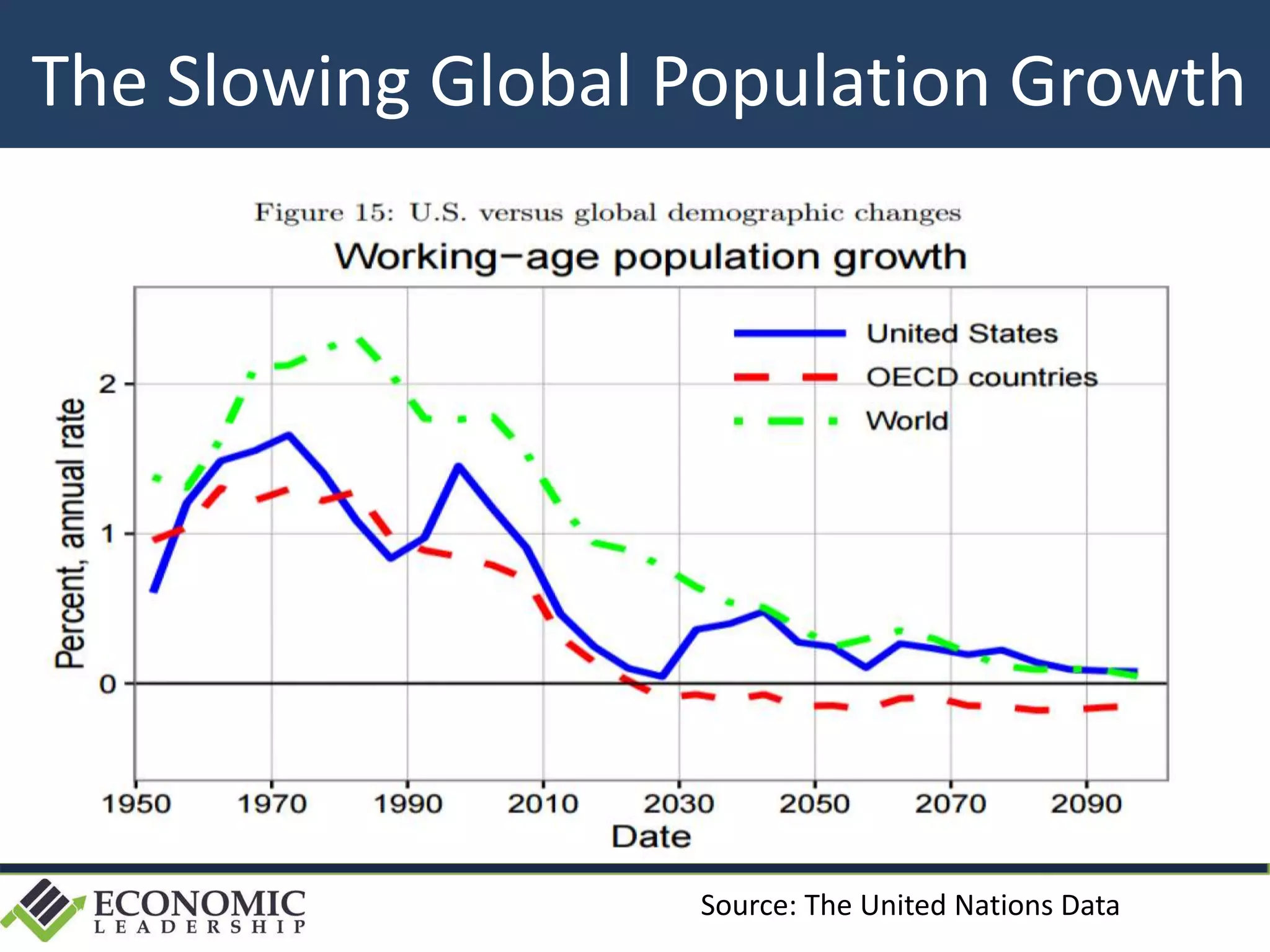
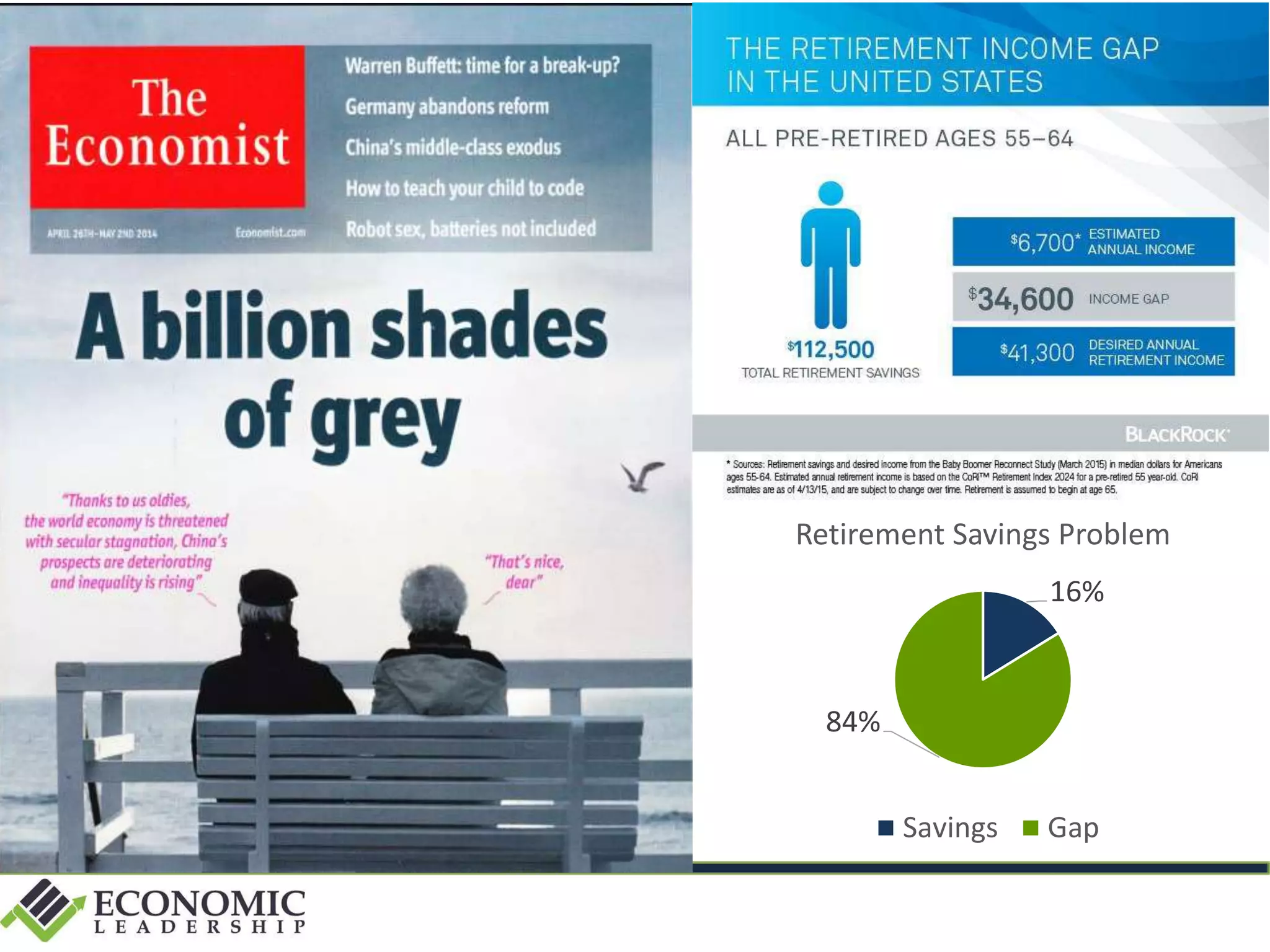
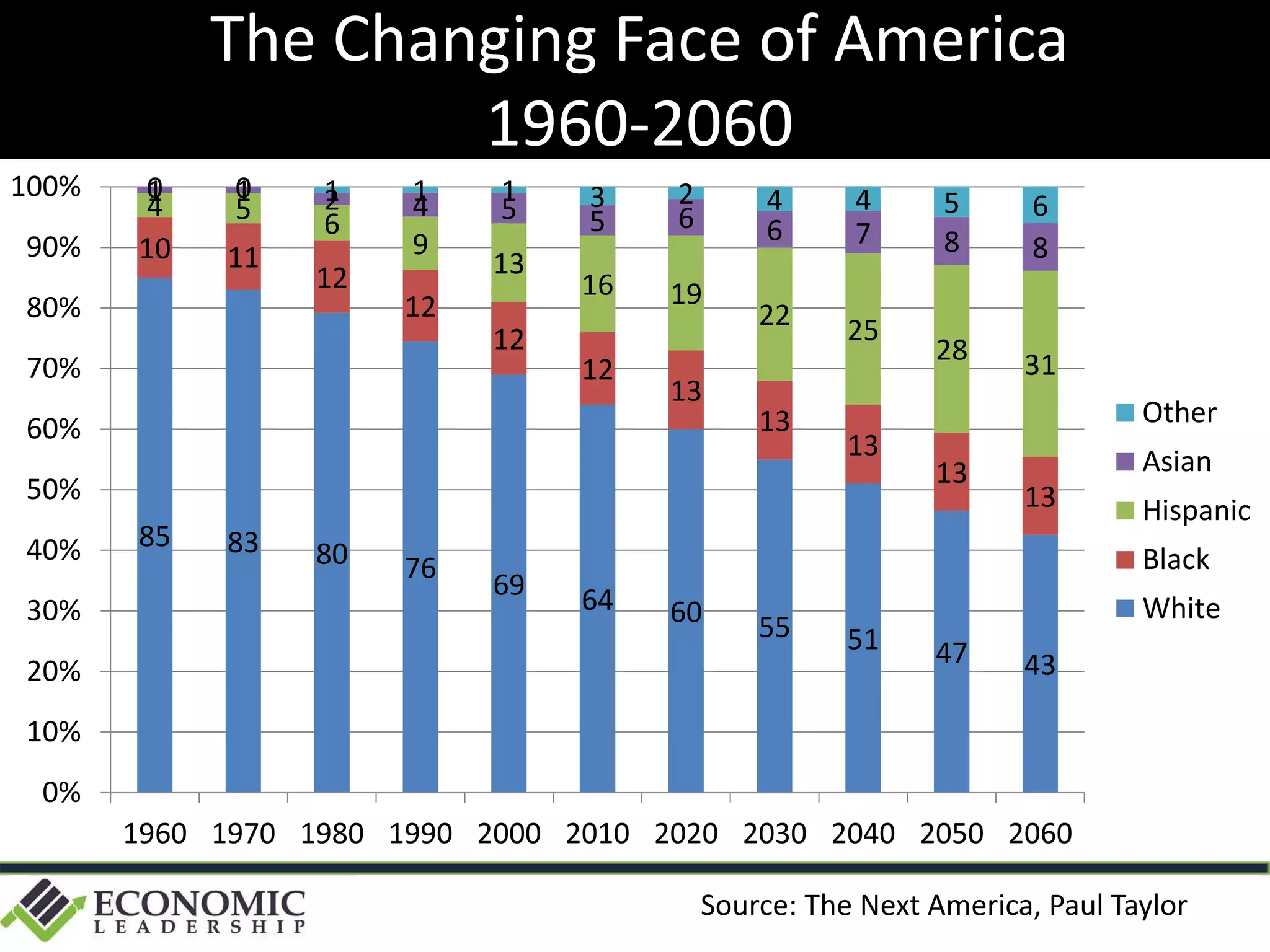
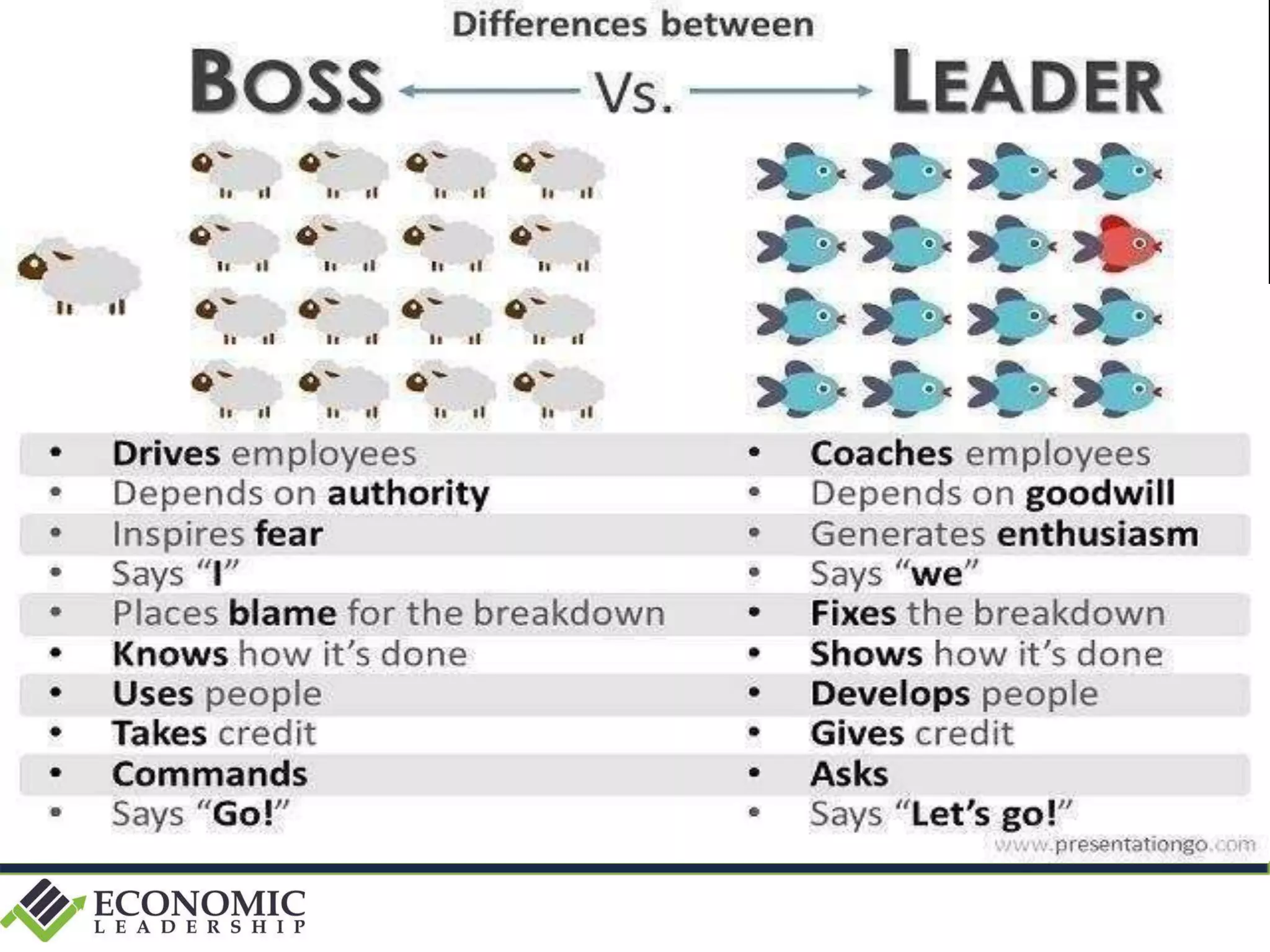
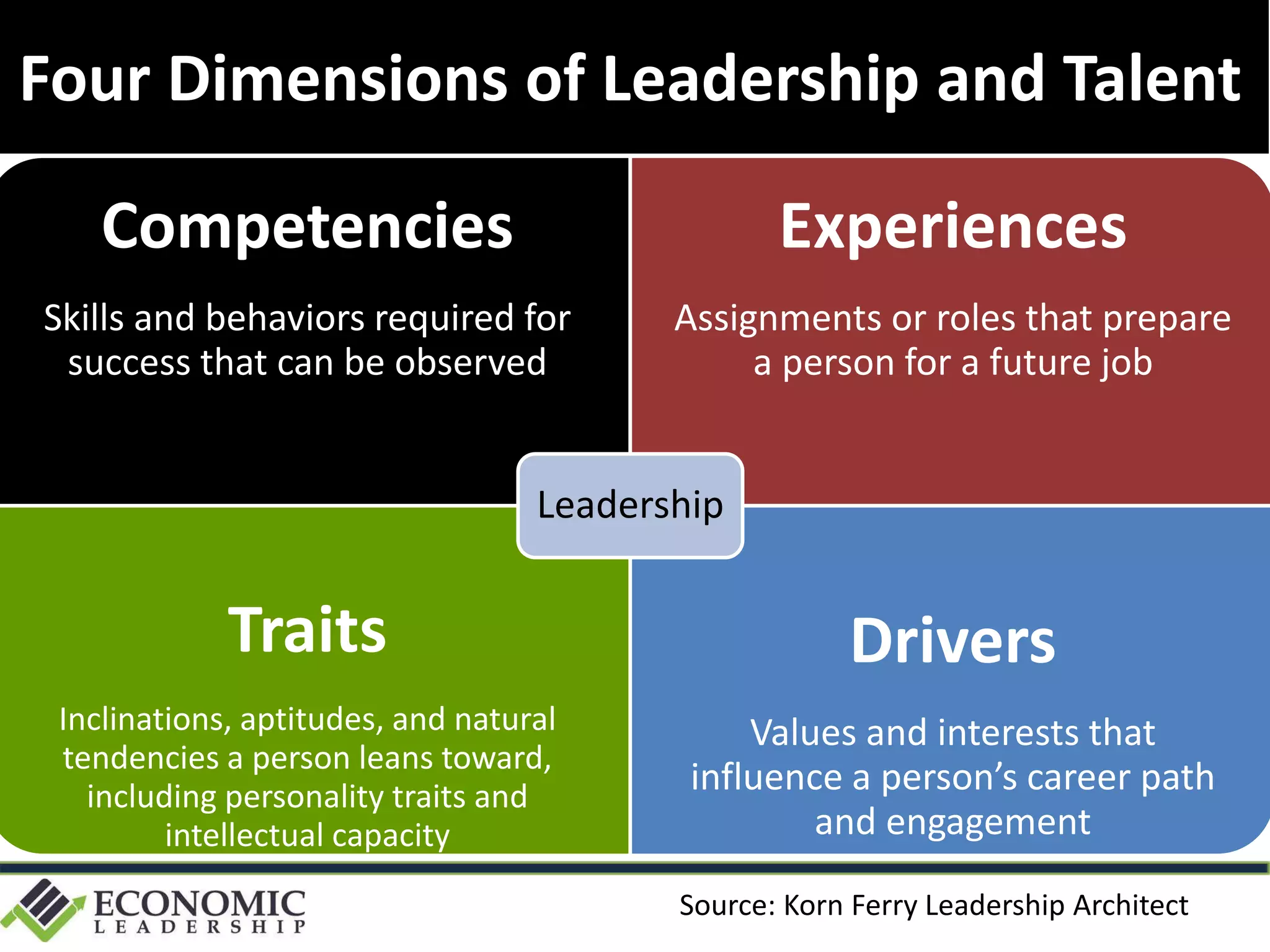
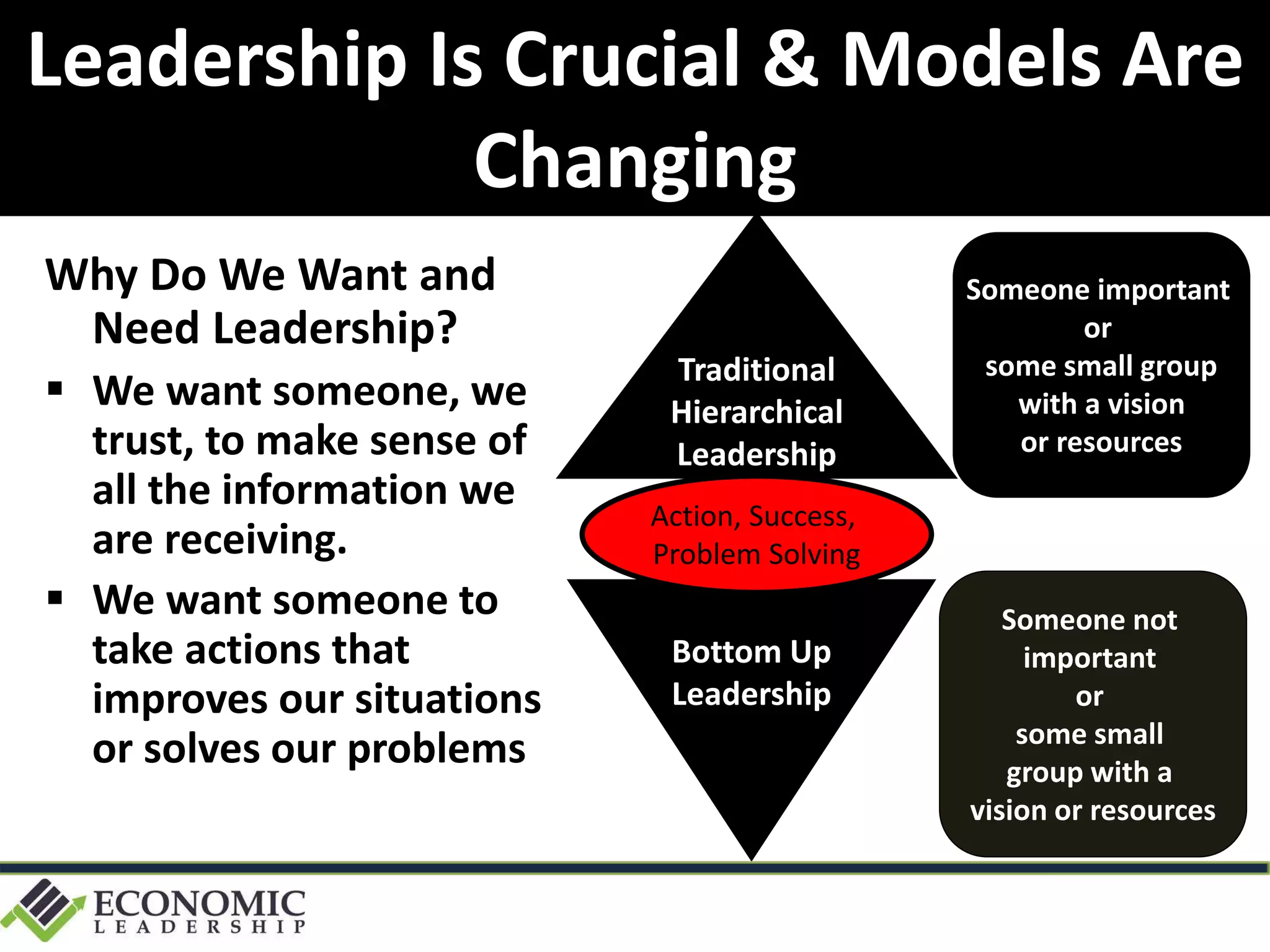
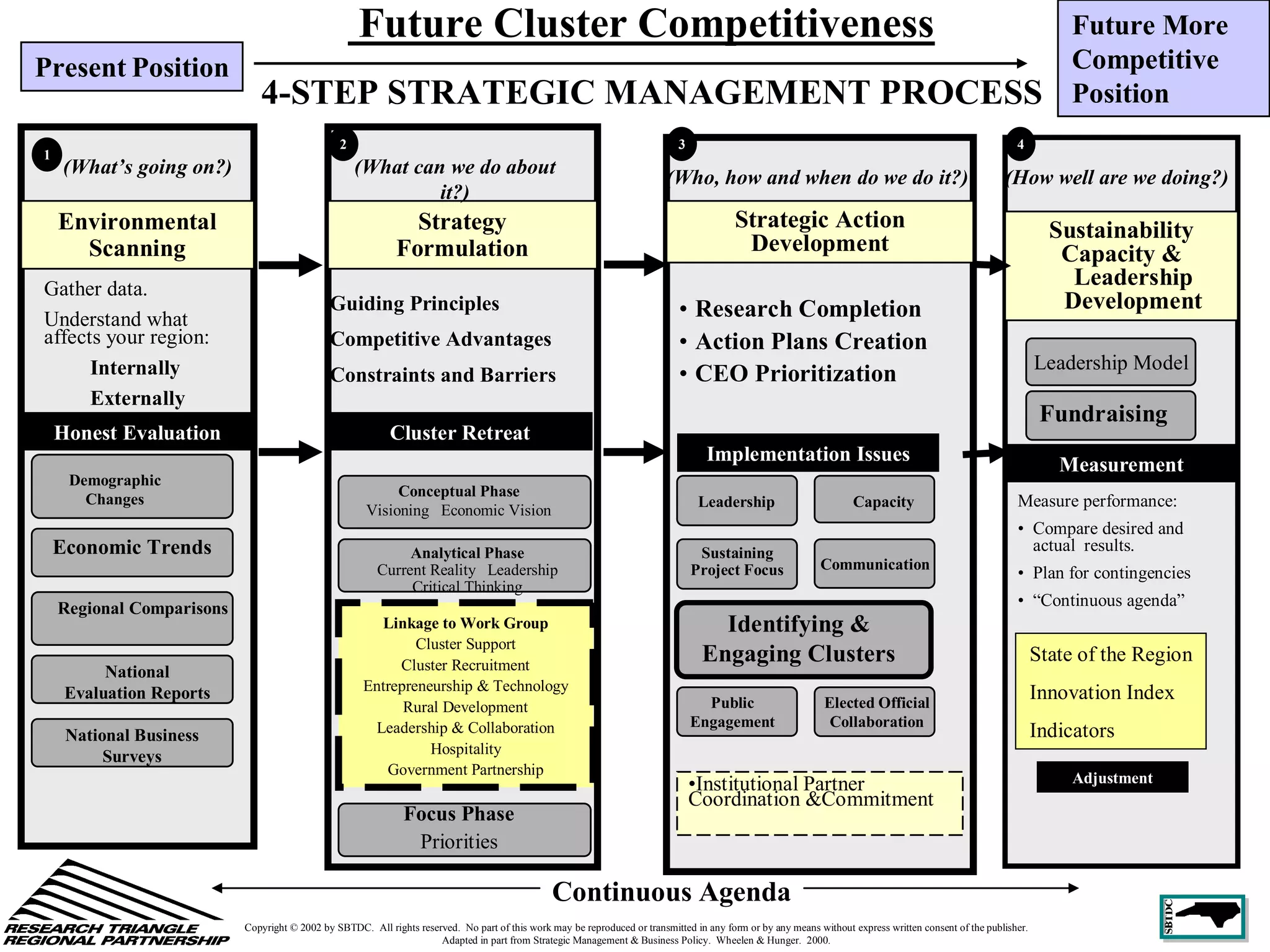
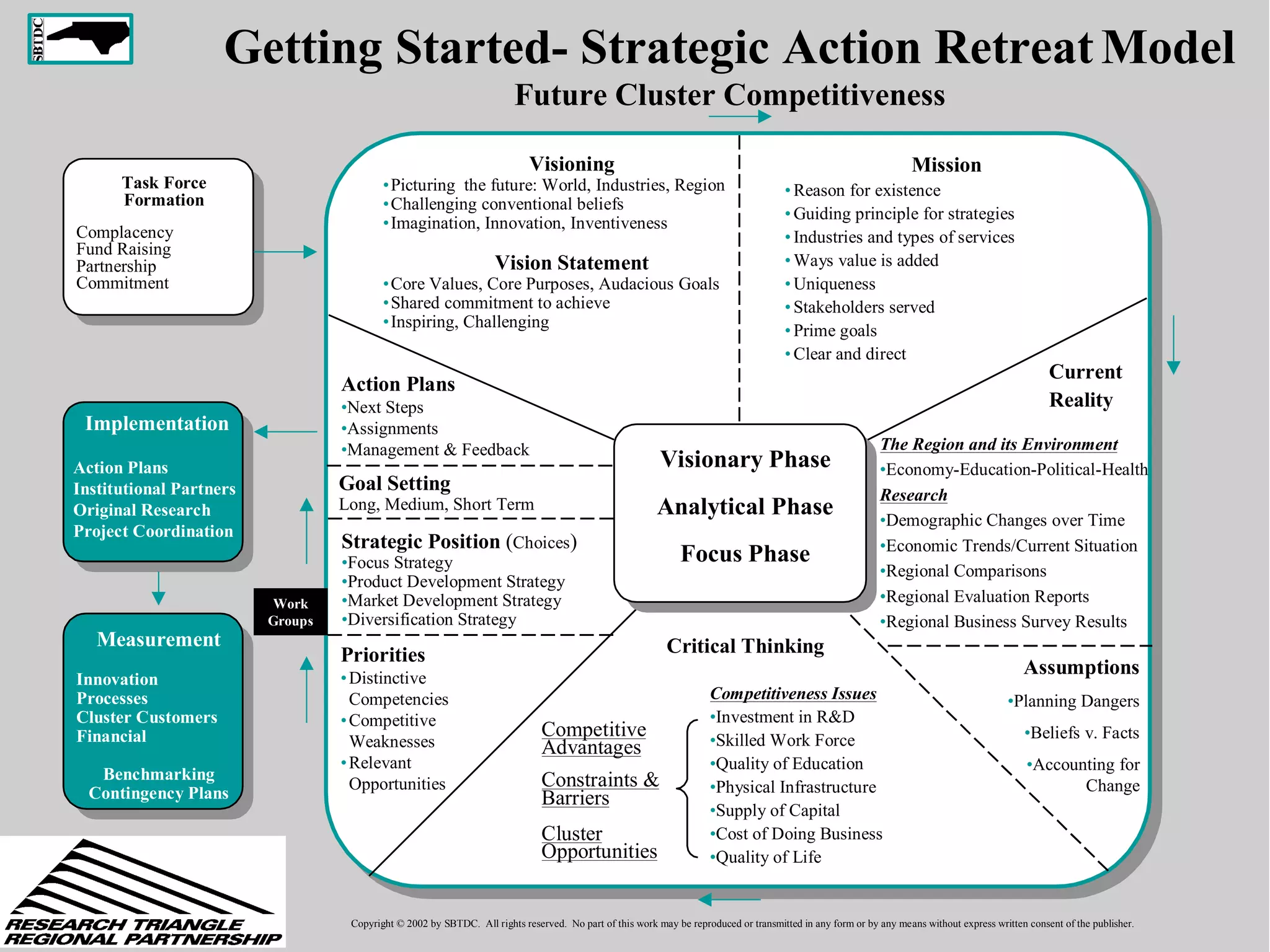
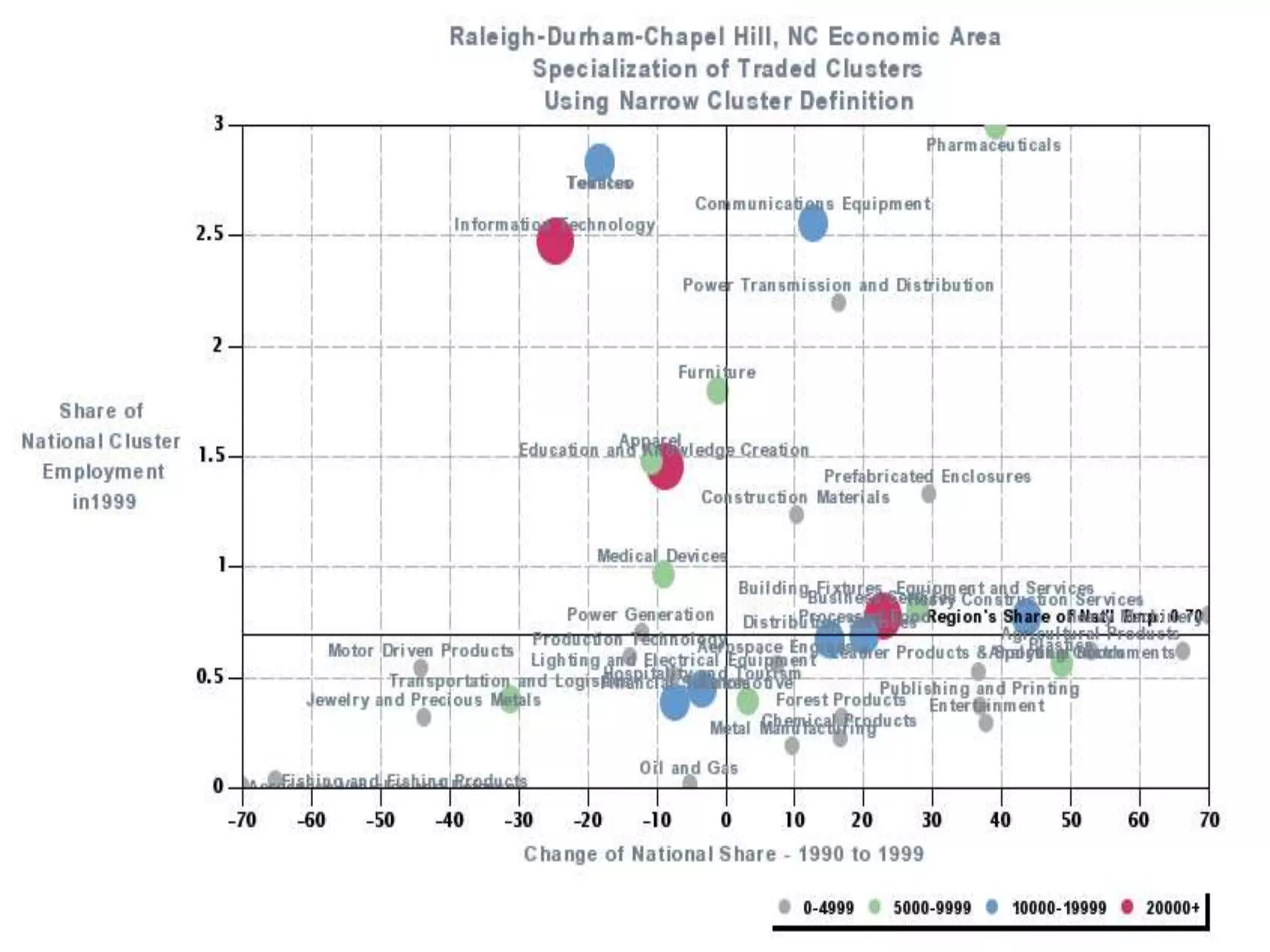
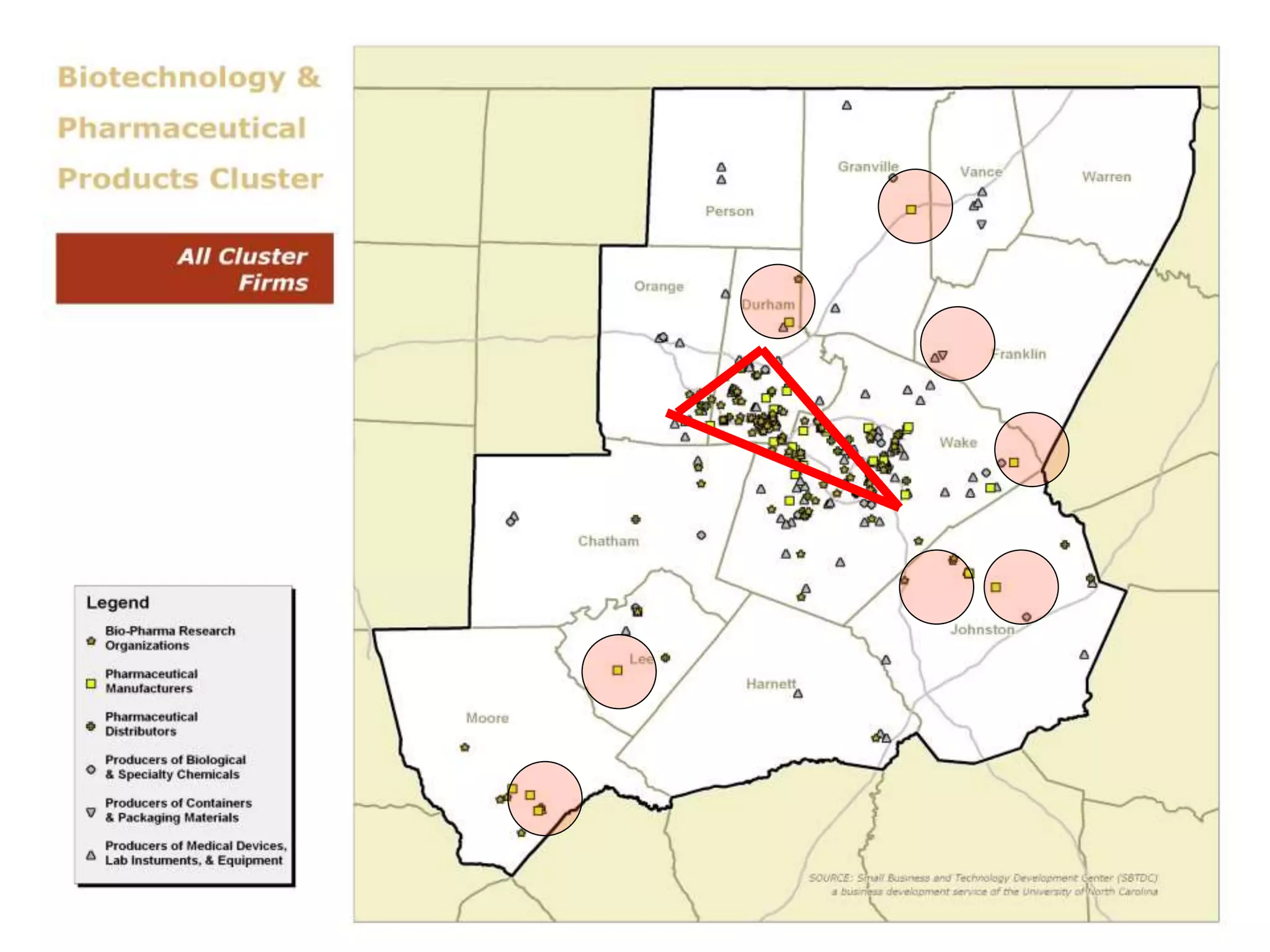
This document discusses leadership development and getting things done. It begins by noting the challenges of leadership in 2017, including fear of the future, fragmentation of cultural reference points, and the matrix paradox of wanting more information but easier solutions. It then discusses trends impacting the future like technology, urbanization, and demographics. Key aspects of leadership discussed include having an innovation mindset, getting things done, and working with others. The document emphasizes that great leaders are continuously learning and able to communicate a narrative. It also discusses the importance of collaboration for regional success and offers tips for creating and leading successful regional collaborations.