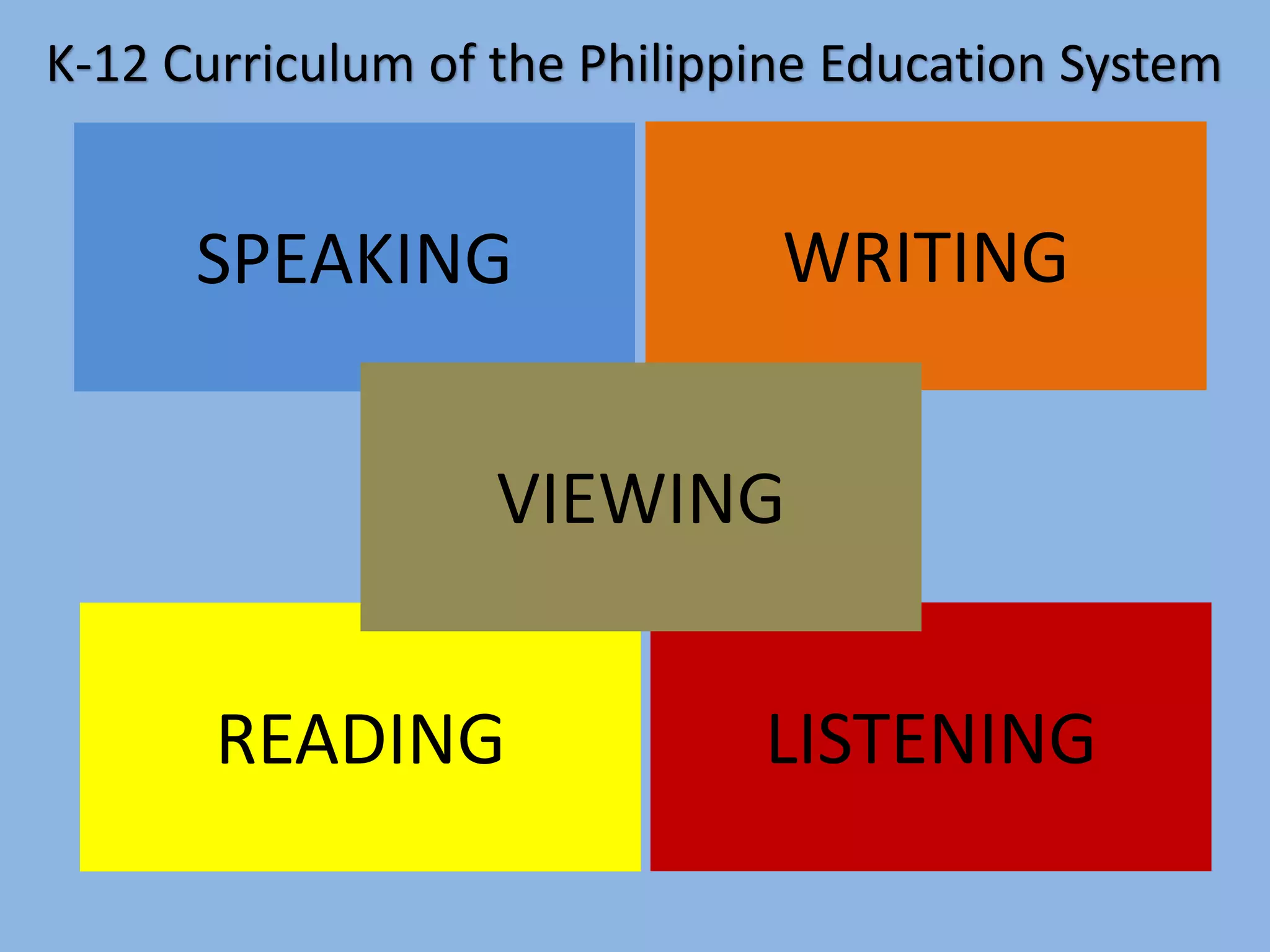
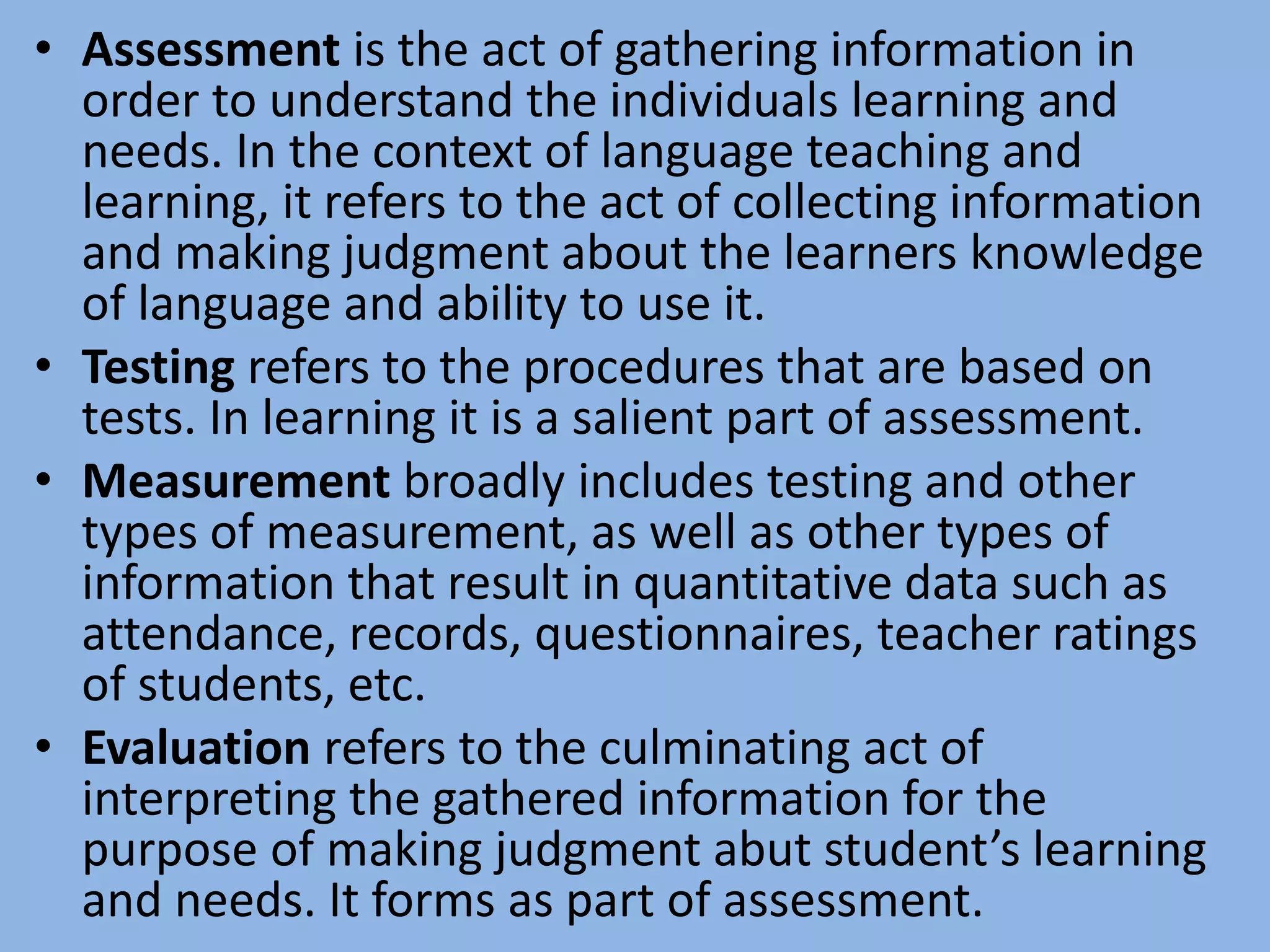
This document discusses language assessment and evaluation. It defines key concepts related to assessment, outlines principles of assessment and evaluation, and describes different types and purposes of assessment including diagnostic, formative, and summative assessment. Different assessment tools are also discussed, such as observations, anecdotal records, checklists, and rating scales. The goal of assessment is to improve teaching and learning by gathering information on students' knowledge and abilities.