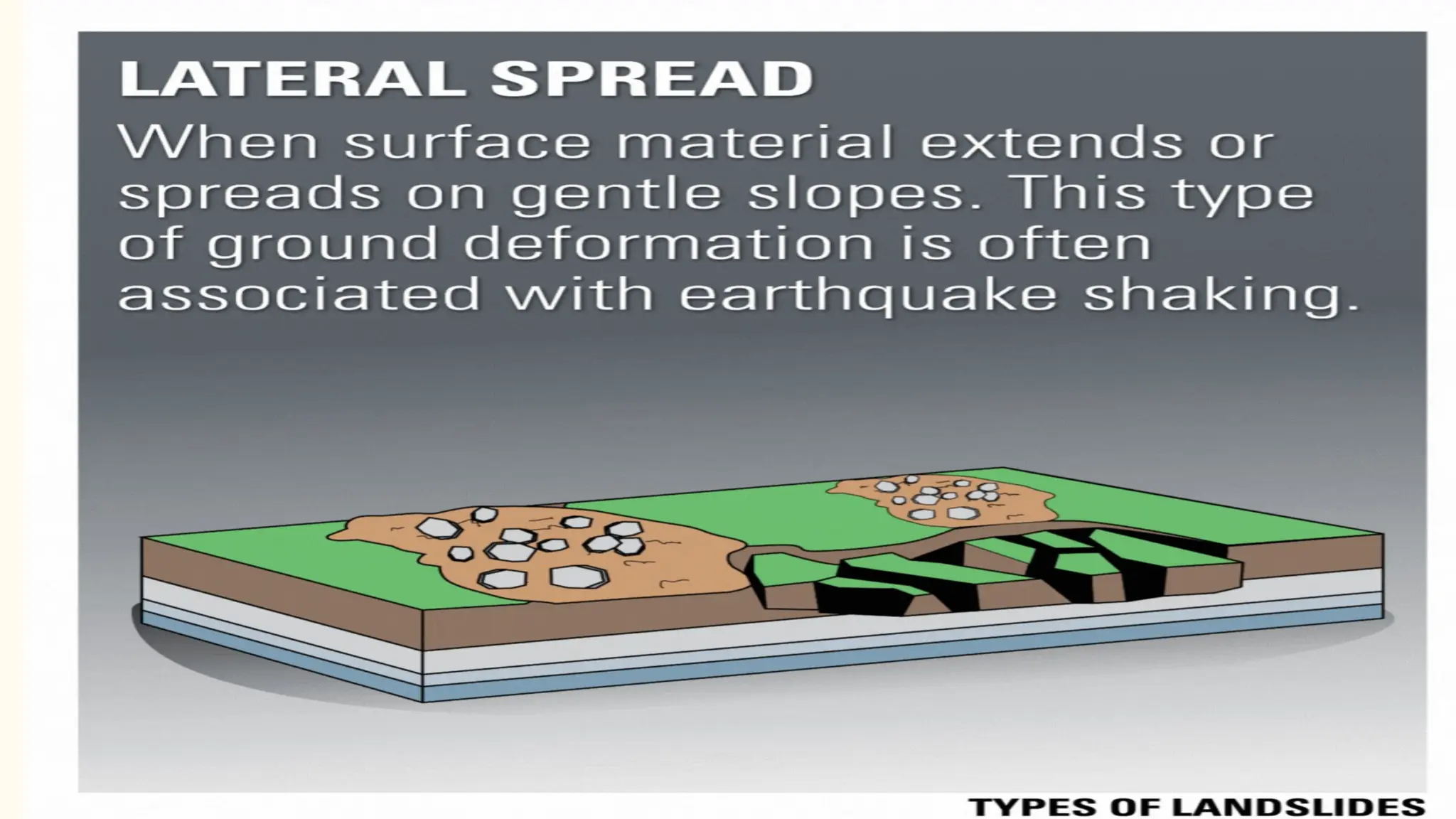
This document discusses landslides, defining them as the mass movement of material down a slope influenced by gravity and detailing various types such as rotational slides, translational slides, and debris flows. It outlines causes, including gravity, rainfall, earthquakes, and human activity, as well as the physical damage and casualties they can cause. Preventative measures suggested include selecting safe building locations, maintaining vegetation, and ensuring proper drainage to mitigate the occurrence of landslides.
![WELCOME
BSC GEOLOGY FIRST YEARS
PRESENTS
M. E. S PONNANI COLLEGE
[SEMINAR]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/scienceproject-240919084618-4b021102/75/Landslide-Natural-Hazard-1-2048.jpg)