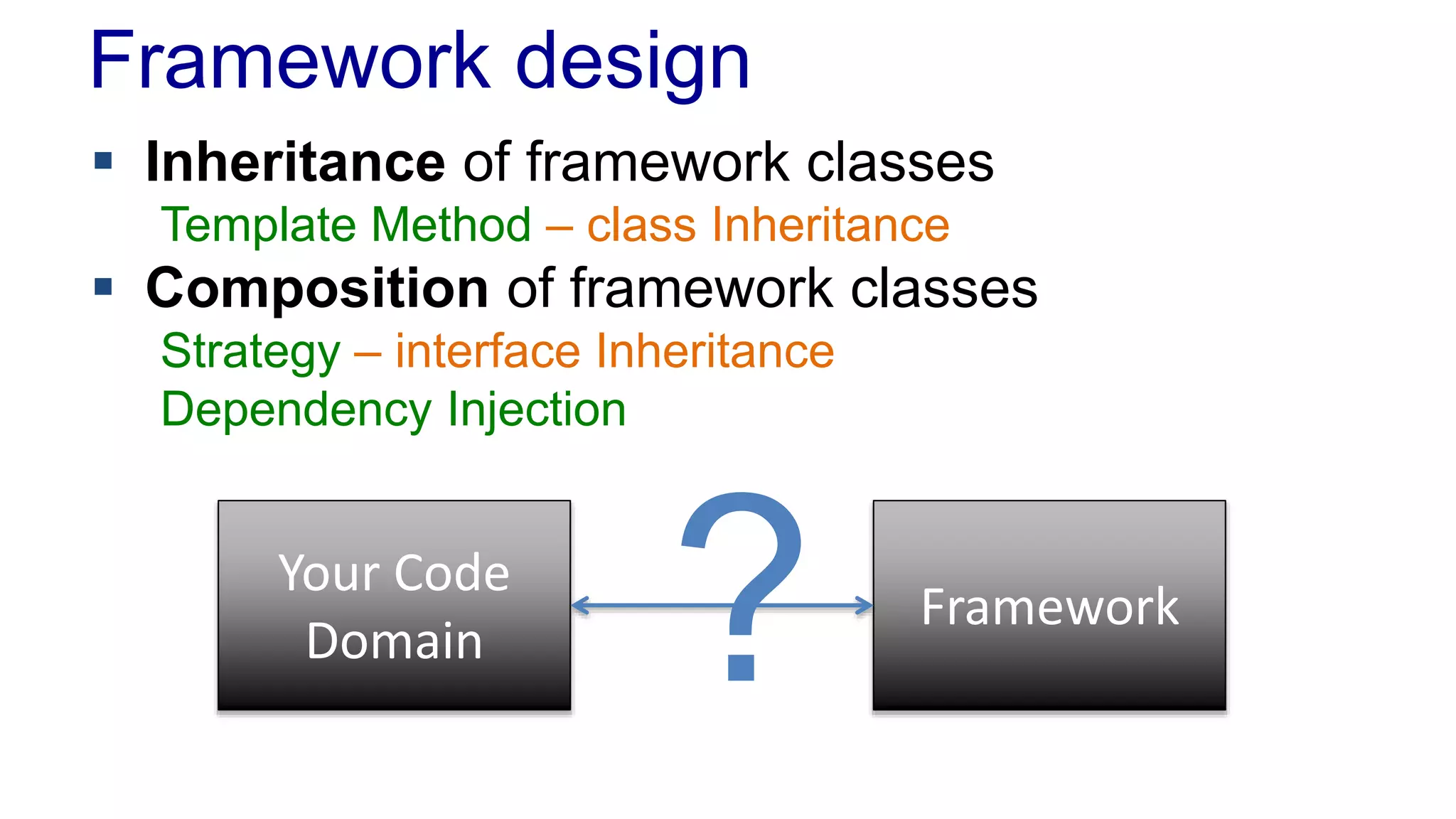
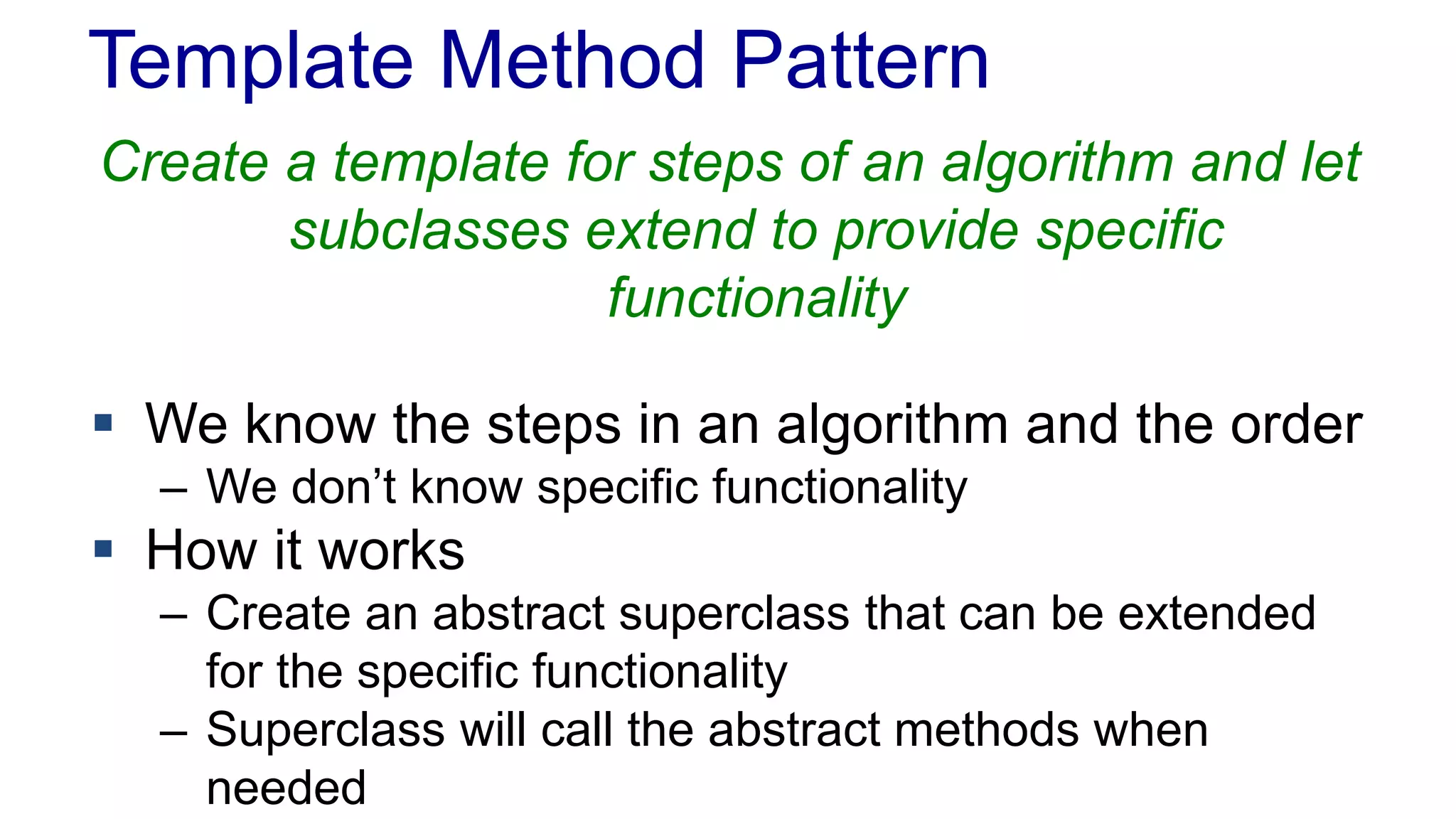
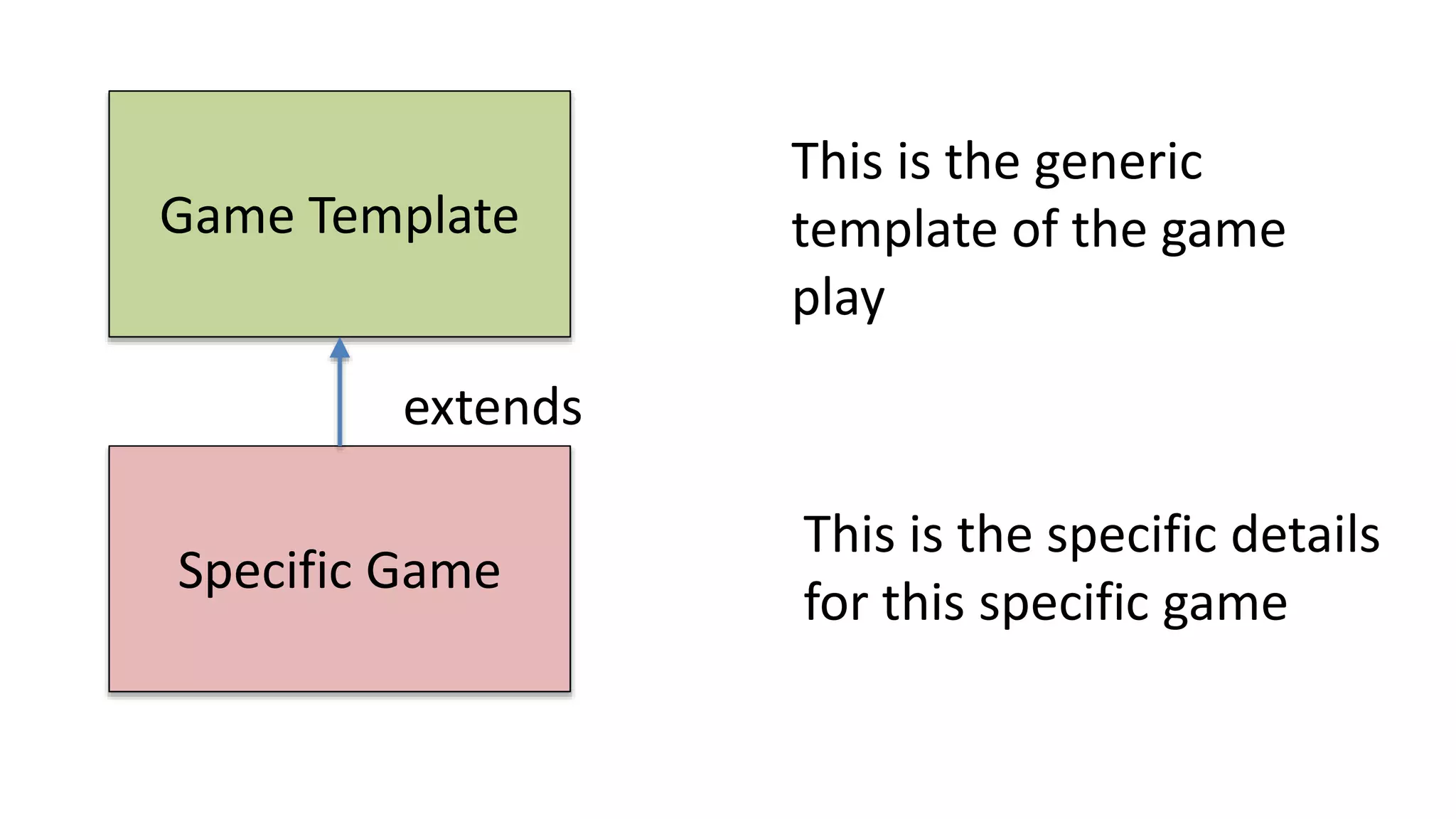
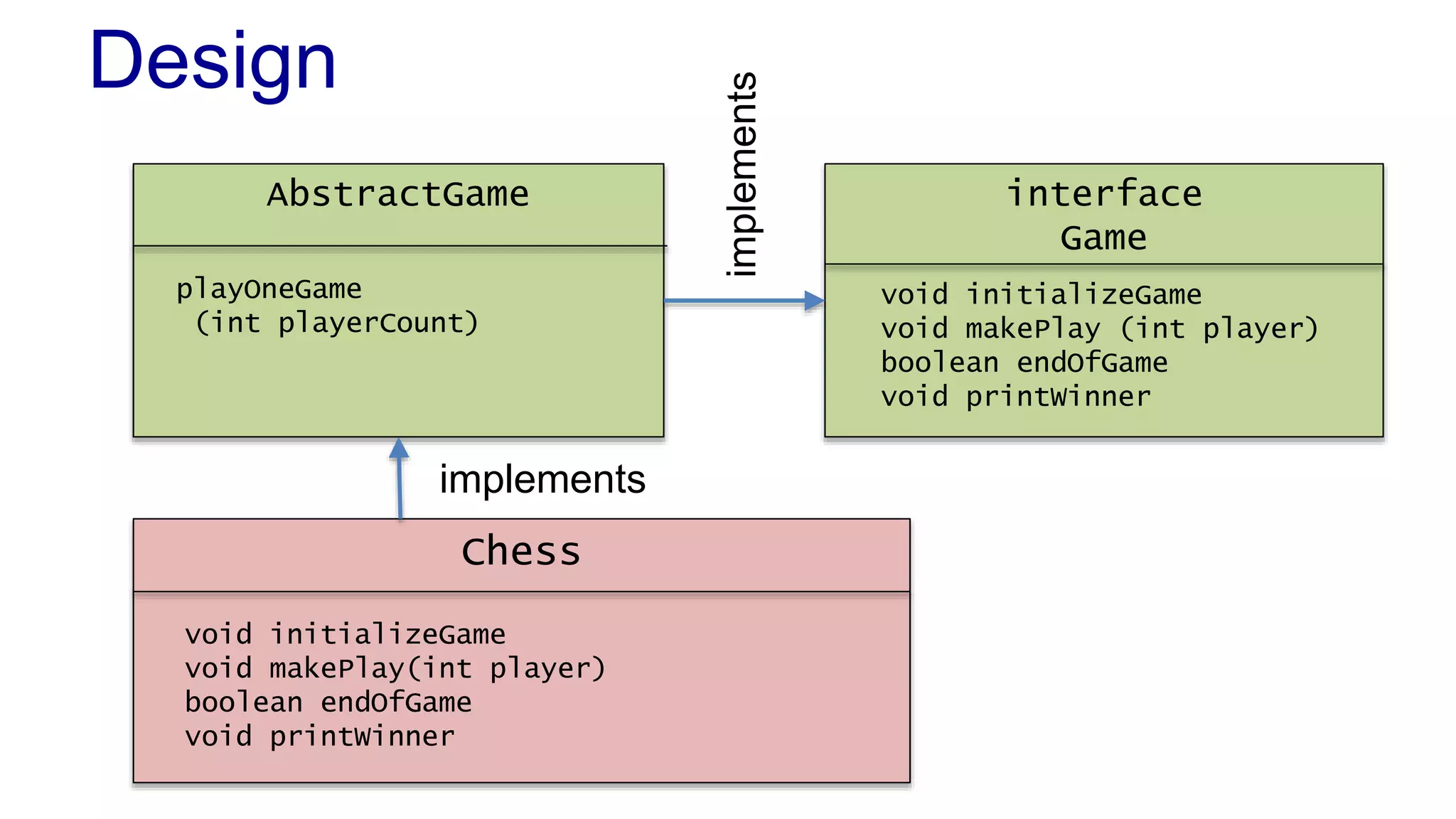
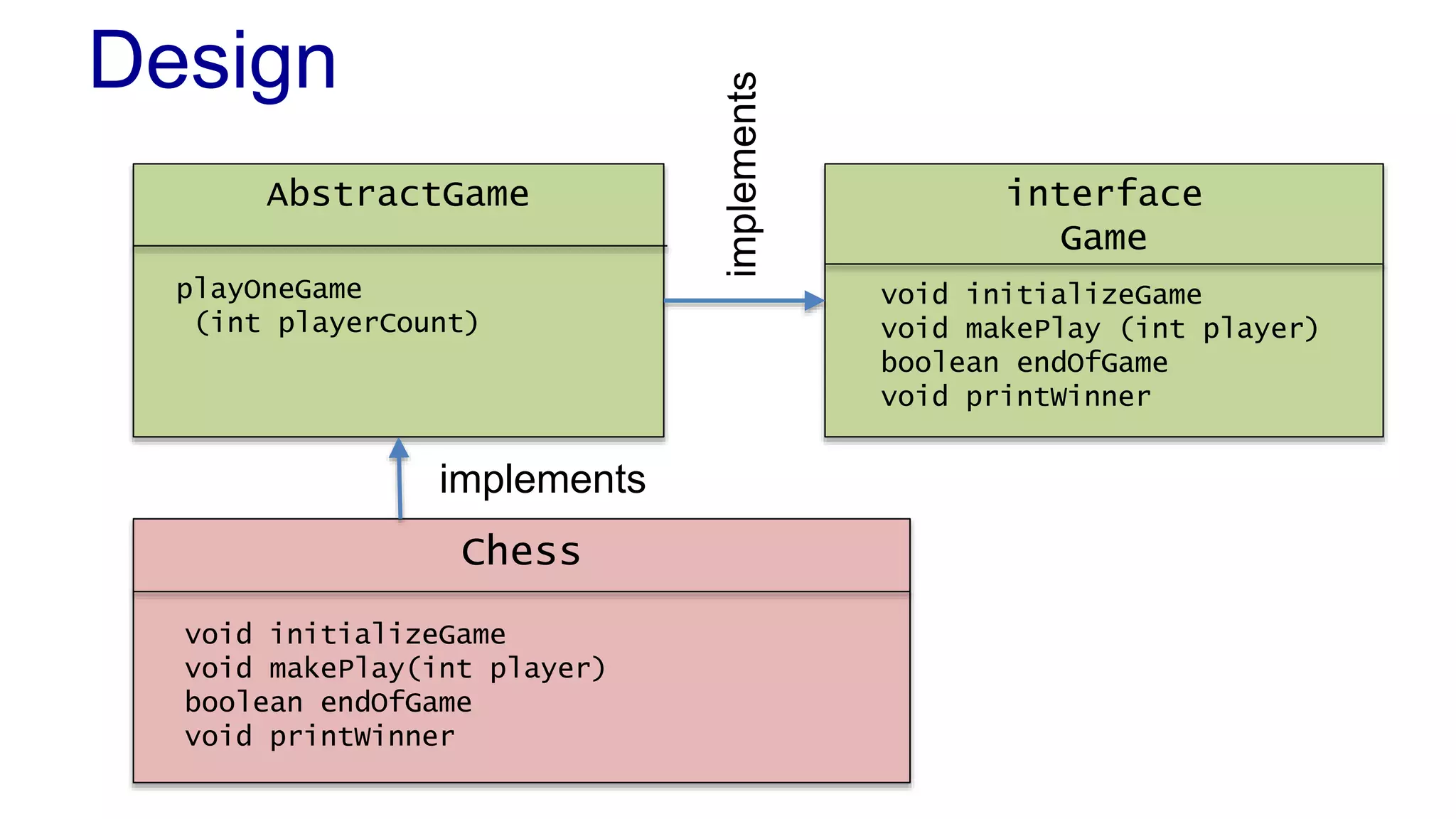
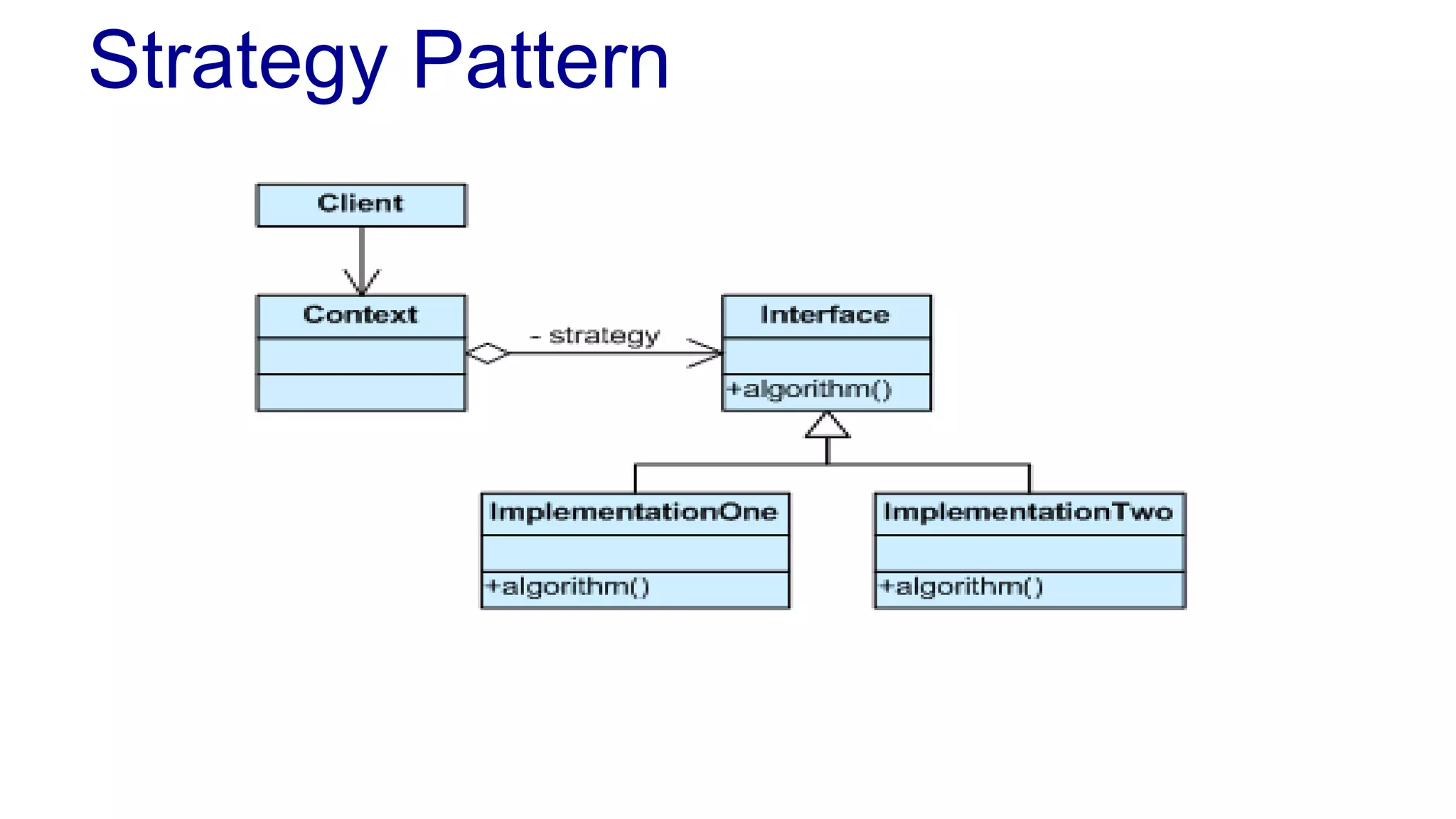
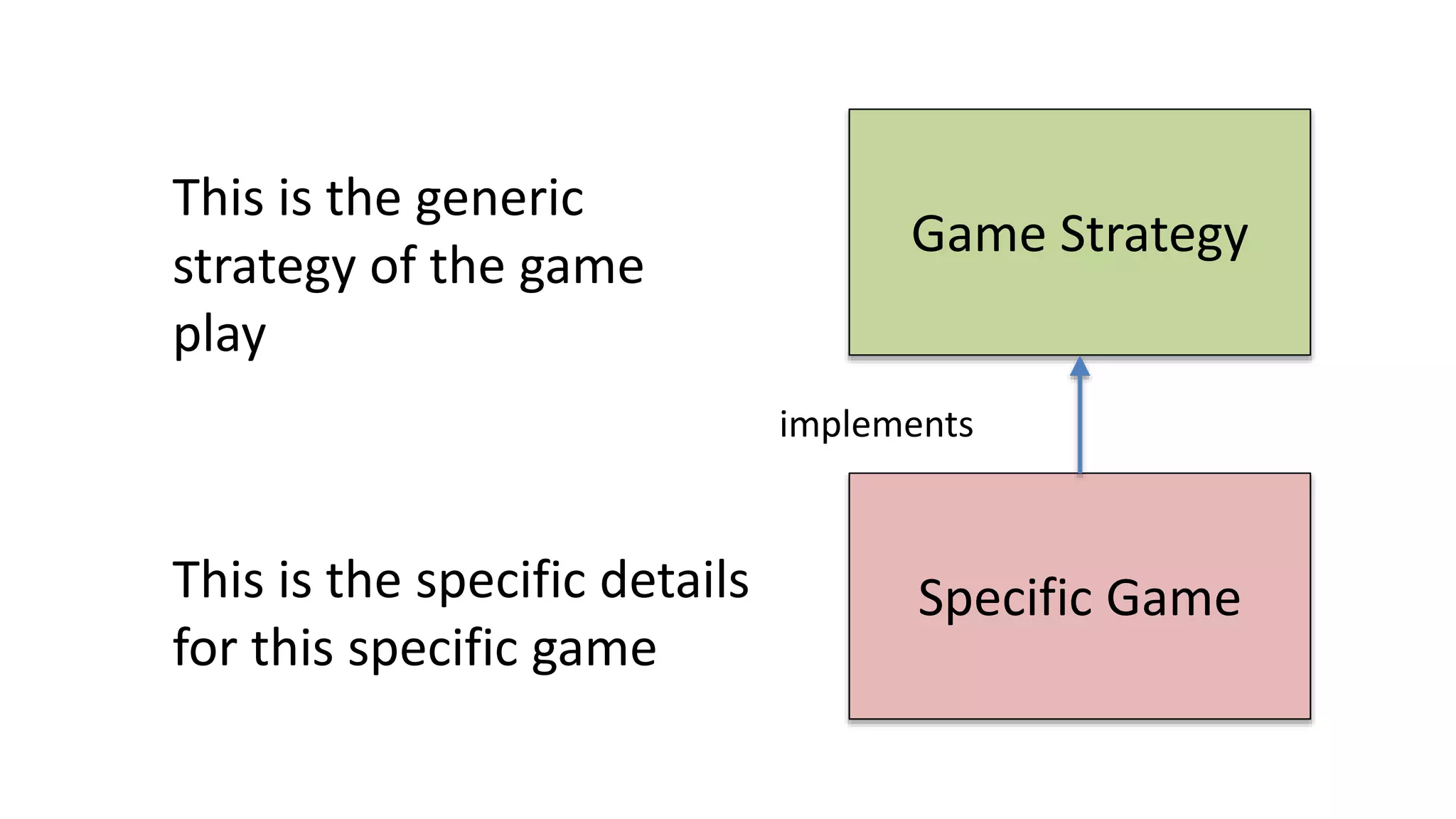
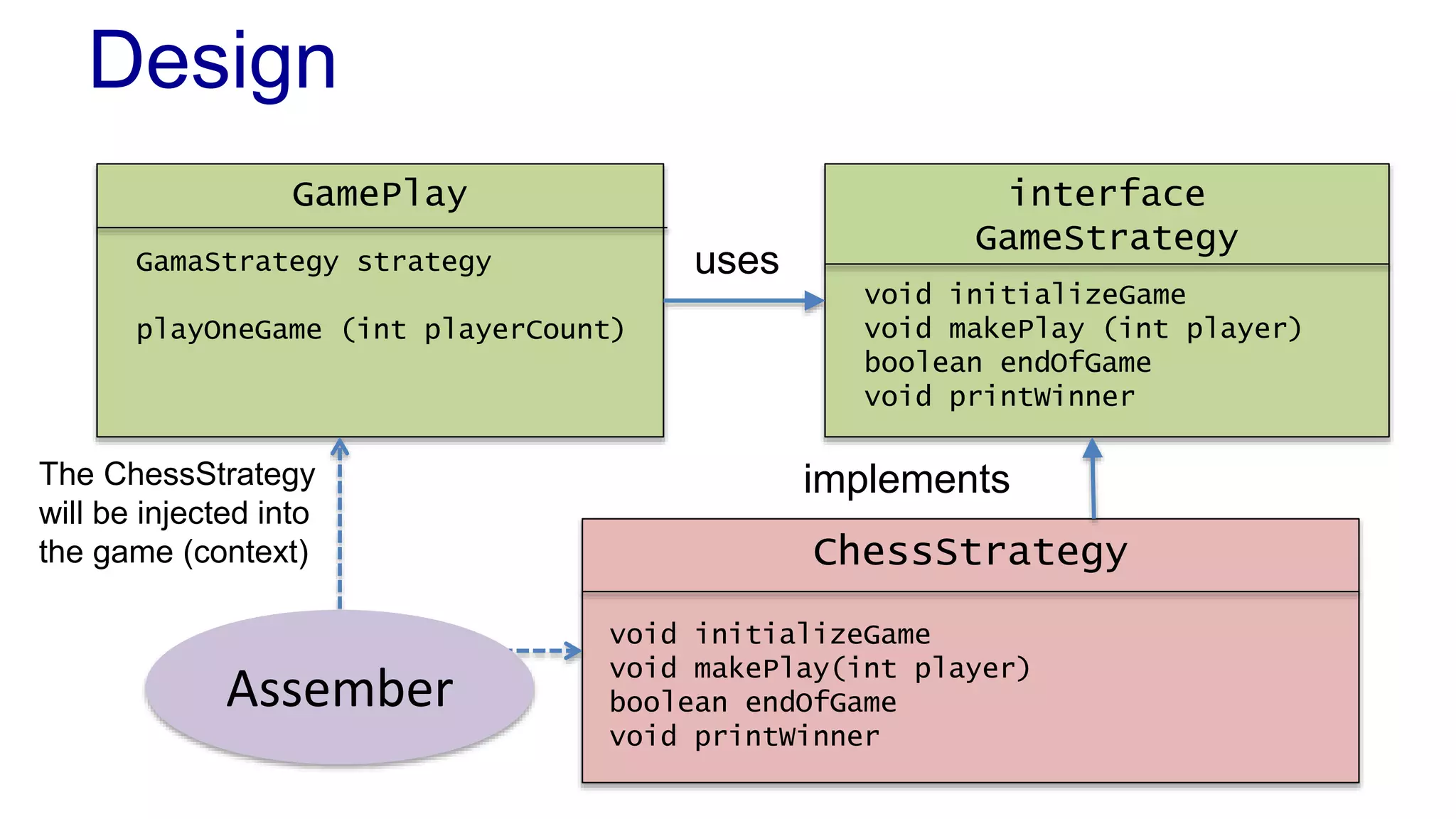
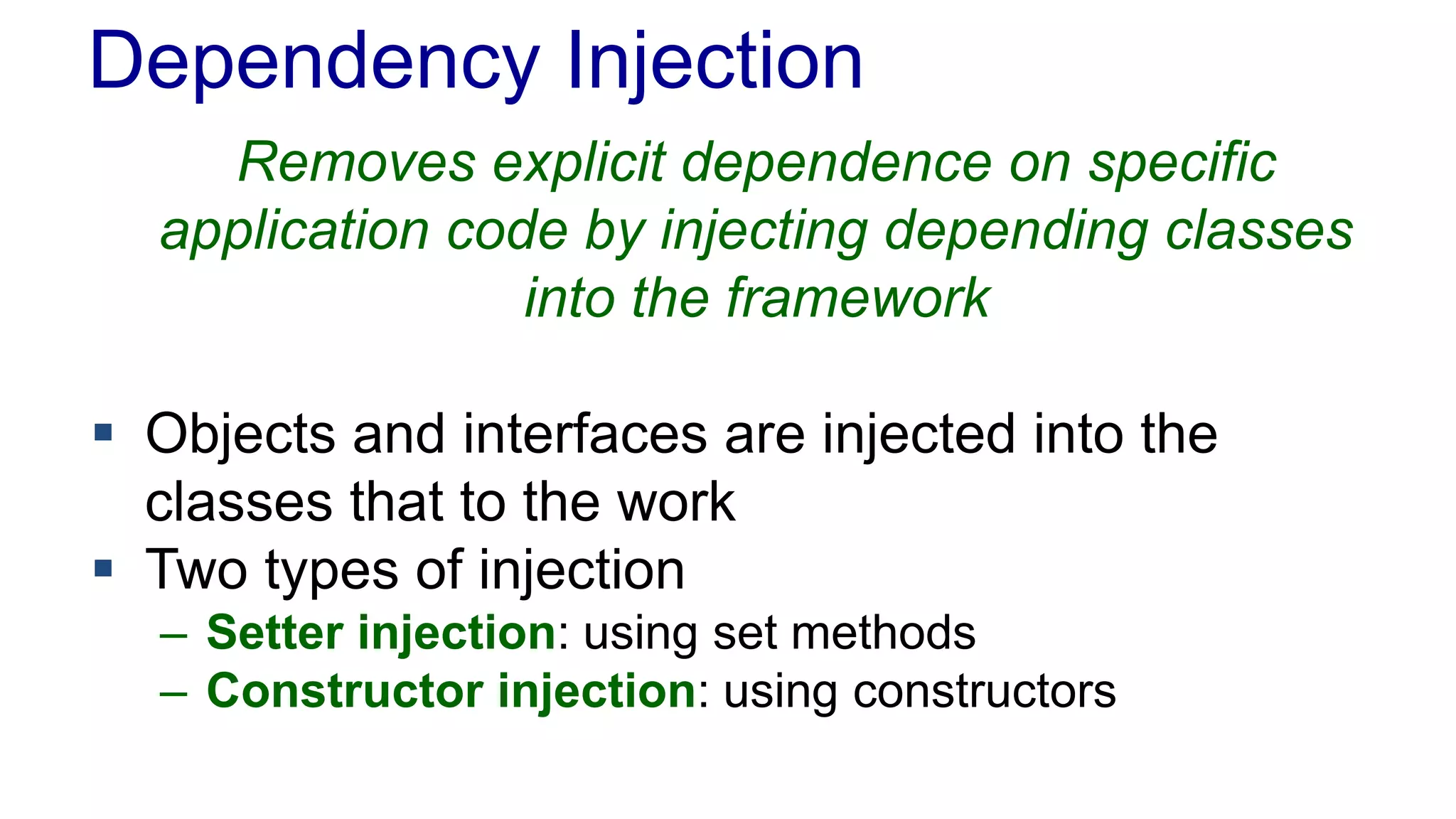
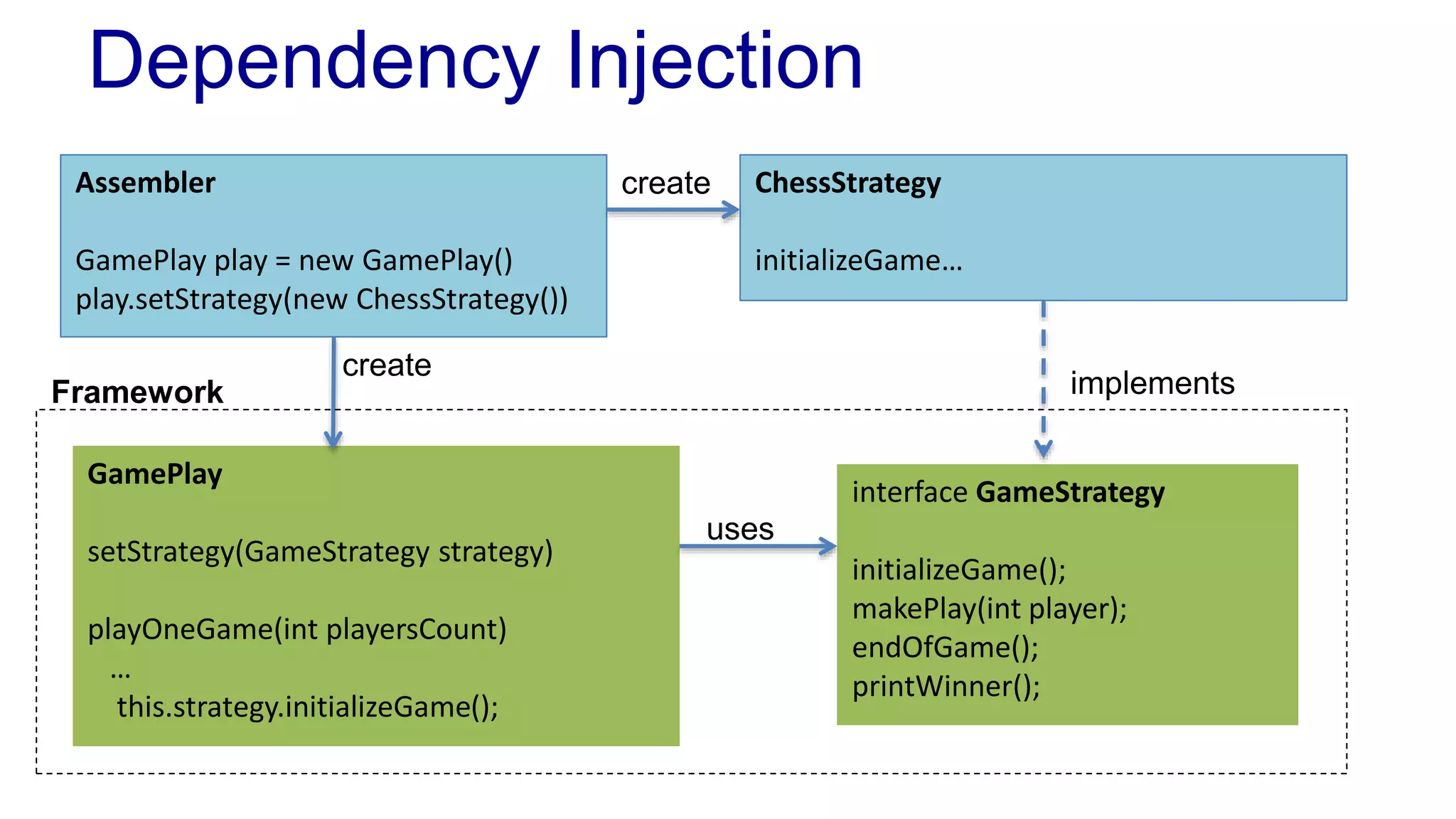
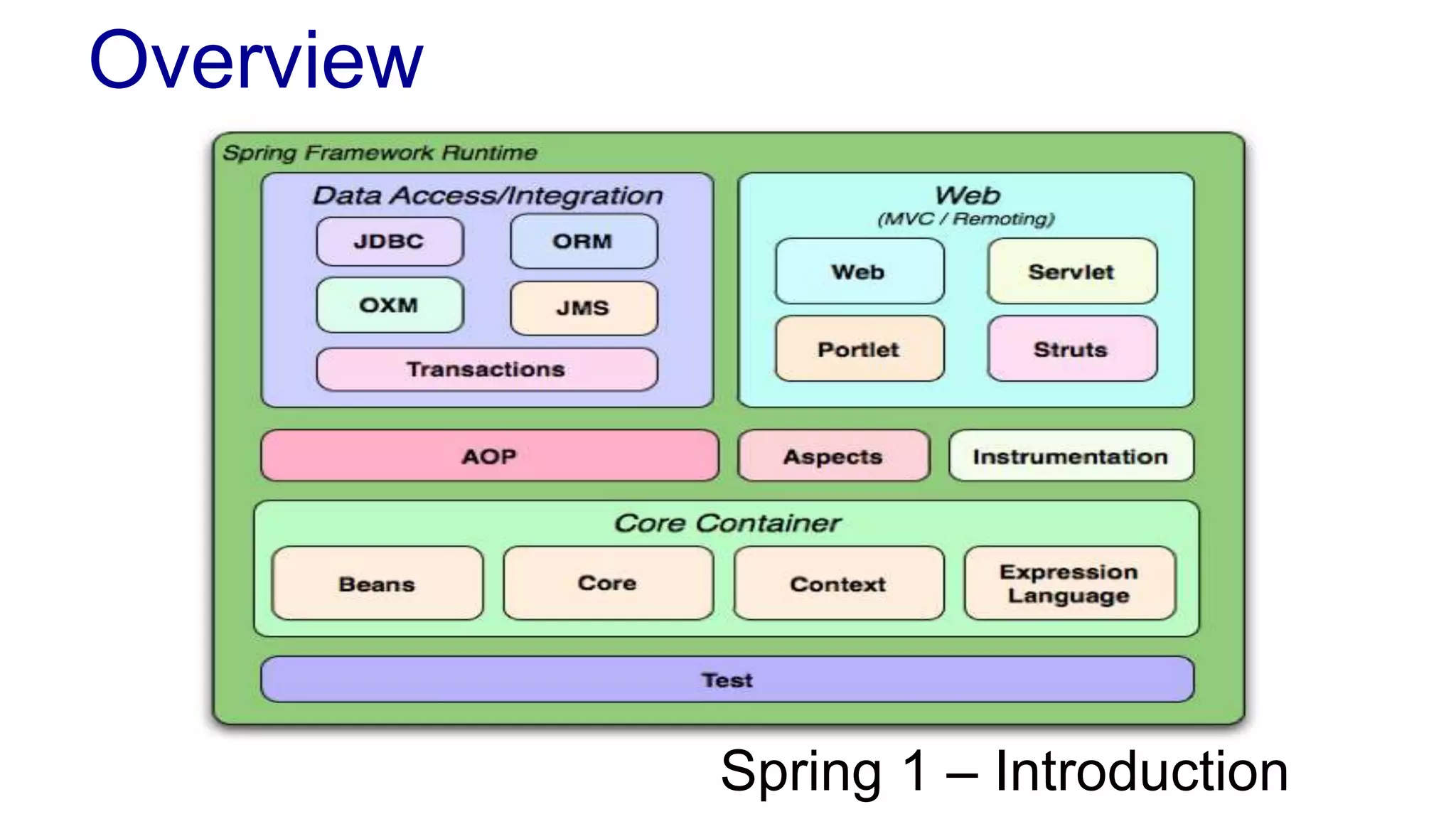
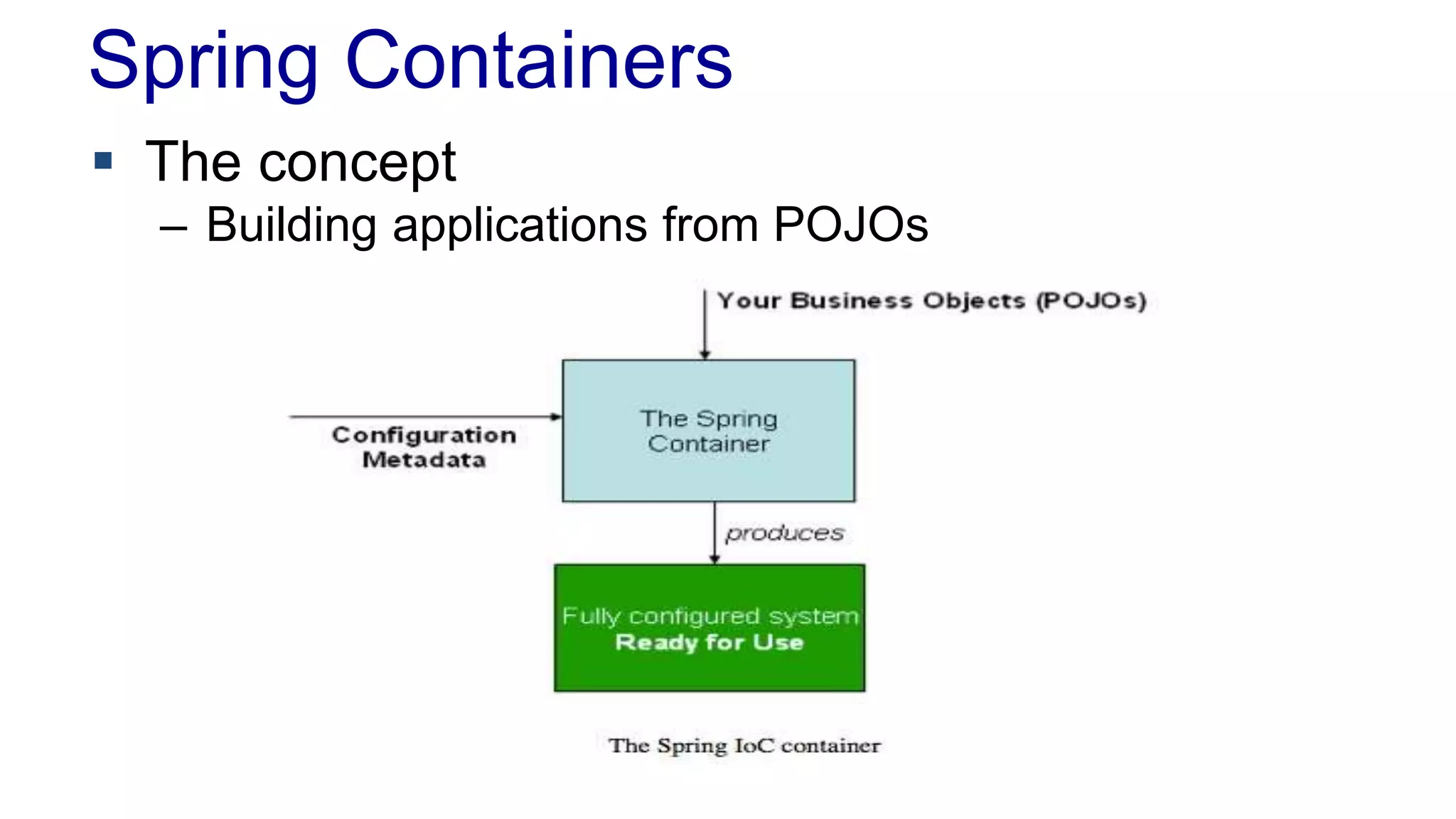
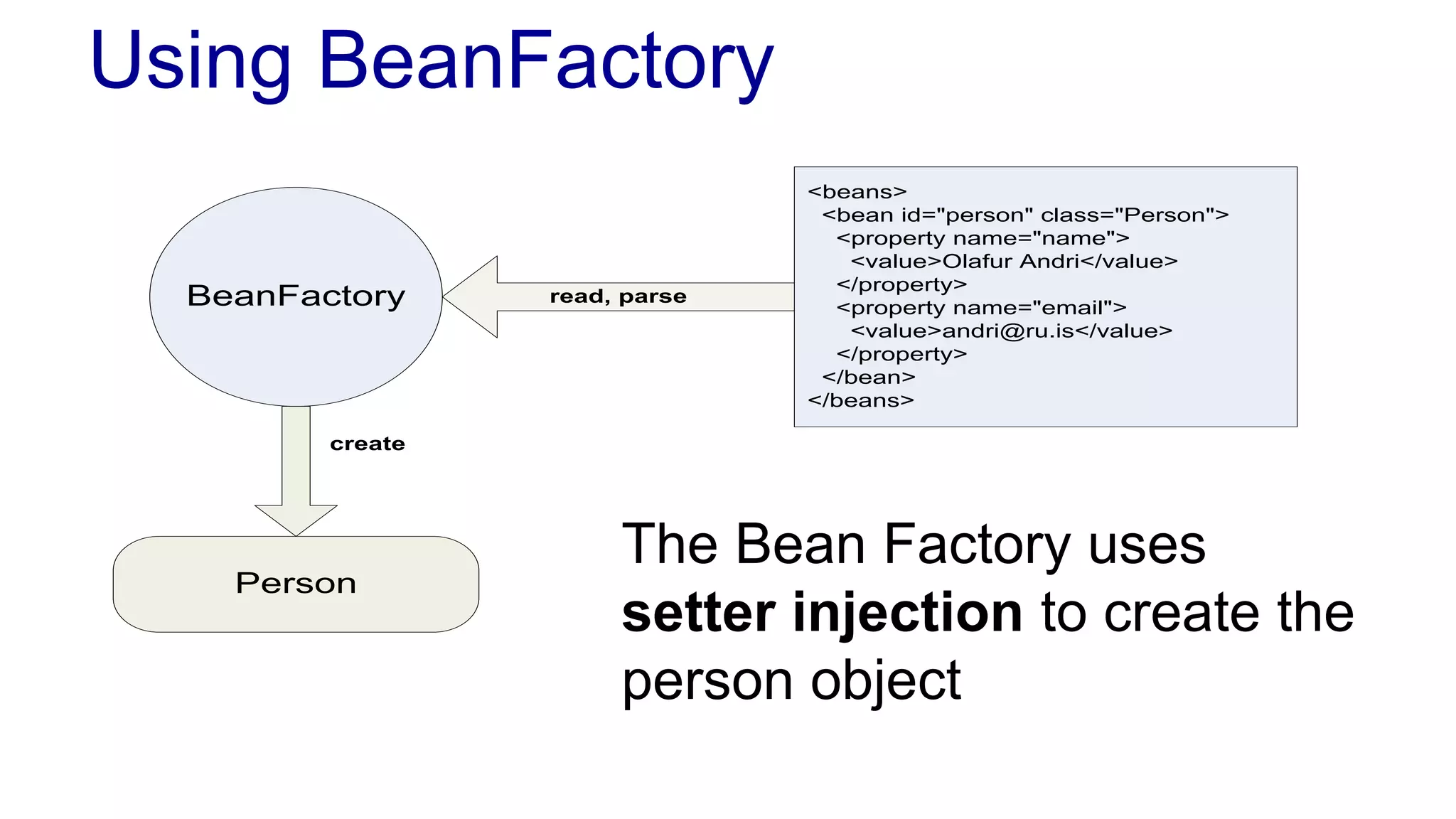
The document discusses the design of a game framework using various design patterns, including Template Method and Strategy, while also emphasizing the importance of Dependency Injection. It highlights how these patterns can be applied to common board games to create a flexible and extensible game architecture. Additionally, it introduces the Spring Framework's lightweight containers for managing object life-cycles and applications through Inversion of Control.



















![FileSystemXmlApplicationContext
Loads the context from an XML file
public class AppTest
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
ApplicationContext ctx =
new FileSystemXmlApplicationContext("app.xml");
Application contexts are intended as central
registries
– Support of hierarchical contexts (nested)
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/l10usingframeworks-140919054937-phpapp02/75/L10-Using-Frameworks-35-2048.jpg)
