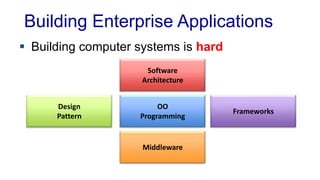
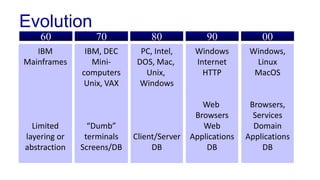
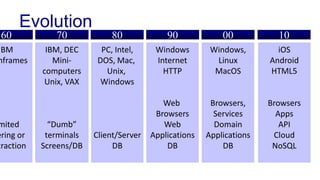
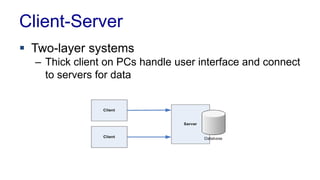
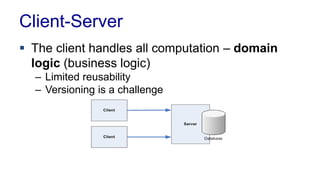
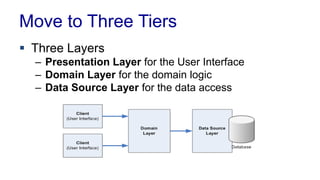
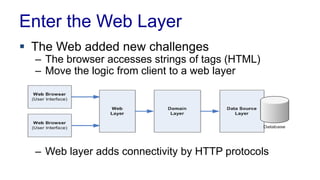
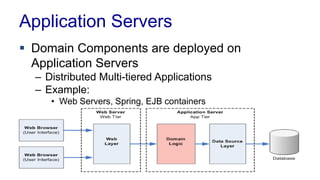
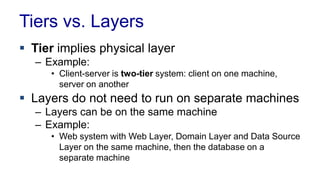
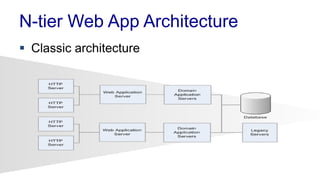
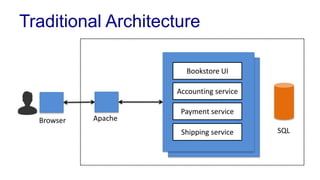
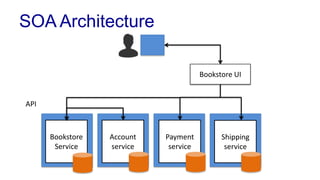
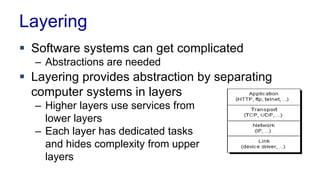
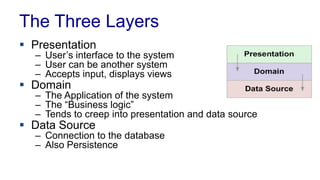
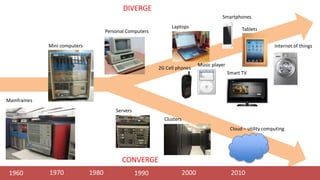
The document discusses enterprise application architecture, detailing the evolution from the personal computer era to the post-PC era characterized by mobile devices and cloud computing. It outlines the importance of service-oriented architecture, software as a service, and layering in building robust enterprise applications. Key concepts include the challenges in software integration, the necessity of middleware, and architecture design patterns for effective system development.






![“[The Personal Computer] can
become the 'Digital Hub'
of our emerging digital lifestyle,
adding tremendous value
to our other devices.”
- Steve Jobs, 2001 Keynote
introducing the iPod
THE DIGITAL
DECADE](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/l01enterpriseapplicationarchitecture-130819124726-phpapp02/85/L01-Enterprise-Application-Architecture-8-320.jpg)