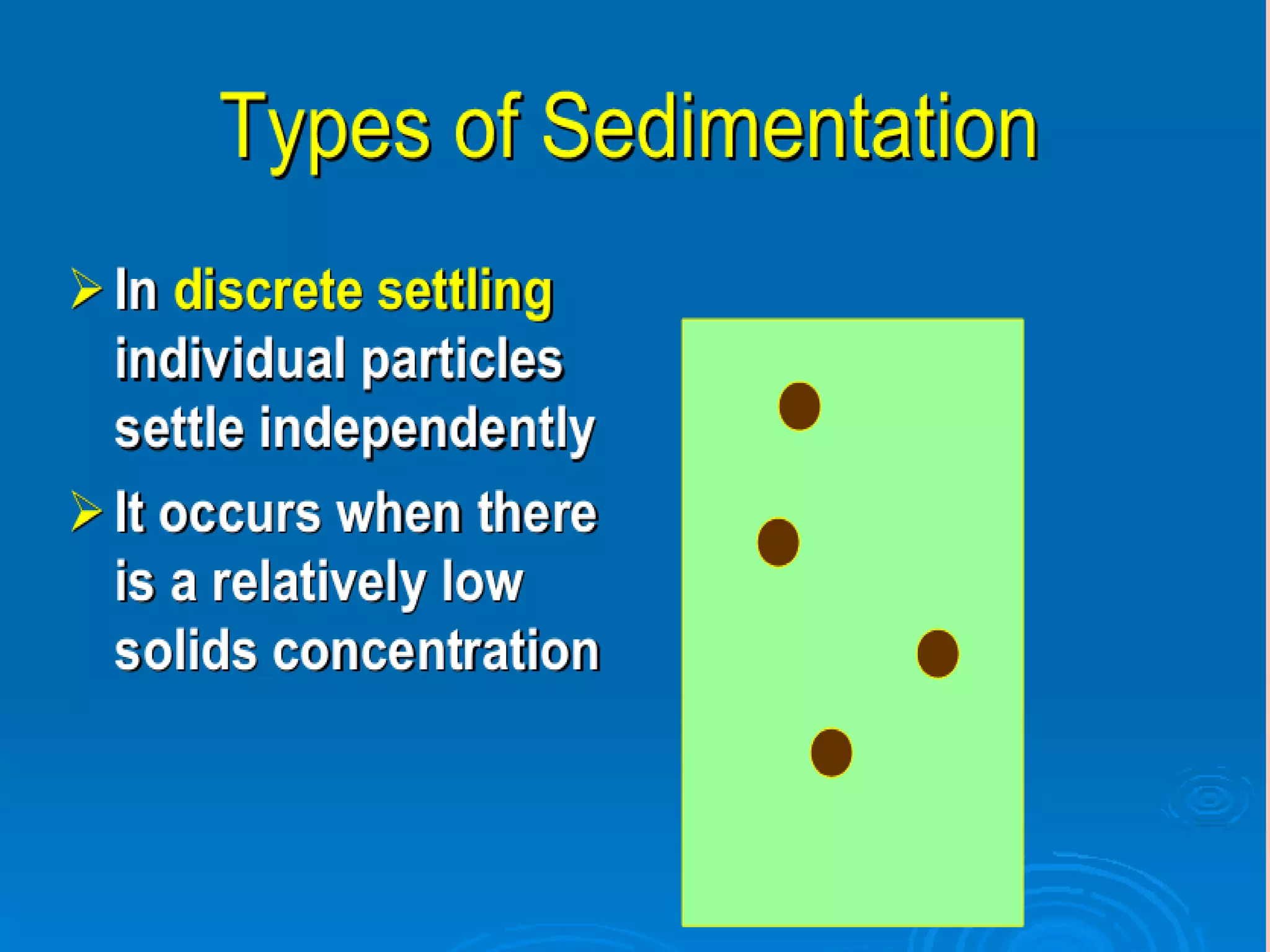
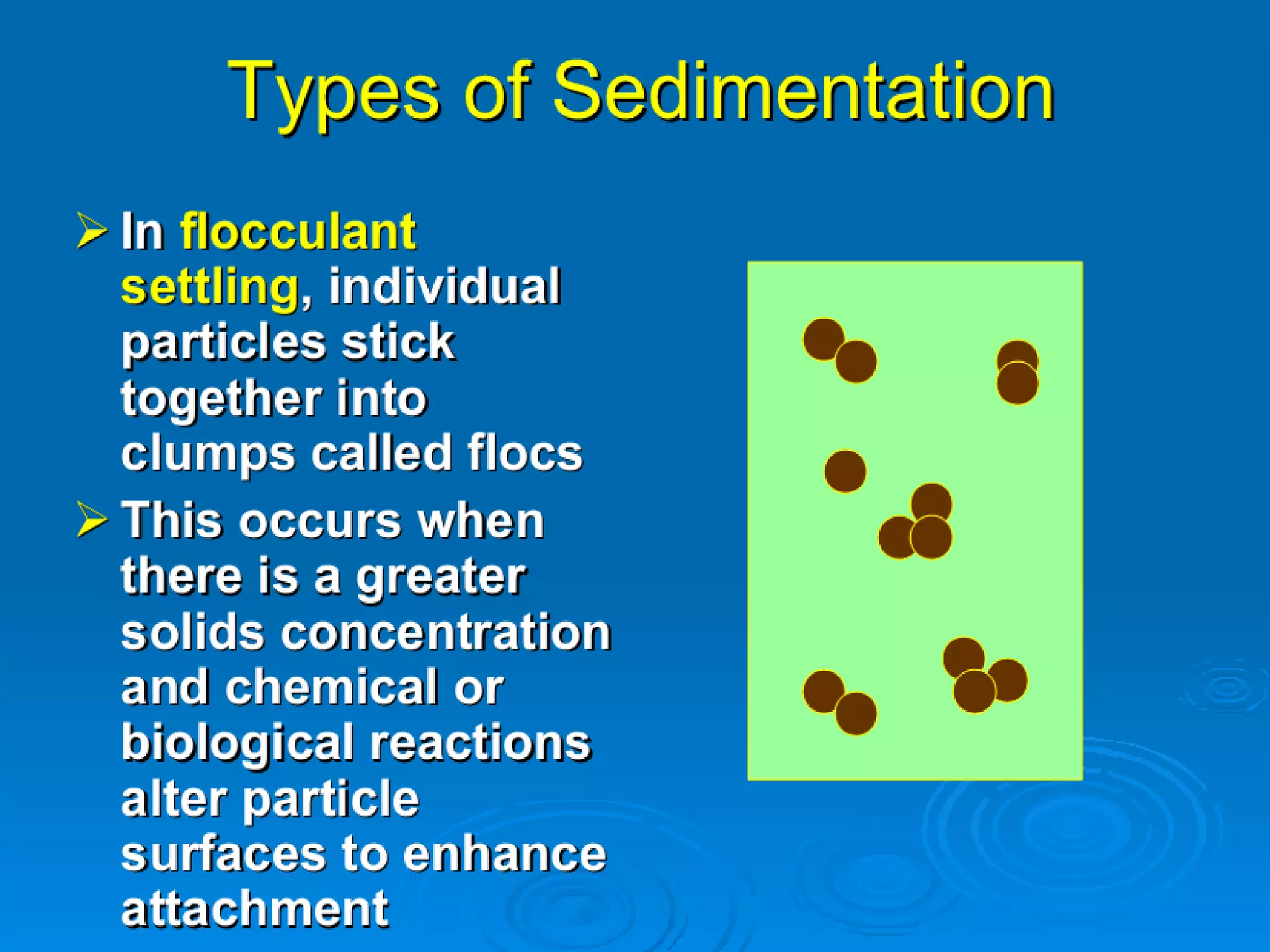
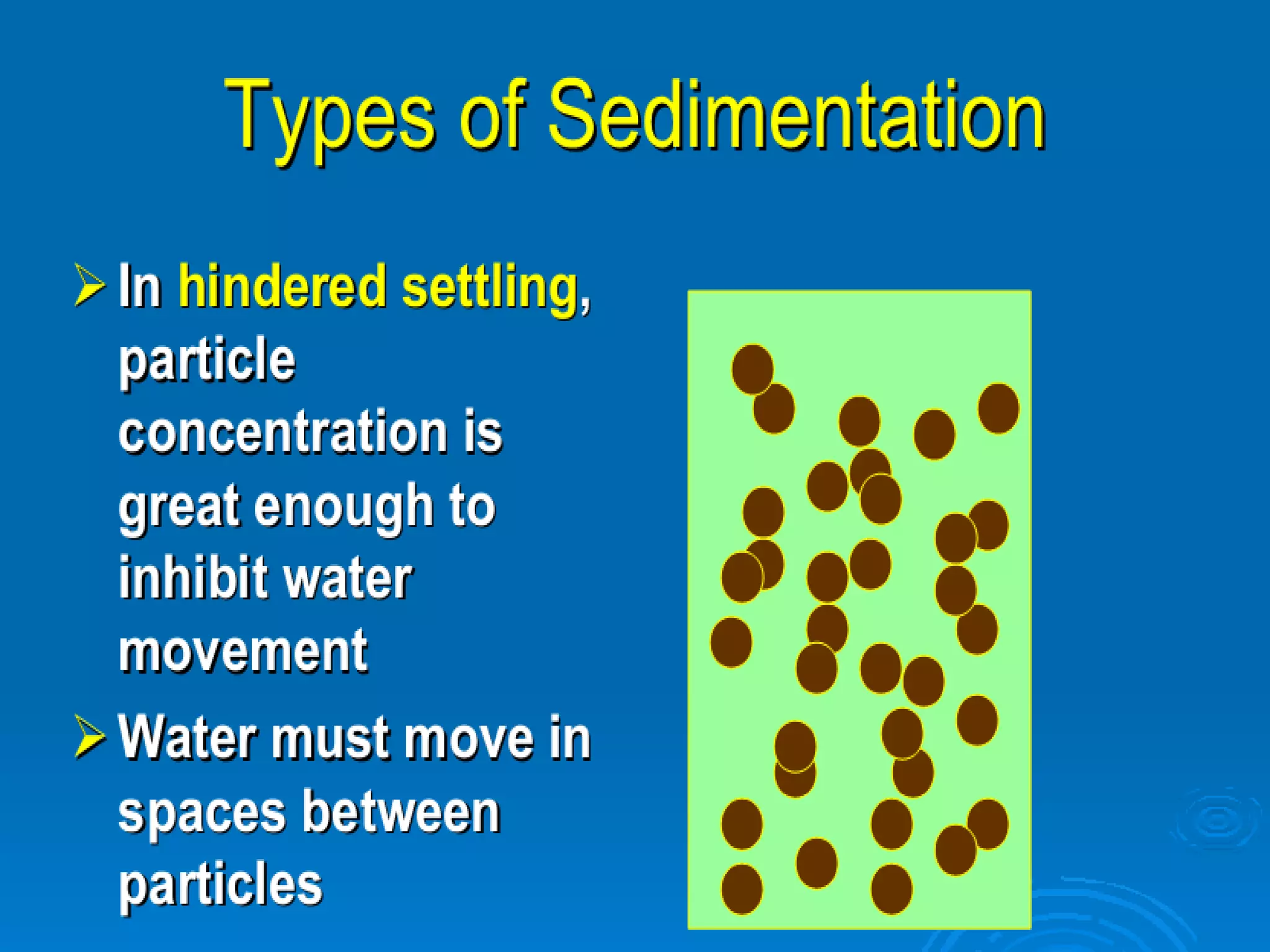
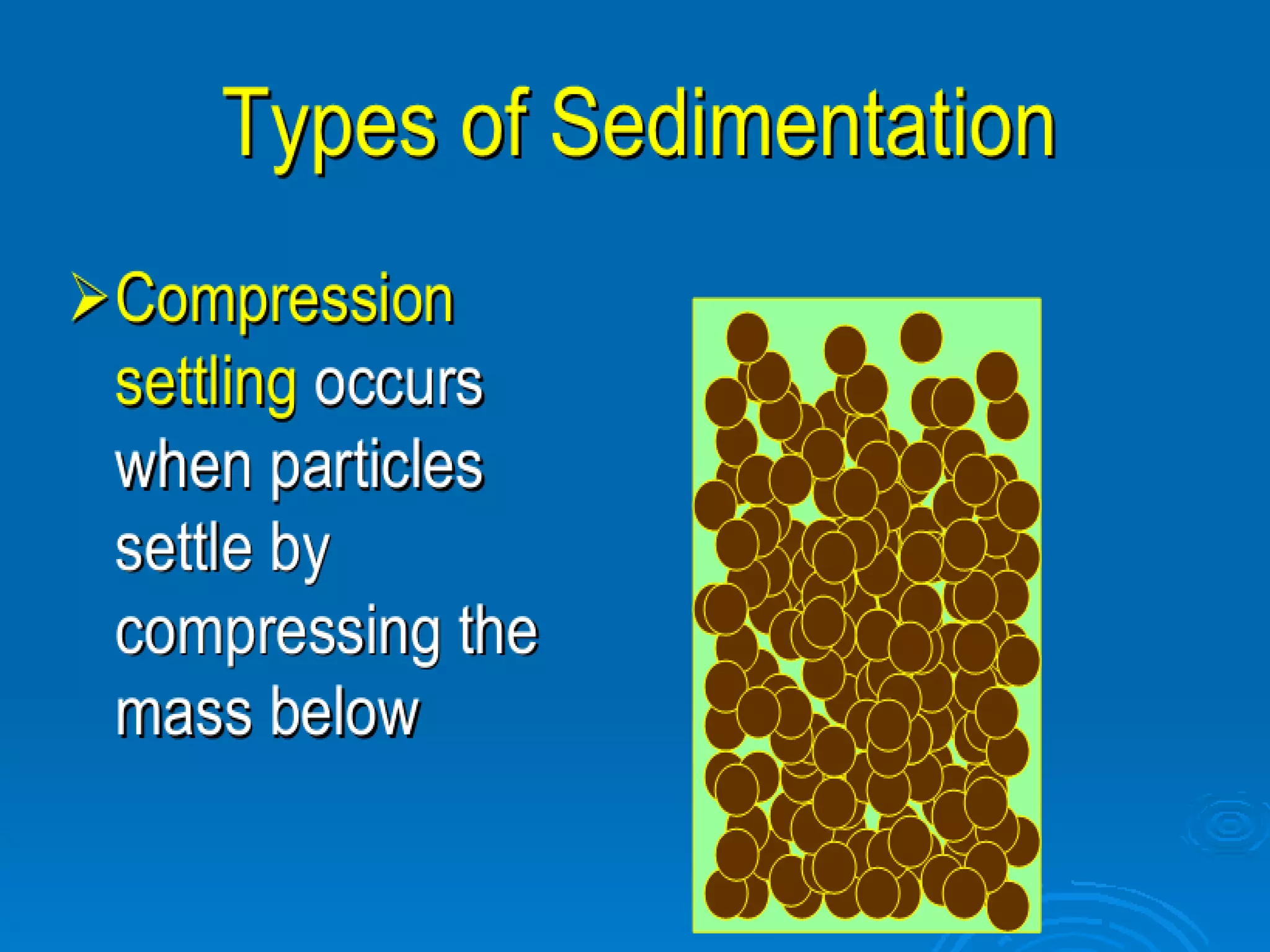
This document discusses sedimentation and settling tank design. It covers types of settling, zones in settling tanks, ideal settling conditions, design of settling basins, inlet and outlet arrangements, types of settling tanks including rectangular and circular, and objective and theory questions related to settling tank design and performance. Key factors discussed include overflow rate, flow velocity, detention time, settling velocity, and factors that affect settling efficiency such as turbulence.