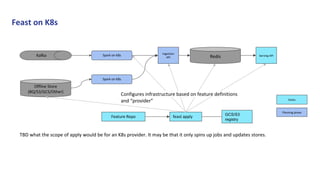
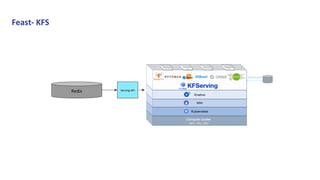
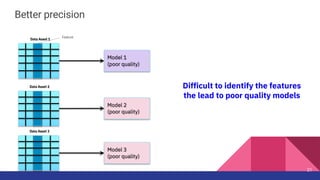
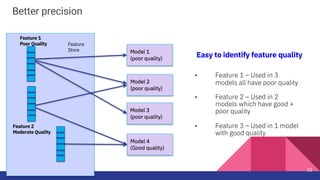
1. KFServing and Feast provide capabilities for serving machine learning models and managing features respectively.
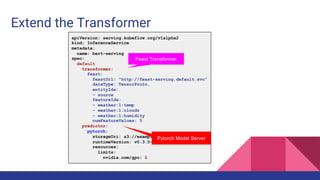
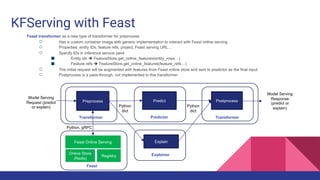
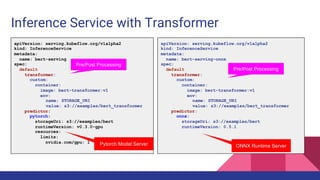
2. The Feast feature store is proposed as a new type of transformer for KFServing to preprocess requests by retrieving online features from Feast to augment the input for models.
3. This would allow models deployed using KFServing to leverage curated features stored in Feast for more accurate inferences.



![Hidden Technical Debt in Machine Learning Systems
5
Tech/User
Trends
Coming up with features is difficult, time-consuming,
requires expert knowledge. "Applied machine
learning" is basically feature engineering.
- Andrew Ng, Founder of deeplearning.ai
...some machine learning projects succeed and
some fail. What makes the difference? Easily the
most important factor is the features used.
- Pedro Domingos, author of ‘The Master Algorithm
algorithms we used are very standard for Kagglers. […]
We spent most of our efforts in feature engineering.
[...]
- Xavier Conort, Chief Data Scientist DataRobot
Feature Engineering is essential, difficult, and costly](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/kfserving-feast-210501194315/85/KFServing-and-Feast-5-320.jpg)