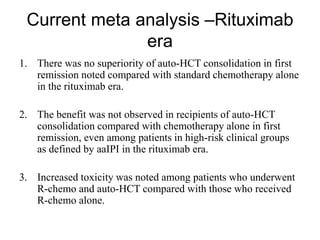
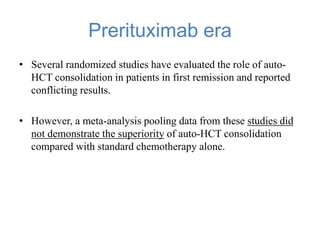
This systematic review and meta-analysis evaluated the role of upfront autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (auto-HCT) consolidation for patients with aggressive B-cell lymphomas in first remission in the rituximab era. The analysis included 4 randomized controlled trials comparing R-chemotherapy alone to R-chemotherapy plus auto-HCT. There were no differences in overall survival, progression-free survival, or response rates between the two treatment arms. Patients receiving auto-HCT had significantly higher rates of grade 3-4 infections and gastrointestinal toxicities. The review concludes that in the rituximab era, auto-HCT consolidation does not provide a benefit over chemotherapy alone, even for




![• Data collection:
Study characteristics -- design, timing of study, and location.
Patient characteristics -- age, sex, and disease characteristics.
Treatment characteristics -- dose and cotherapies.
Outcomes related to benefits -- overall survival [OS],
progression-free survival [PFS], and response rates.
Harms - treatment-related mortality [TRM] and adverse events
• The risk of bias in individual studies was evaluated using the
Cochrane Risk of Bias assessment tool for RCTs.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/journalautobmt-210518064854/85/Journal-auto-bmt-9-320.jpg)


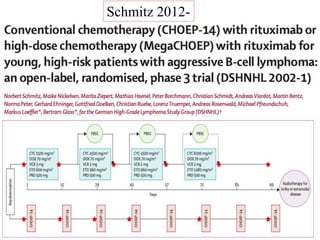
![• After a median of 42 months
• Patients with age-adjusted IPI 2 had significantly better event-free
survival if treated with R-CHOEP-14 (75·5% [95% CI 66·5–84·5] in
the R-CHOEP-14 group vs 63·5% [53·5–73·5] in the R-
MegaCHOEP group; p=0·0509) and overall survival (91·0% [95% CI
85·1–96·9] vs 77·1% [68·3–85·9]; p=0·01 .
• No significant differences were seen if patients with age- adjusted IPI
3 only were assessed (event-free survival: 53·9% [95% CI 37·2–
70·6] vs 55·5% [38·6–72·4];
R-CHOEP R-MegaCHOEP
3yr EFS 69.5% 61.4% (p=0.14)
3yr PFS 73.7% 69.8% (P=0.48)
3yr OS 84.6% 77% (P=0.08)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/journalautobmt-210518064854/85/Journal-auto-bmt-15-320.jpg)
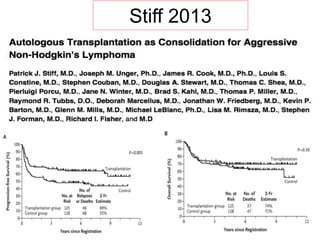
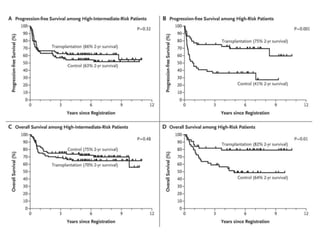



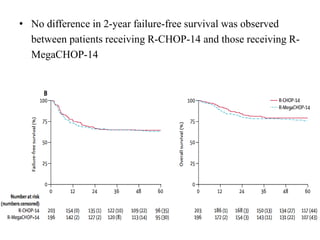
![• 2-year failure-free survival was 71% (95% CI 64–77) in the
transplantation group versus 62% (95% CI 55–68) in the no
transplantation group (hazard ratio [HR] 0·65 [95% CI 0·47–
0·91]; stratified log-rank test p=0·012).
• No difference in 5-year overall survival was observed between
these groups (78% [95% CI 71–83] versus 77% [71–83]; HR
0·98 [0·65–1·48]; stratified log-rank test p=0·91).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/journalautobmt-210518064854/85/Journal-auto-bmt-25-320.jpg)
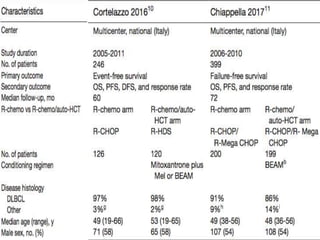
![• Grade 3 or worse haematological adverse events were reported
in 183 (92%) of 199 patients in the transplantation group
versus 135 (68%) of 200 patients in the no transplantation
group.
• Grade 3 or worse non-haematological adverse events were
reported in 90 (45%) versus 31 (16%)
• The most common grade 3 or worse non-haematological
adverse event was gastrointestinal (49 [25%] vs 19 [10%]).
• Treatment-related deaths occurred in 13 (3%) patients; eight in
the transplantation group and five in the no transplantation
group.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/journalautobmt-210518064854/85/Journal-auto-bmt-27-320.jpg)

![Survival Outcomes
• There was no difference in OS noted for patients who received
R-chemo and auto- HCT compared with those who received
R-chemo alone (HR, 1.01; 95% CI, 0.74-1.37 [P = .96]) .](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/journalautobmt-210518064854/85/Journal-auto-bmt-29-320.jpg)
![• There was no difference in OS noted between the 2 groups, even when
the analysis was limited to the high-risk aaIPI group (HR, 0.75; 95%
CI, 0.47-1.19 [P = .22]).
• One study that demonstrated significantly improved OS in the R-
chemo and auto- HCT treatment arm compared with the R-chemo
alone arm among the patients with high-risk aaIPI (HR, 0.35; 95% CI,
0.16-0.78) was based on the ad hoc analysis.(Stiff 2013)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/journalautobmt-210518064854/85/Journal-auto-bmt-30-320.jpg)
![Progression Free Survival
• There was no difference in PFS noted for patients who received R-
chemo and auto-HCT compared with those who received R-chemo
alone (HR, 0.77; 95% CI, 0.58- 1.04 [P = .09])](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/journalautobmt-210518064854/85/Journal-auto-bmt-31-320.jpg)
![• PFS stratified by aaIPI was provided in only 2 studies.
• There was no difference in PFS observed between the 2 groups
when the analysis was limited to the group of patients with
high-risk aaIPI (HR, 0.51; 95% CI, 0.23- 1.10 [P = .09])](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/journalautobmt-210518064854/85/Journal-auto-bmt-32-320.jpg)
![Response Rates
• Response rates (ORR and CR) were reported in 3 studies.
• There was no difference in the ORR observed for patients who
received R-chemo compared with those treated with R-chemo
and auto-HCT (RR, 0.98; 95% CI, 0.92-1.04 [P = .46])](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/journalautobmt-210518064854/85/Journal-auto-bmt-33-320.jpg)
![• There was no difference in the CR rate noted between
the 2 groups (RR, 0.99; 95% CI, 0.91-1.07 [P = .78])](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/journalautobmt-210518064854/85/Journal-auto-bmt-34-320.jpg)
![Treatment-Related Mortality
• There was no difference in the risk of TRM noted between
patients who received R-chemo and auto-HCT and those who
received R-chemo alone (RR, 1.57; 95% CI, 0.92- 2.69 [P =
.10]) .](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/journalautobmt-210518064854/85/Journal-auto-bmt-35-320.jpg)
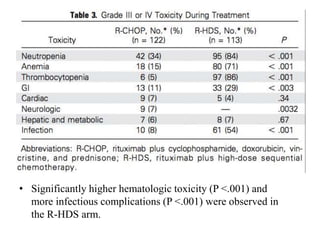
![Adverse Events
• All 4 studies reported grade 3 or 4 infections.
• Patients who received R-chemo and auto-HCT had a
significantly higher risk of grade 3 or 4 infections (RR, 4.20;
95% CI, 2.32-7.59 [P < .00001])
• Patients in the R-chemo and auto- HCT arm were found to
have significantly higher rates of grade 3 or 4 hematologic
toxicities compared with patients in the R-chemo alone group](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/journalautobmt-210518064854/85/Journal-auto-bmt-36-320.jpg)
![• Nonhematologic toxicities were reported in 3 studies.
• Patients in the R-chemo and auto- HCT arm were found to
have significantly higher rates of grade 3 or 4 gastrointestinal
AEs compared with patients in the R-chemo alone group (RR,
3.15; 95% CI, 2.14-4.64 [P < .00001])
• However, there was no difference in the rates of grade 3 or 4
cardiac (RR, 1.50; 95% CI, 0.48-4.63 [P = .49]) or neurologic
(RR, 0.57; 95% CI, 0.10-3.16 [P = .52]) AEs noted between
the 2 groups.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/journalautobmt-210518064854/85/Journal-auto-bmt-37-320.jpg)


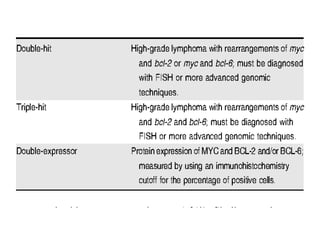
![• The results of the current meta-analysis demonstrated that the
clinical prognostic markers (incorporated into aaIPI) are
unlikely to identify a high-risk DLBCL cohort in whom the
application of auto-HCT may improve outcomes.
• In recent years, various immunohistochemistry-based assays
(eg, Hans algorithm to identify cell of origin, double expressor
lymphoma based on c-MYC and BCL2
immunohistochemistry) or genomic assays (gene expression
profiling or fluorescence in situ hybridization [FISH] assays to
identify subsets of patients with DLBCL with c-MYC, BCL2,
and/or BCL6 rearrangements) have helped to identify
biologically high-risk subgroups of patients with DLBCL.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/journalautobmt-210518064854/85/Journal-auto-bmt-42-320.jpg)