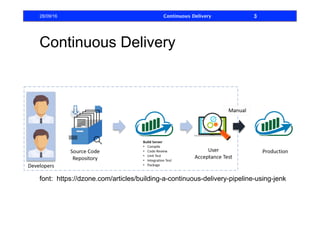
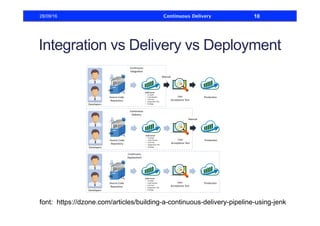
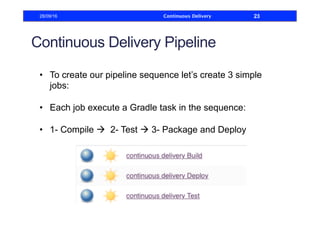
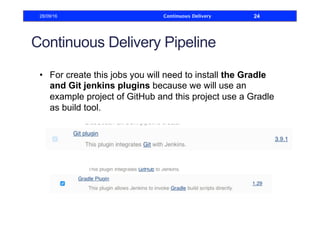
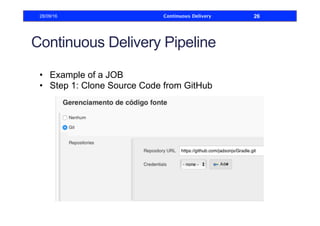
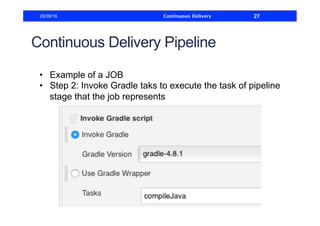
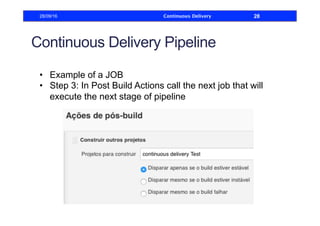
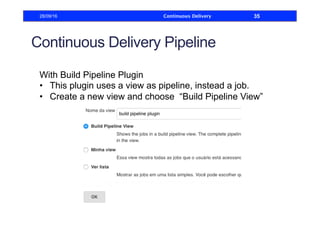
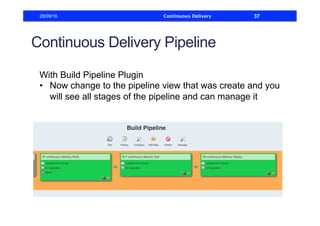
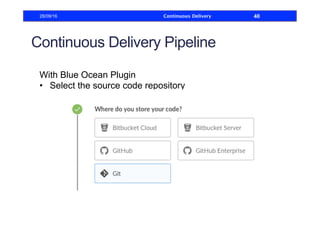
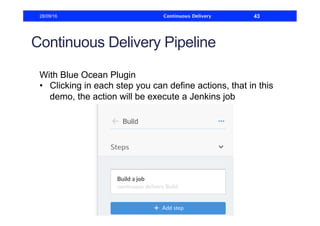
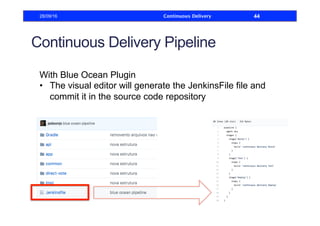
This document discusses how to build a continuous delivery pipeline using Jenkins. It describes setting up continuous integration, continuous delivery, and continuous deployment processes. Continuous integration involves testing code commits, continuous delivery means software can be released at any time, and continuous deployment automatically deploys releases. The document outlines configuring Jenkins jobs to compile code, run tests, and deploy packages across three stages of a pipeline. It also explains plugins for defining and visualizing the pipeline in Jenkins.