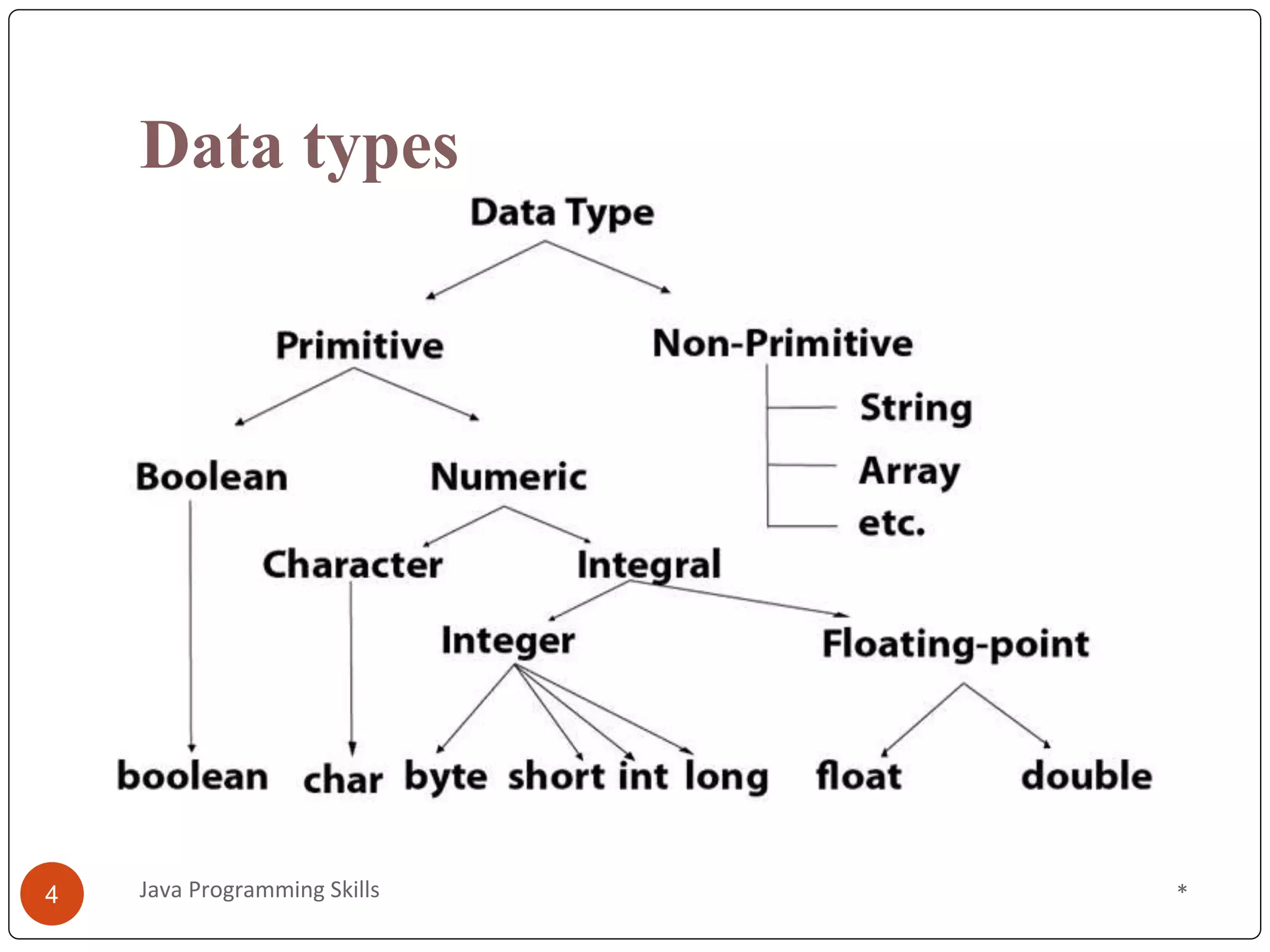
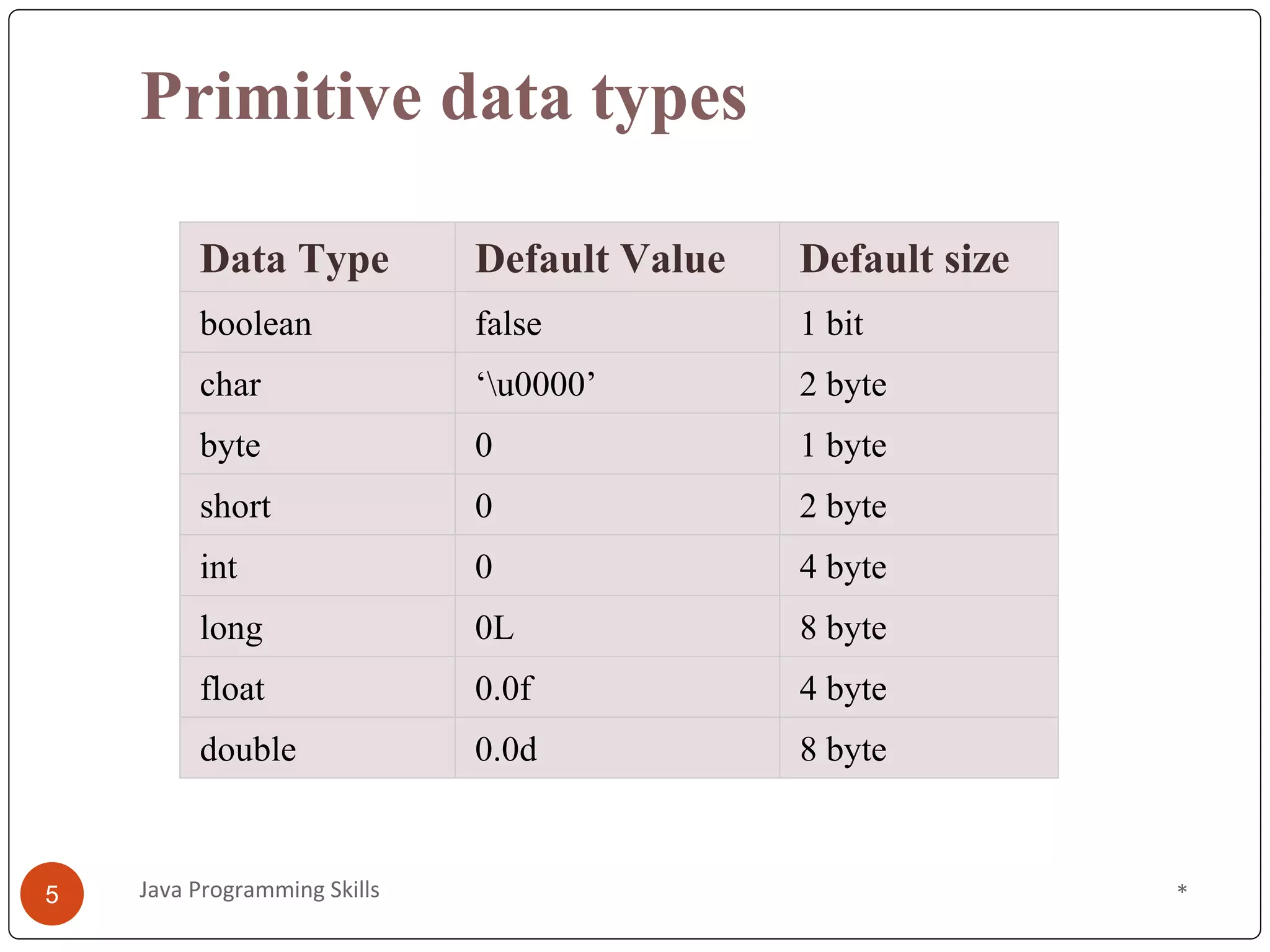
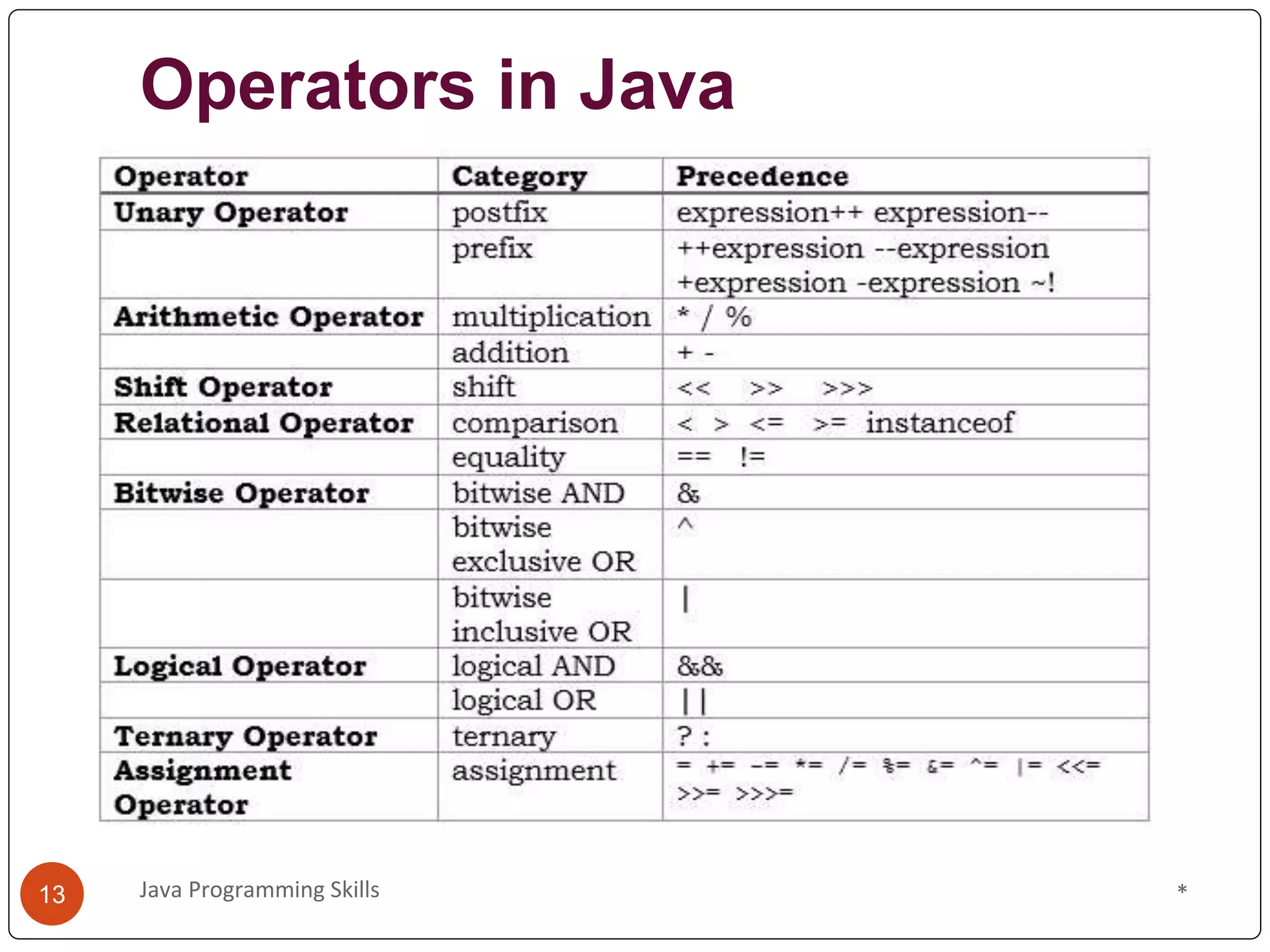
This document provides an overview of Java programming skills, including data types, variables, and operators. It discusses the different primitive and non-primitive data types in Java, like int, float, boolean, and String. It also covers variable scope and types, like local, instance, and static variables. Finally, it examines various operators in Java, such as arithmetic, logical, bitwise, shift, ternary, and assignment operators, illustrated with code examples. An online quiz link is provided at the end for readers to evaluate their understanding of these Java programming concepts.


![//Data type demo program
import java.util.*;
public class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int myNum = 5;
float myFloatNum = 9829.33f;
char myLetter = 'D';
boolean myBool = true;
byte myByte = 100;
short myShort = 5000;
long myLong = 2500000;
double myDouble = 9829.23d;
String myText = "Hello";
String[] myBranch = {"CSE", "ECE", "EEE", “CIVIL","MECH"};
*
7 Java Programming Skills](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javapskills-session2-230206143358-9dbfebb4/75/Java-PSkills-session2-pptx-7-2048.jpg)



![Variable Demo Program
public class Main
{
int a; // Instance variable
static int b=20; // static variable
public void prints()
{
int c=10; // local variable
System.out.println("Method local variable: "+c);
}
public static void main(String args[])
{ //Instance and static variable
VariableDemo demo=new VariableDemo();
System.out.println("Instance variable: "+demo.a);
System.out.println("Static variable: "+b);
demo.prints();
}
} *
11 Java Programming Skills](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javapskills-session2-230206143358-9dbfebb4/75/Java-PSkills-session2-pptx-11-2048.jpg)

![Unary Operator
class Main{
public static void main(String args[])
{
int x=10;
System.out.println(x++); // 10(11)
System.out.println(++x); //12
System.out.println(x--); //12(11)
System.out.println(--x); //10
}
}
*
Java Programming Skills
14](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javapskills-session2-230206143358-9dbfebb4/75/Java-PSkills-session2-pptx-14-2048.jpg)
![Shift Operators
The left shift operator << is used to shift all of the bits in
a value to the left side of a specified number of times.
The right shift operator >> is used to move left operands
value to right by the number of bits specified by the right
operand.
class Main
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
System.out.println(20<<3); //20*2^3=20*8=160
System.out.println(20>>3); //20/2^3=20/8=2
}
}
*
Java Programming Skills
15](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javapskills-session2-230206143358-9dbfebb4/75/Java-PSkills-session2-pptx-15-2048.jpg)
![Logical and Bitwise
Class Main{
public static void main(String args[])
{
int a=10,b=5,c=20;
System.out.println(a<b&&a<c);//false&&no checking=false
System.out.println(a<b&a<c);//false&true=false
System.out.println(a>b||a<c);//true||no checking=true
System.out.println(a>b|a<c);//true|true=true
}
}
*
Java Programming Skills
16](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javapskills-session2-230206143358-9dbfebb4/75/Java-PSkills-session2-pptx-16-2048.jpg)
![Ternary operator
⚫This is used as one liner replacement for if-else
statement. This is the only conditional operator which
takes three operands.
class Main{
public static void main(String args[])
{
int a=12, b=15;
int min=(a<b)?a:b;
System.out.println(min); //12
}
}
*
Java Programming Skills
17](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javapskills-session2-230206143358-9dbfebb4/75/Java-PSkills-session2-pptx-17-2048.jpg)
![Assignment operator
⚫It is used to assign the value on its right to the
operand on its left.
class Main{
public static void main(String args[]){
int a=10, b=20;
a+=4; //a=a+4(a=10+4)
b-=4; //b=b-4(b=20-4)
System.out.println(a); //14
System.out.println(b); //16
}}
*
Java Programming Skills
18](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javapskills-session2-230206143358-9dbfebb4/75/Java-PSkills-session2-pptx-18-2048.jpg)

