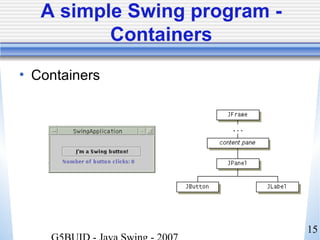
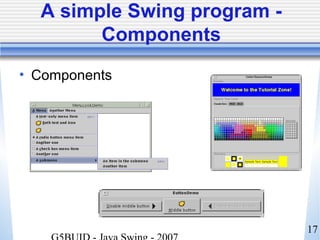
This document provides an introduction to Java Swing. It outlines the timeline for lectures on Swing topics. It emphasizes that a strong understanding of core Java concepts is required before learning Swing. It describes Swing as the Java Foundation Classes toolkit for building graphical user interfaces and distinguishes it from AWT. Finally, it previews that tomorrow's lecture will cover Swing components and containers in more detail.