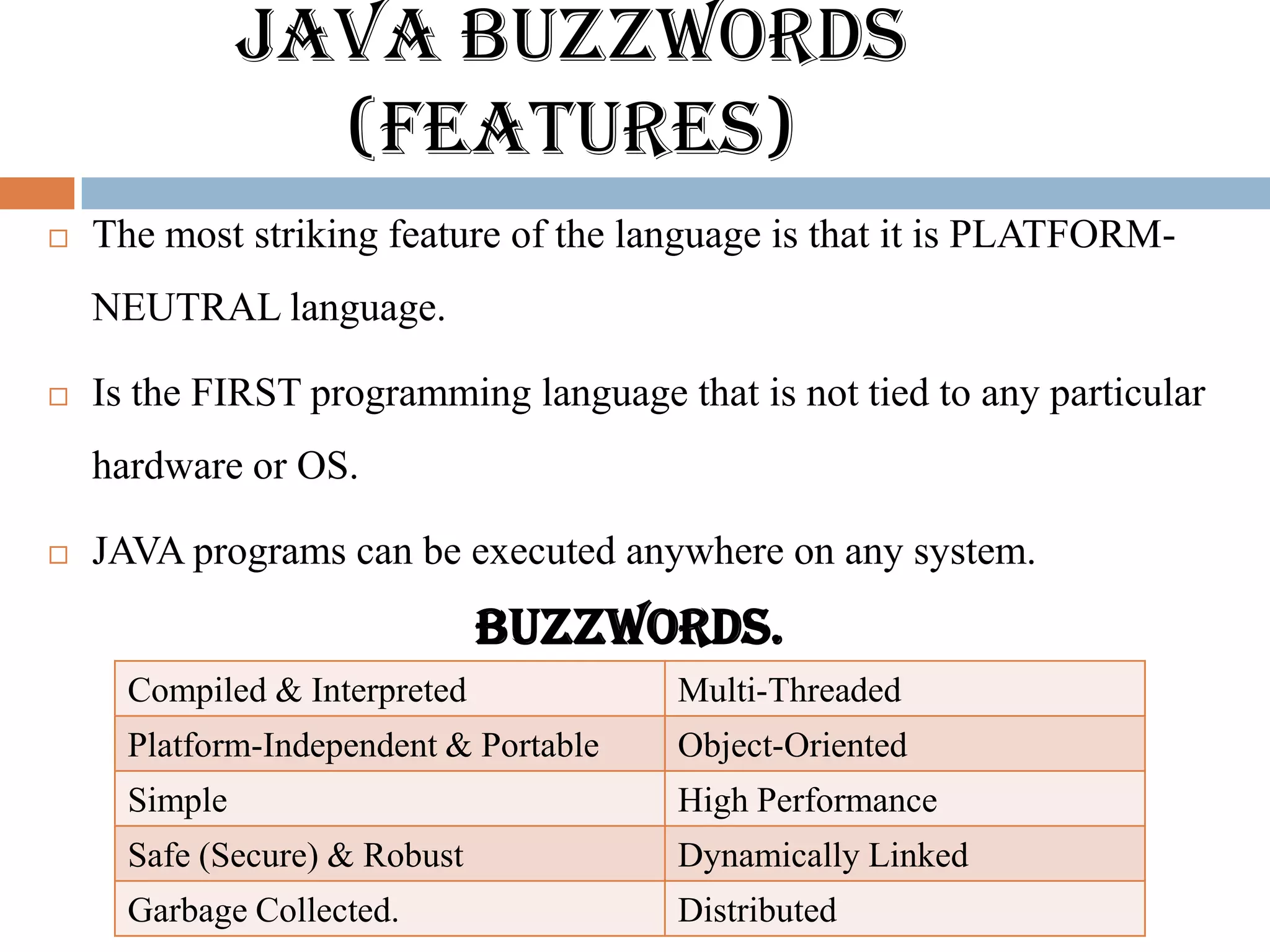
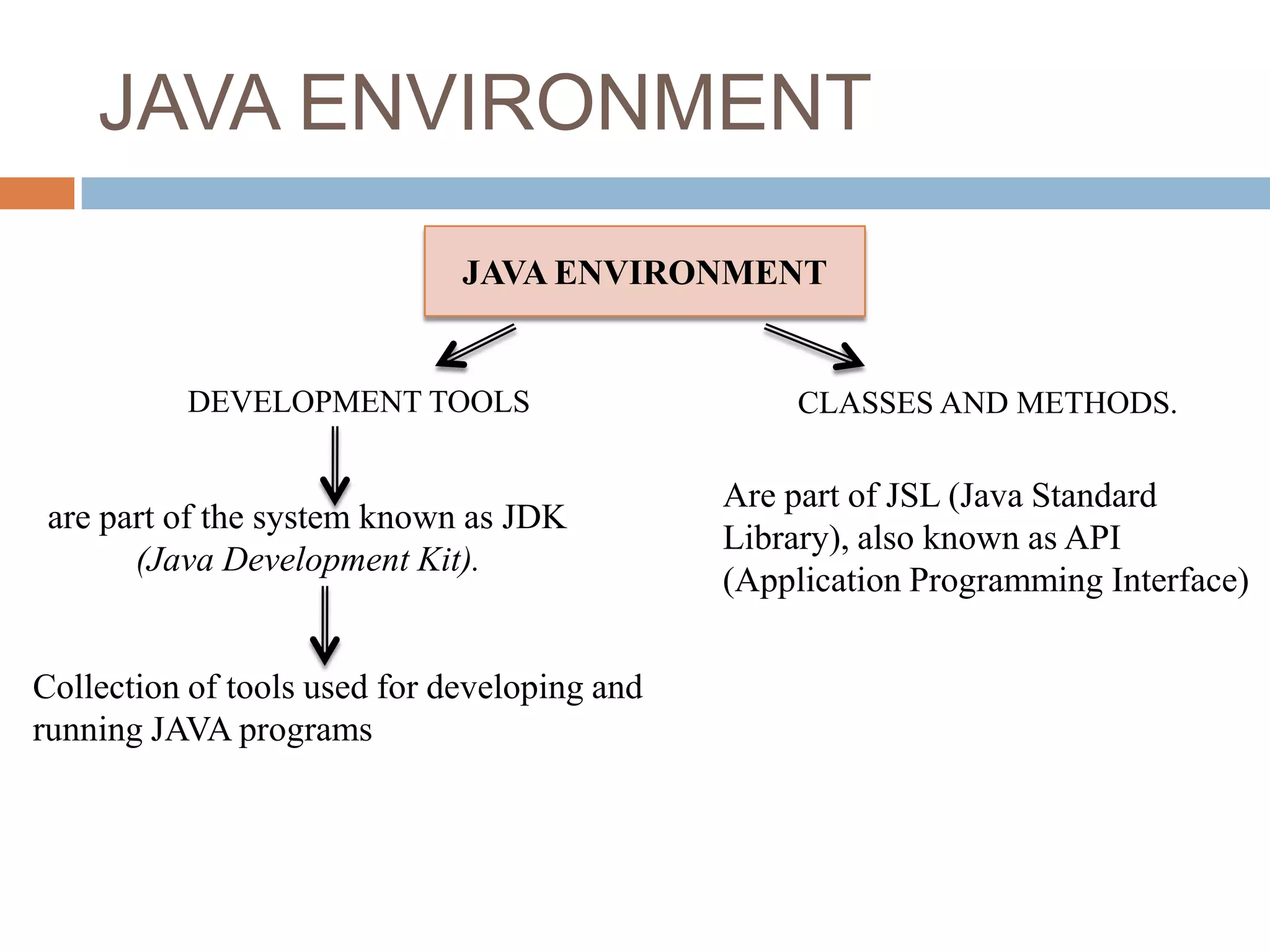
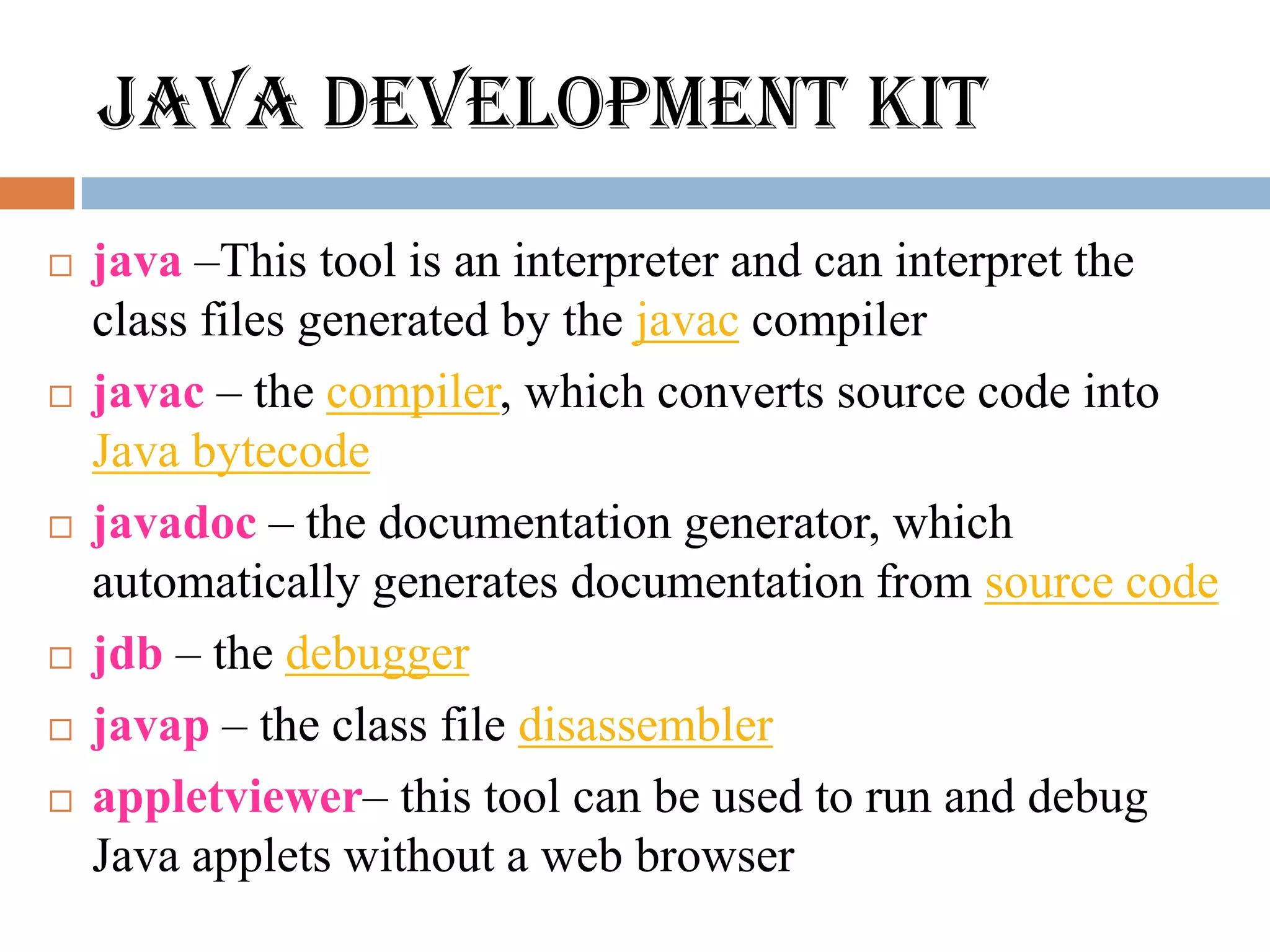
The document discusses key features of the Java programming language. It notes that Java is platform-neutral, meaning Java programs can be executed on any system without being tied to a particular hardware or operating system. It also mentions that Java is compiled and interpreted, object-oriented, multi-threaded, and has features like garbage collection. The document then provides an overview of the Java development environment and tools used like the Java Development Kit.

![HOW TO WRITE
A
JAVA PROGRAM?????
C++ program JAVA Program
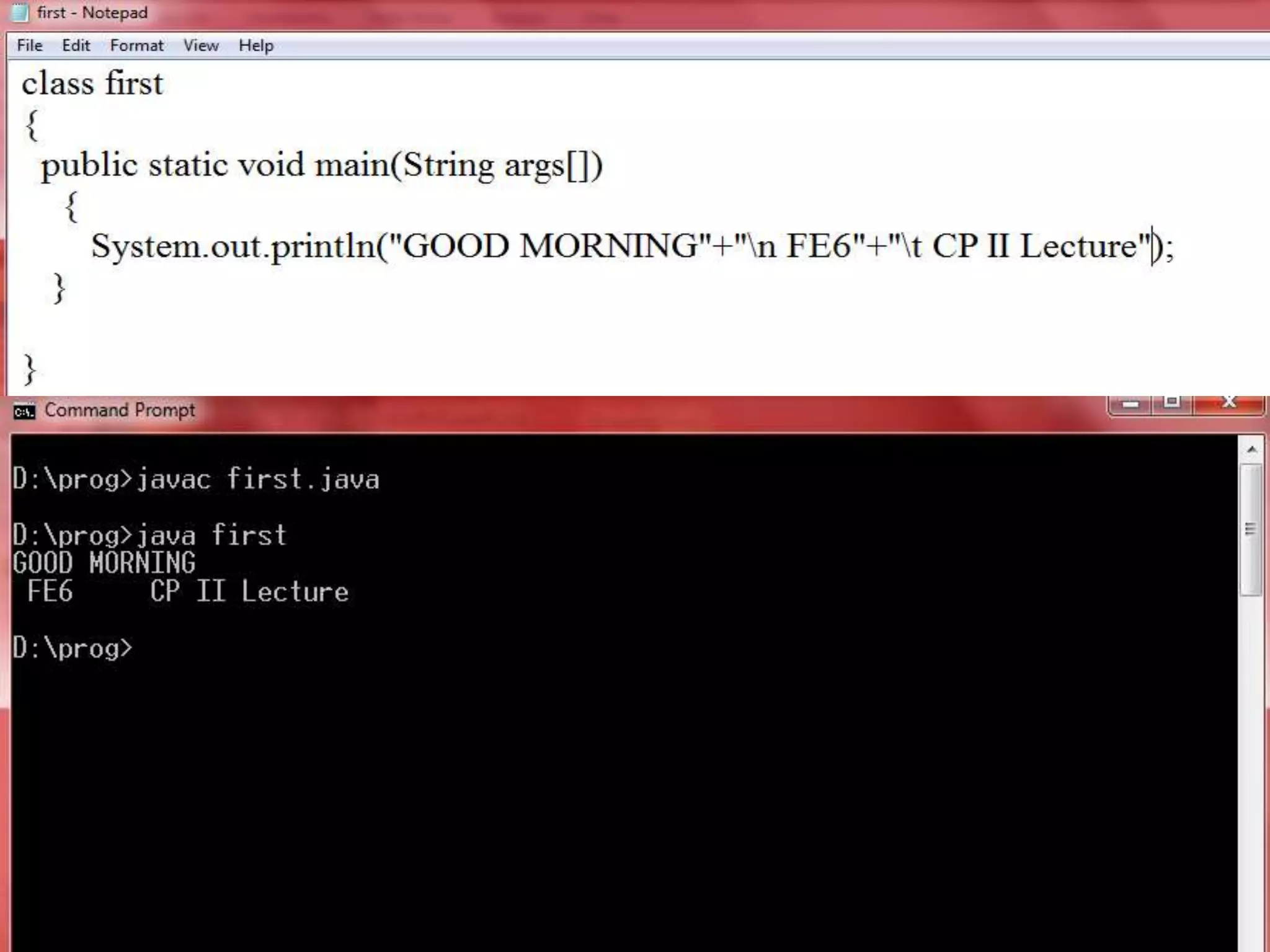
class First
{
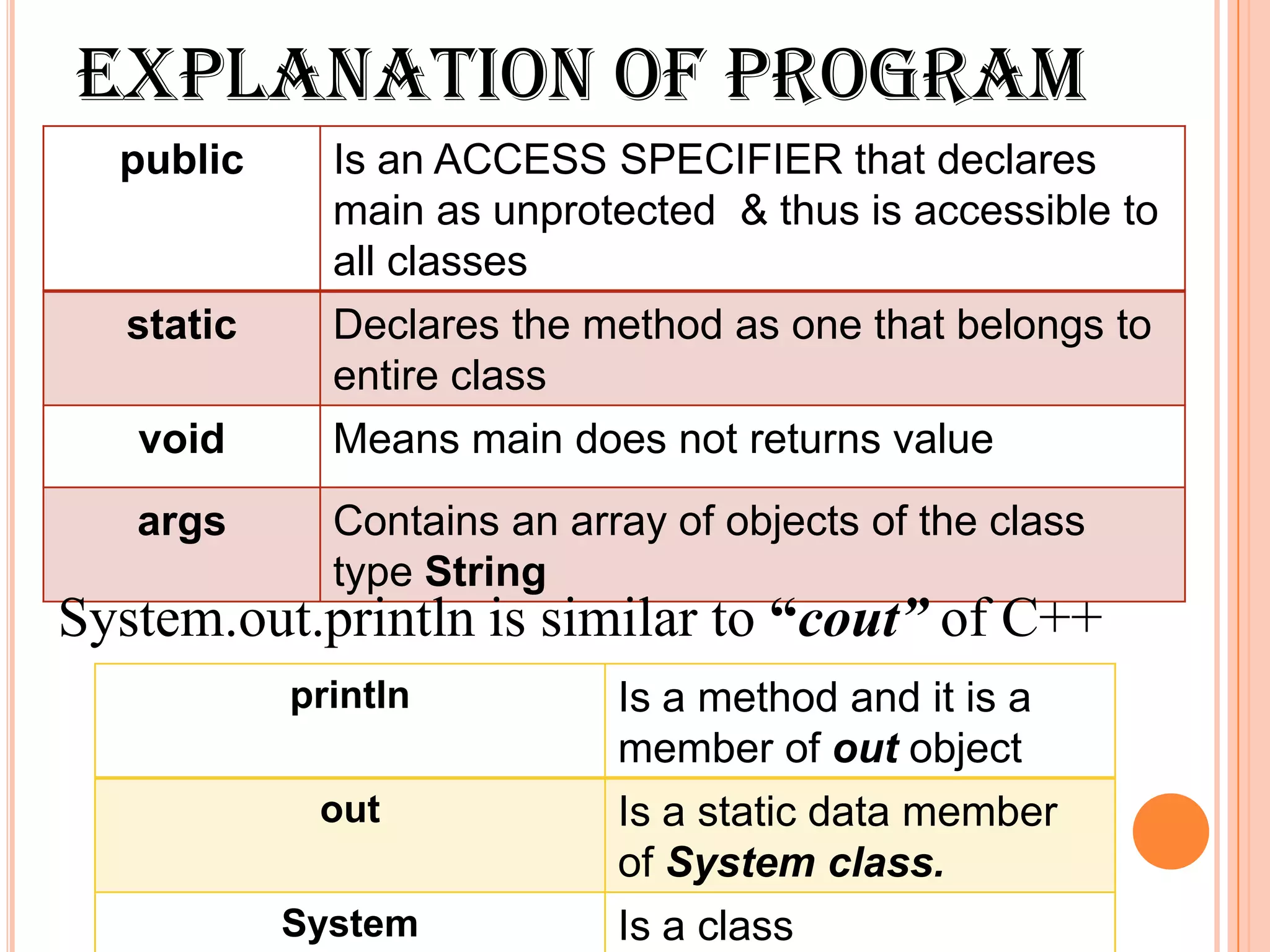
void main() public static void main( String args[])
{ {
cout<< “ My first C++ System.out.println(“My first JAVA
program”; program”);
getch(); }
} }
Since, JAVA is a true OO Language,
Everything must be placed inside a class.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lec2-120125095143-phpapp02/75/Programming-in-Java-6-2048.jpg)