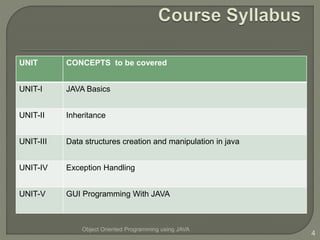
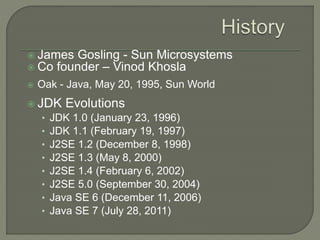
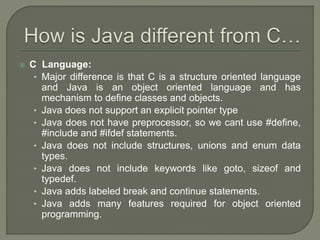
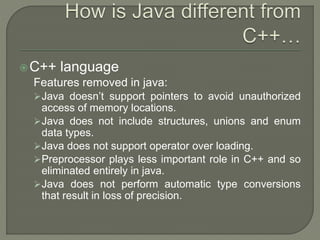
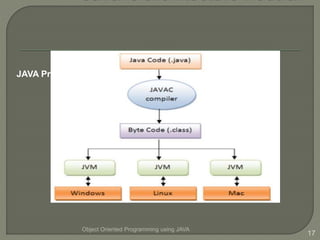
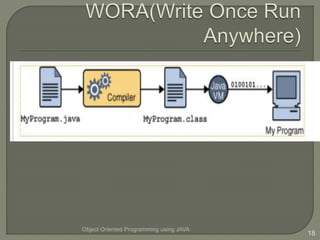
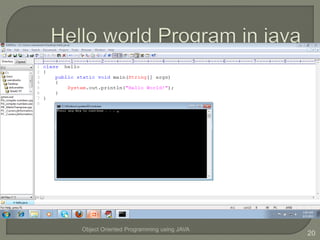
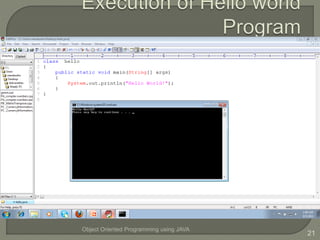
This document introduces an object oriented programming course in Java that will cover core computer science concepts needed to create software applications in Java. The course objectives are listed and include learning Java features and applying OOP principles like encapsulation, inheritance, polymorphism. The course will be divided into units covering Java basics, inheritance, data structures, exception handling, and GUI programming. An overview of Java is also provided, noting its portability, object oriented nature, and standard library of classes and methods.