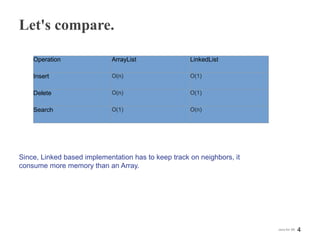
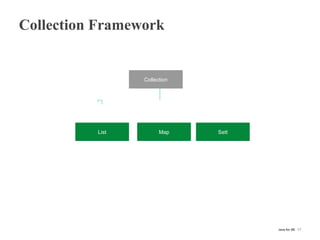
This document provides information on Java collection frameworks like List, Set, and Map. It discusses the common implementations of each and their performance characteristics for different operations. Key points covered include the differences between ArrayList and LinkedList, when to use HashSet vs LinkedHashSet, and how HashMap performance is related to load factor. The document also mentions utility methods in Collections class and best practices like avoiding null returns.