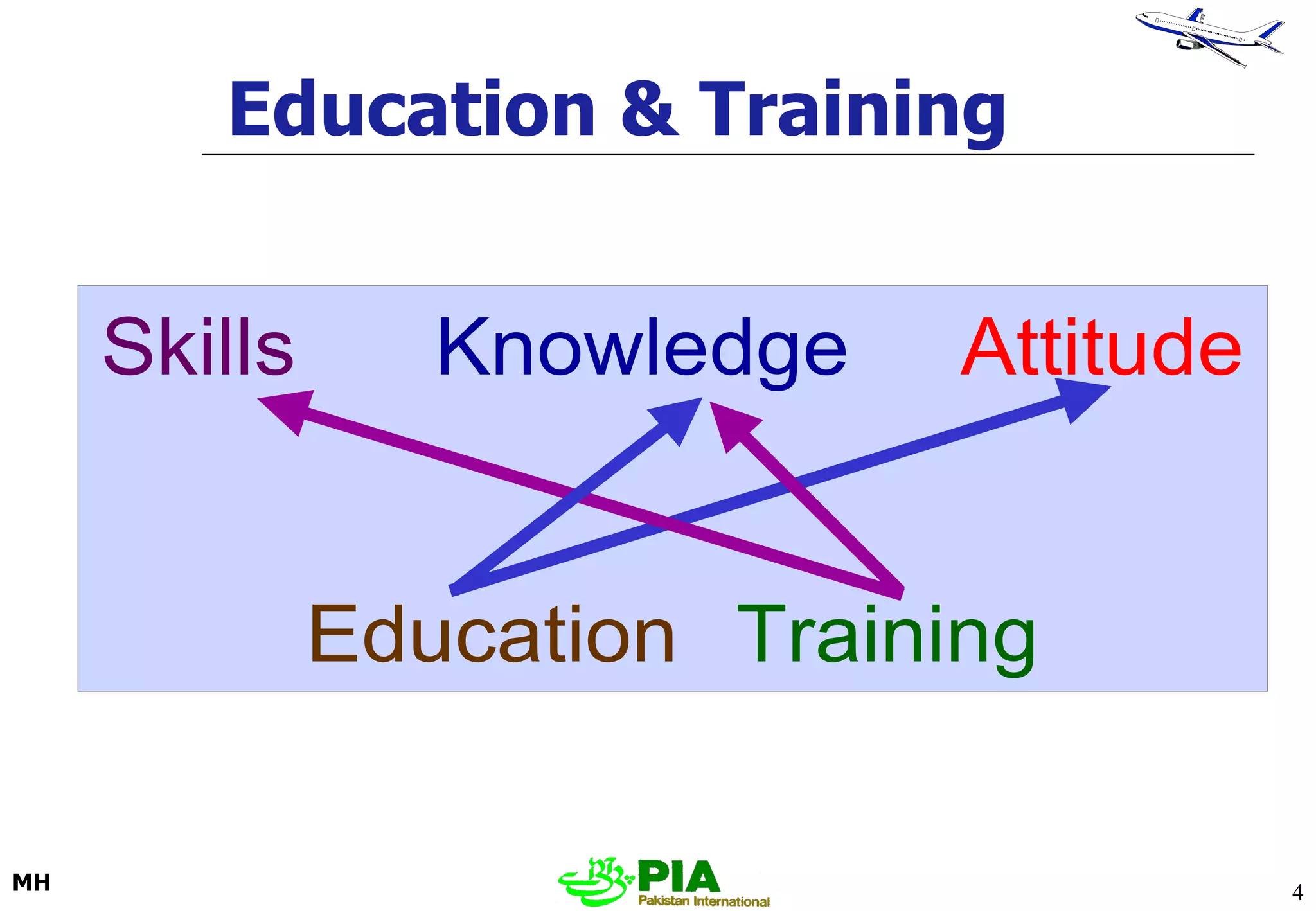
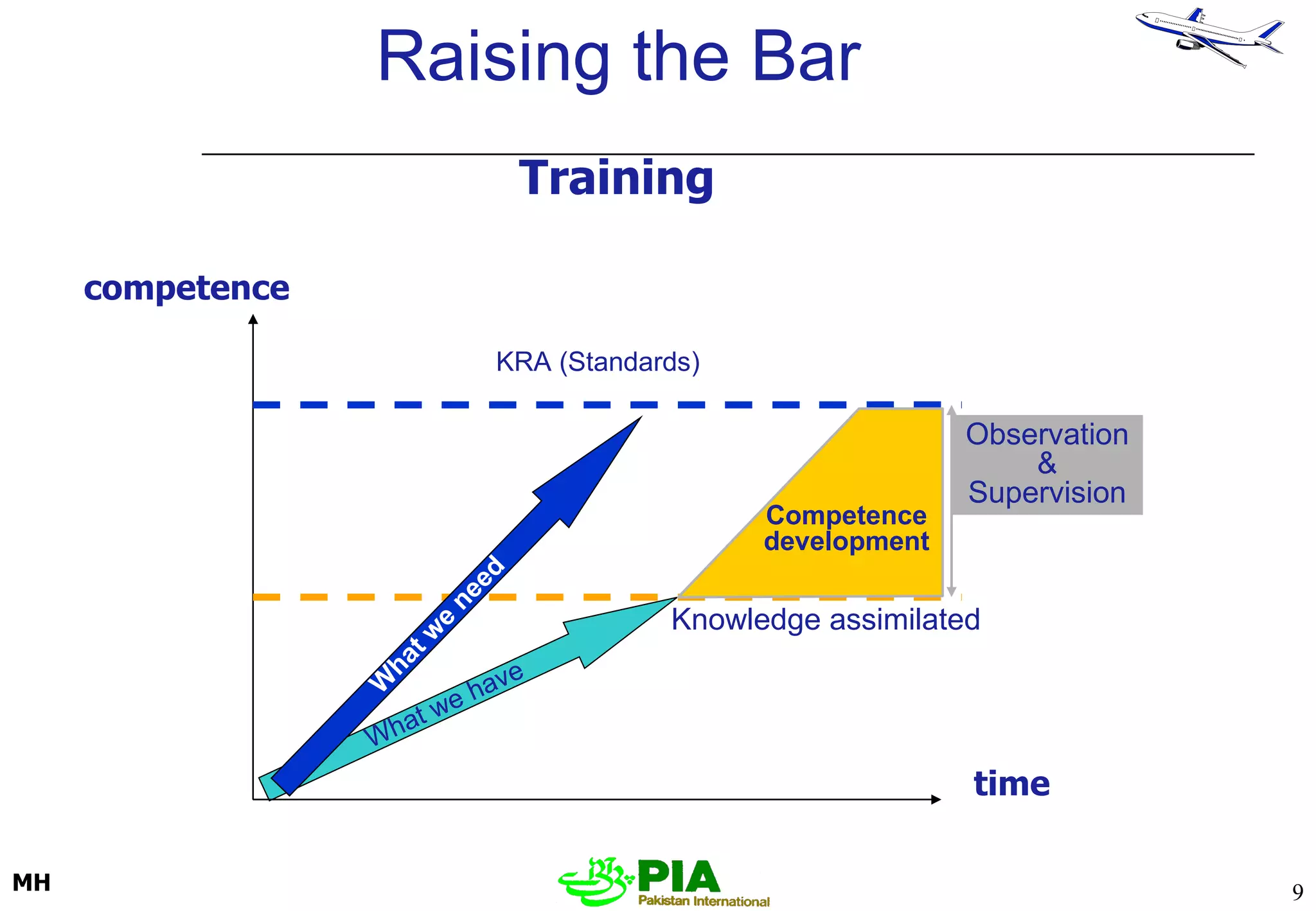
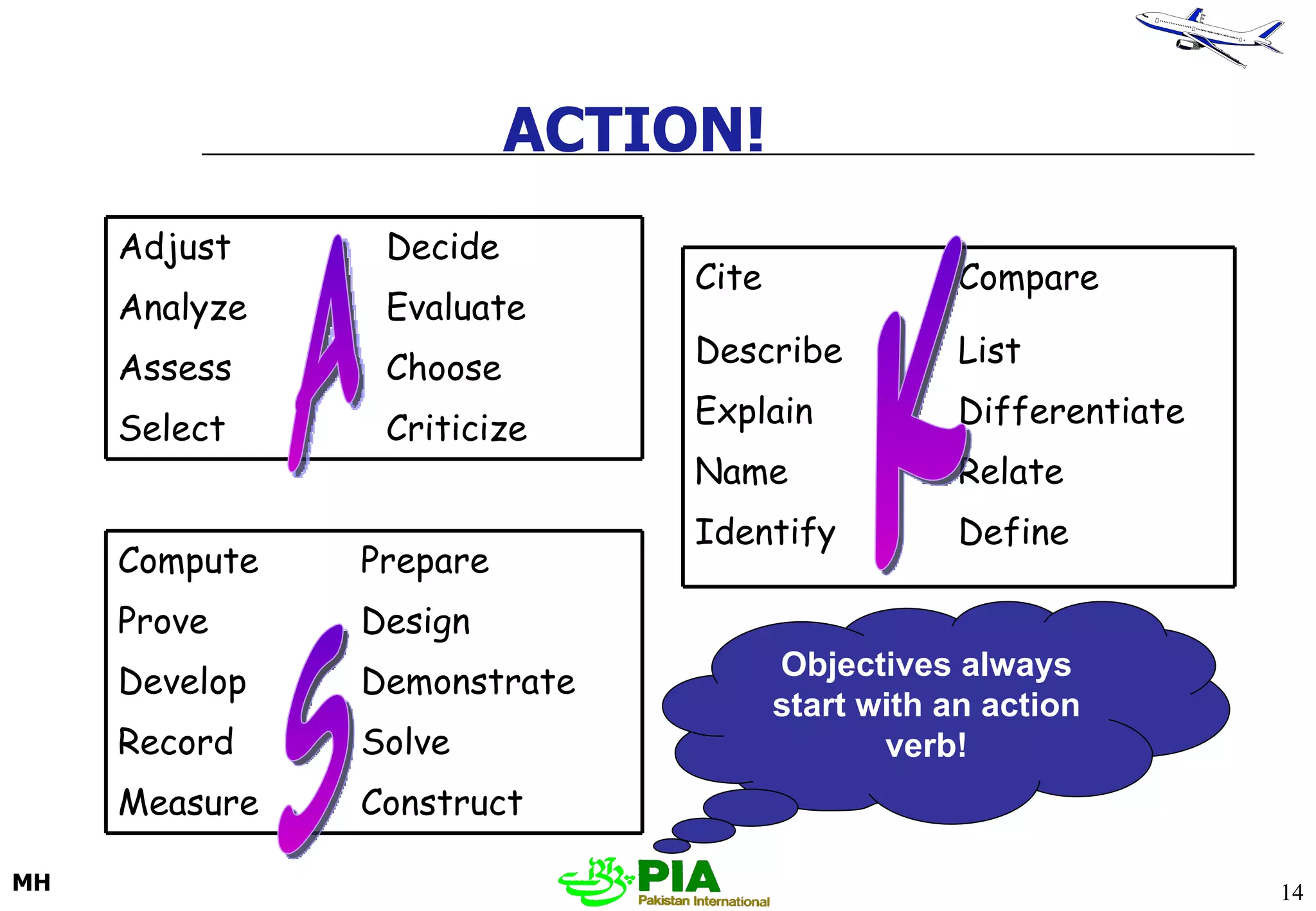
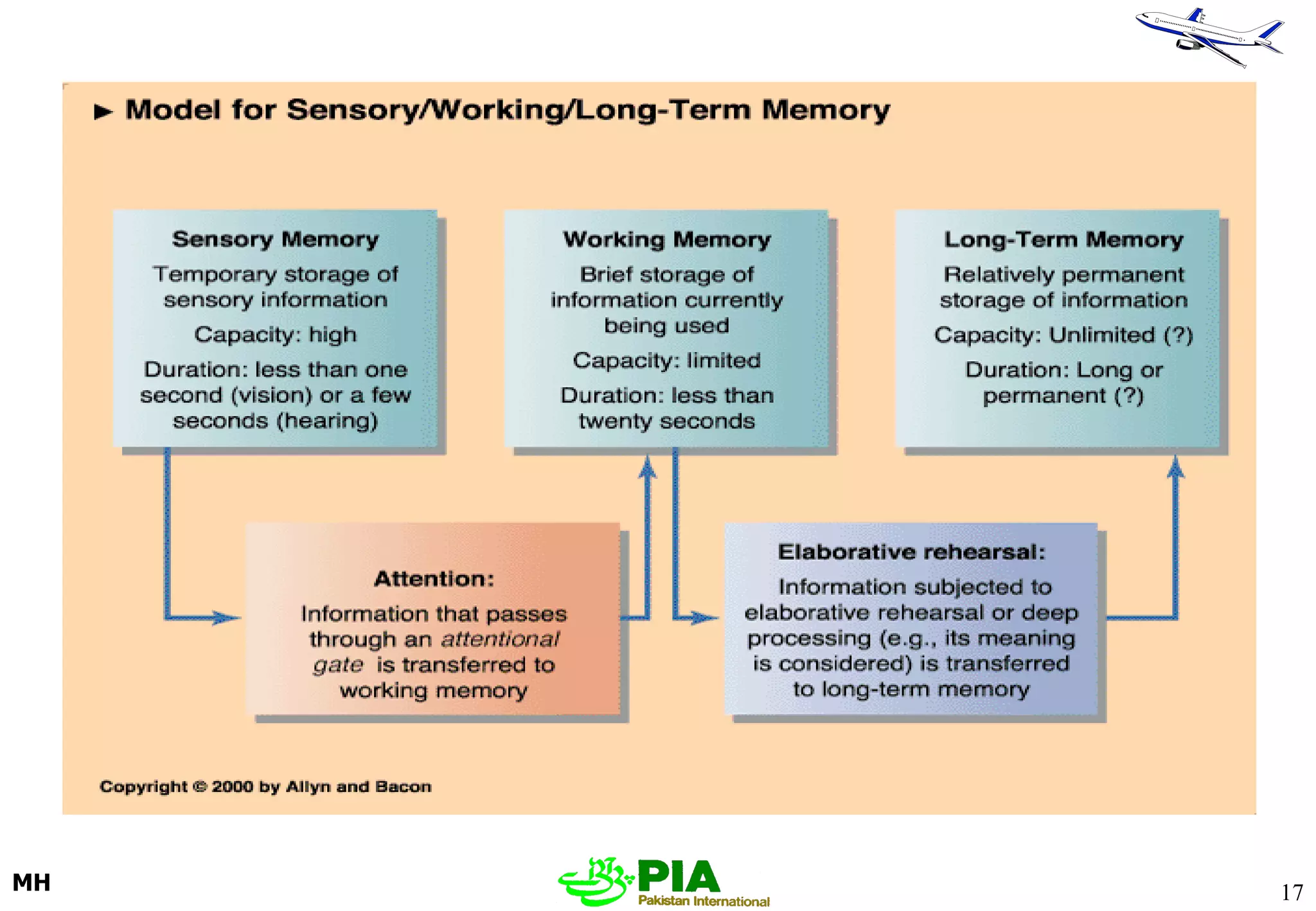
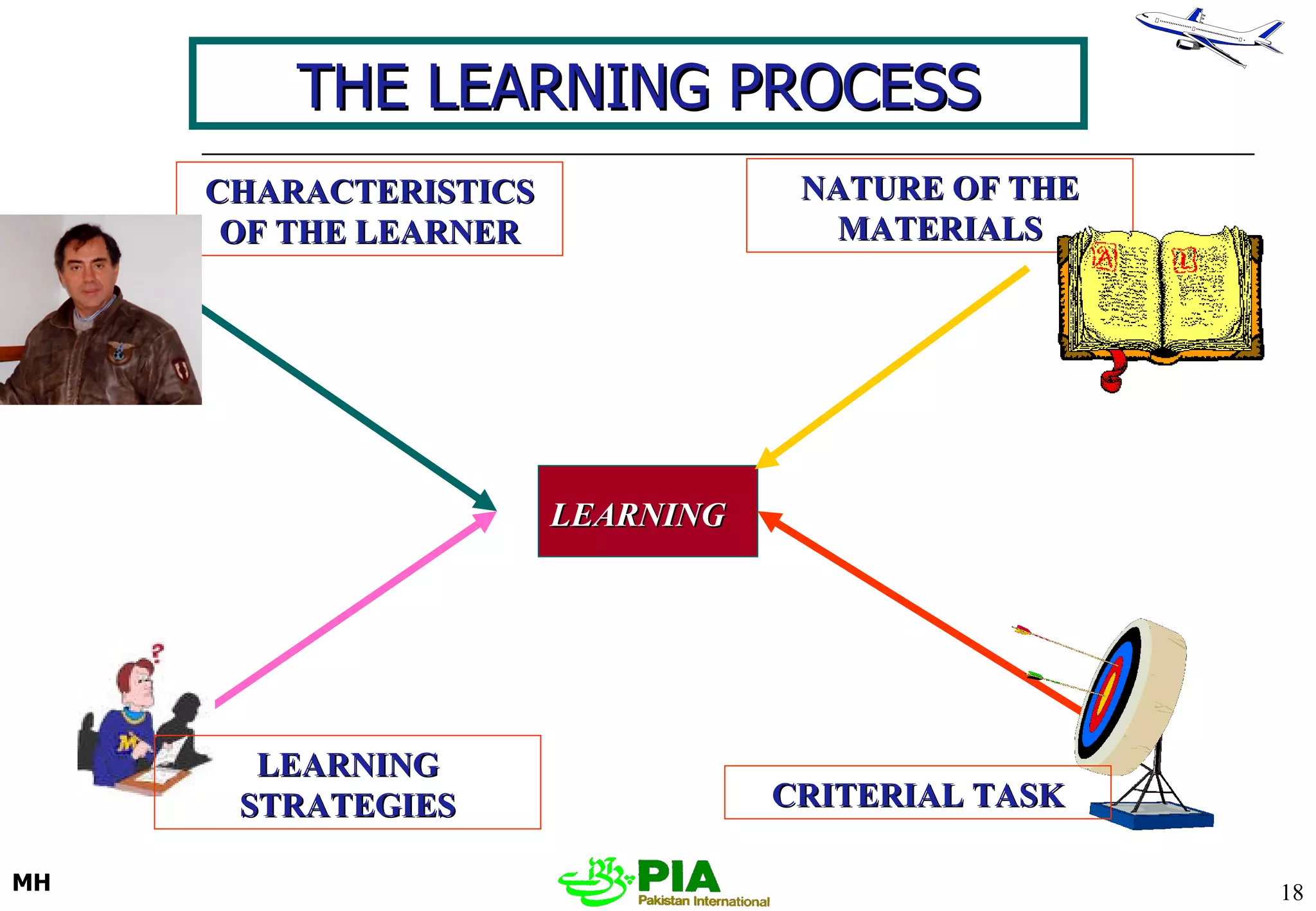
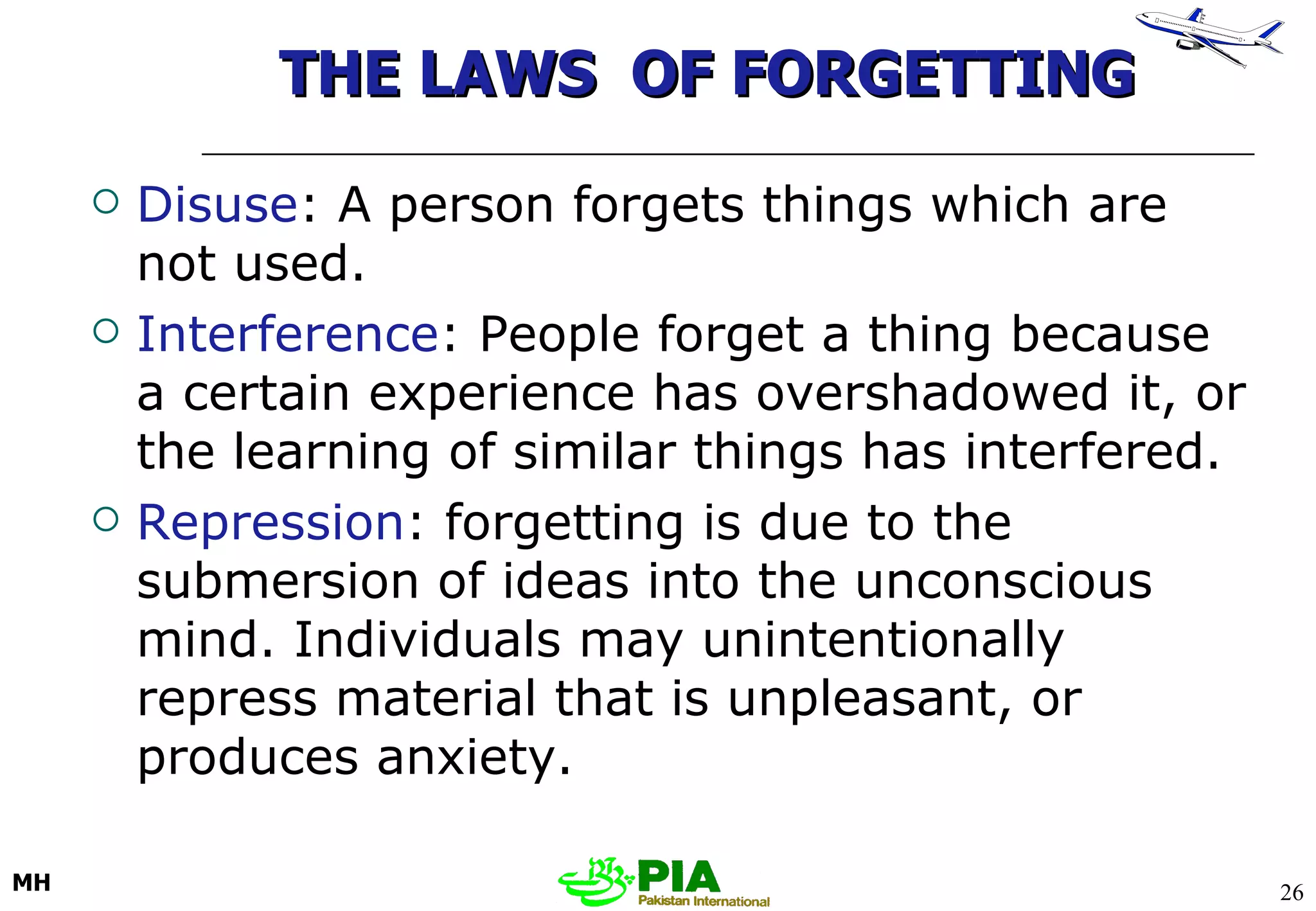
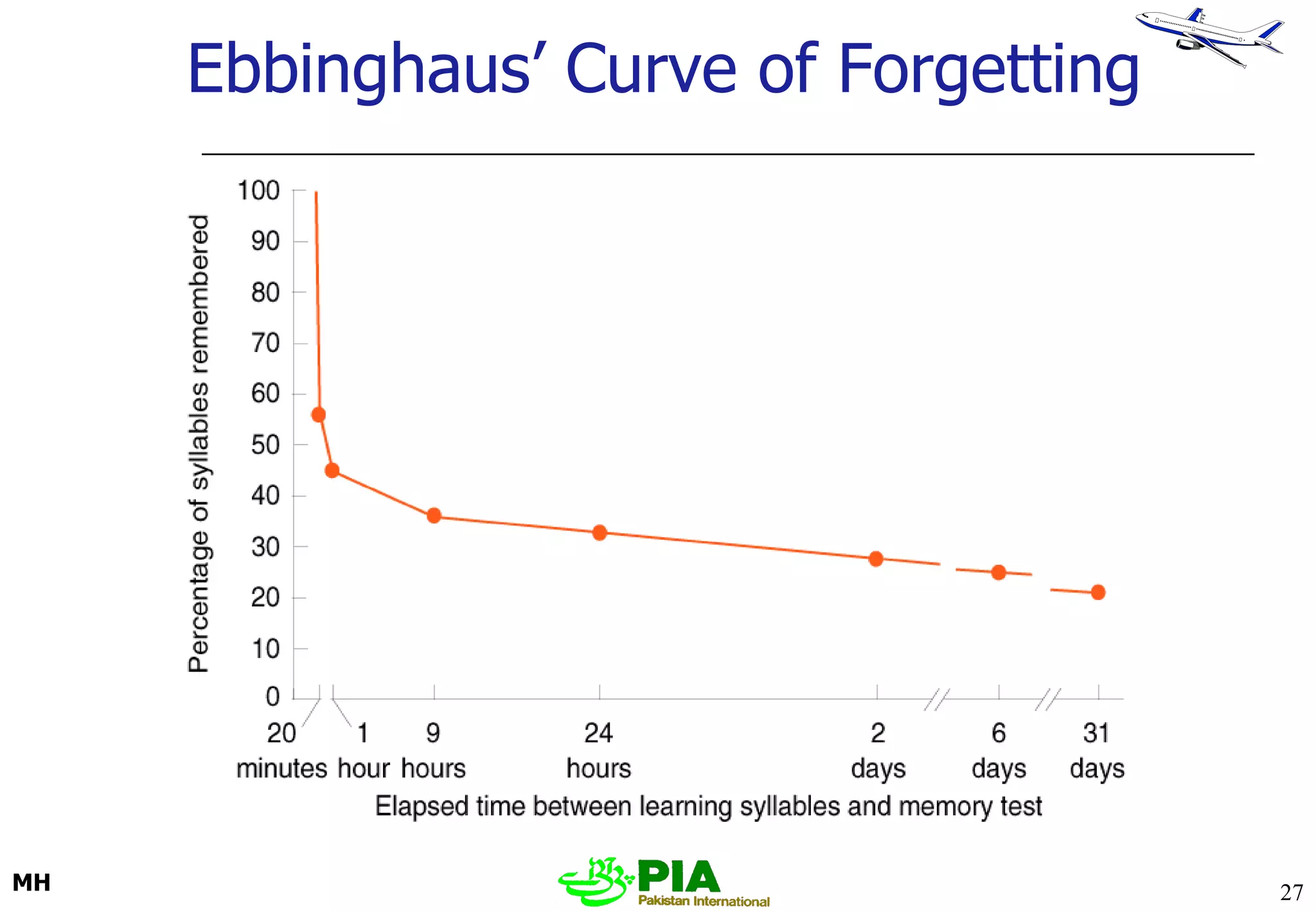
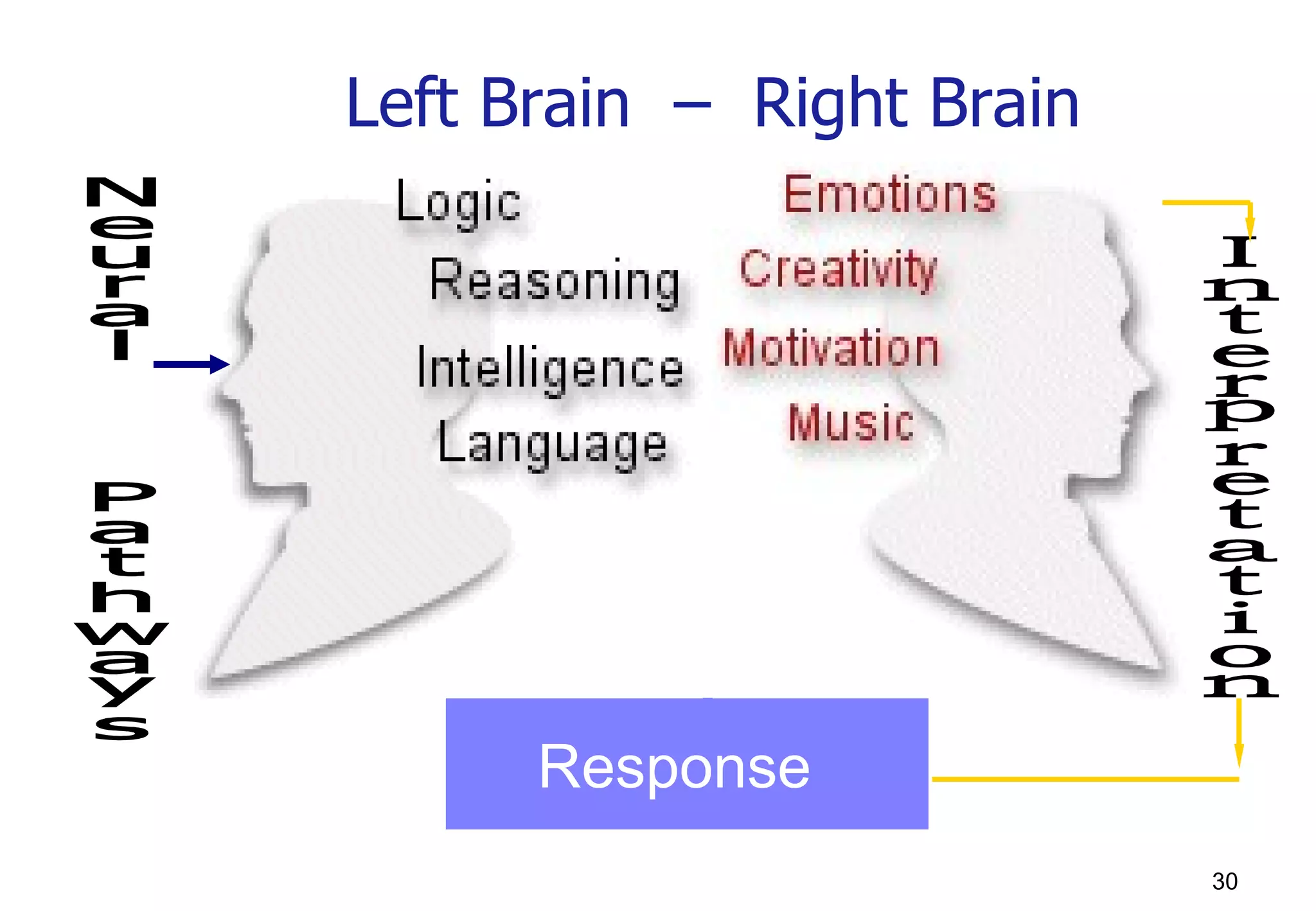
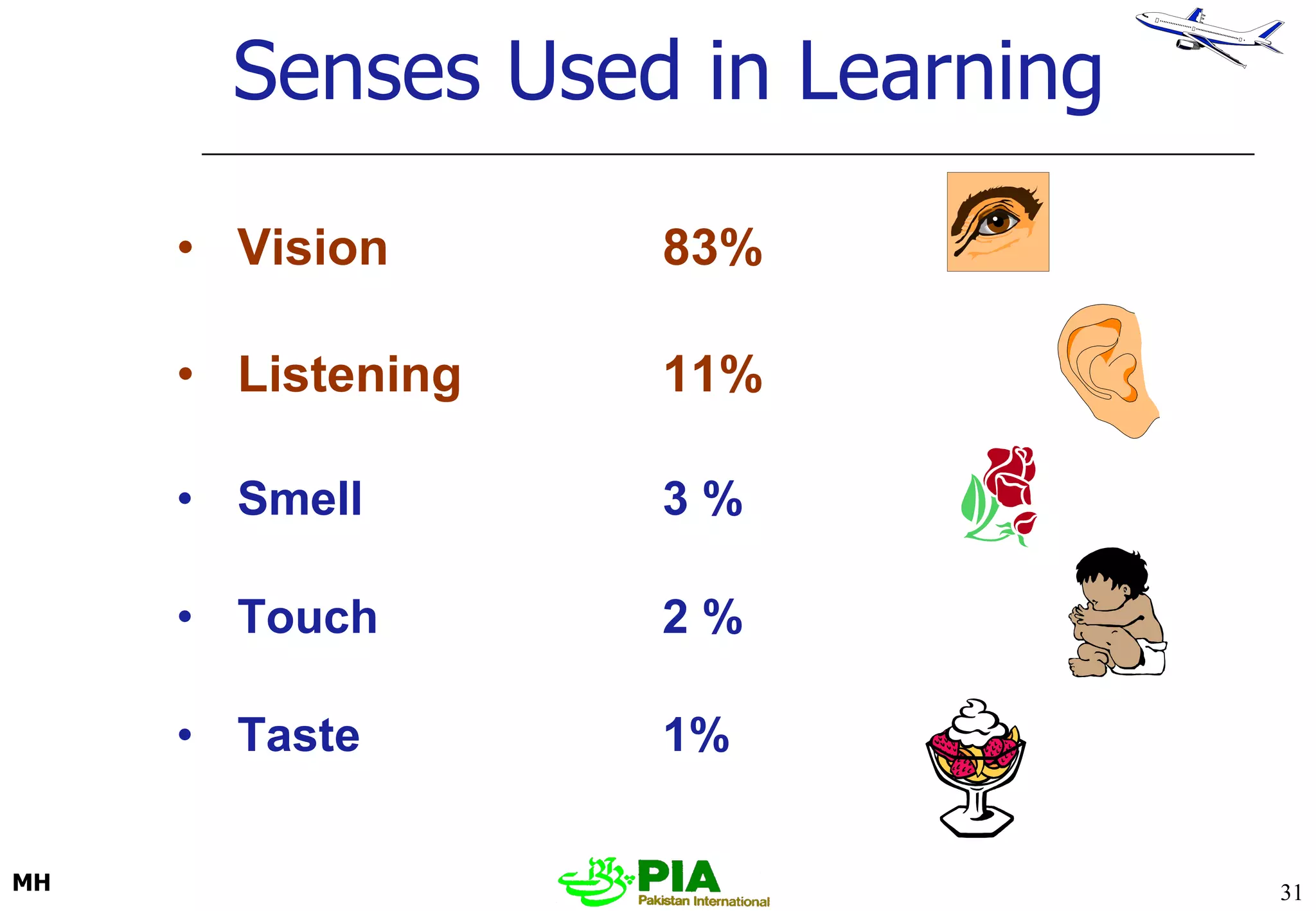
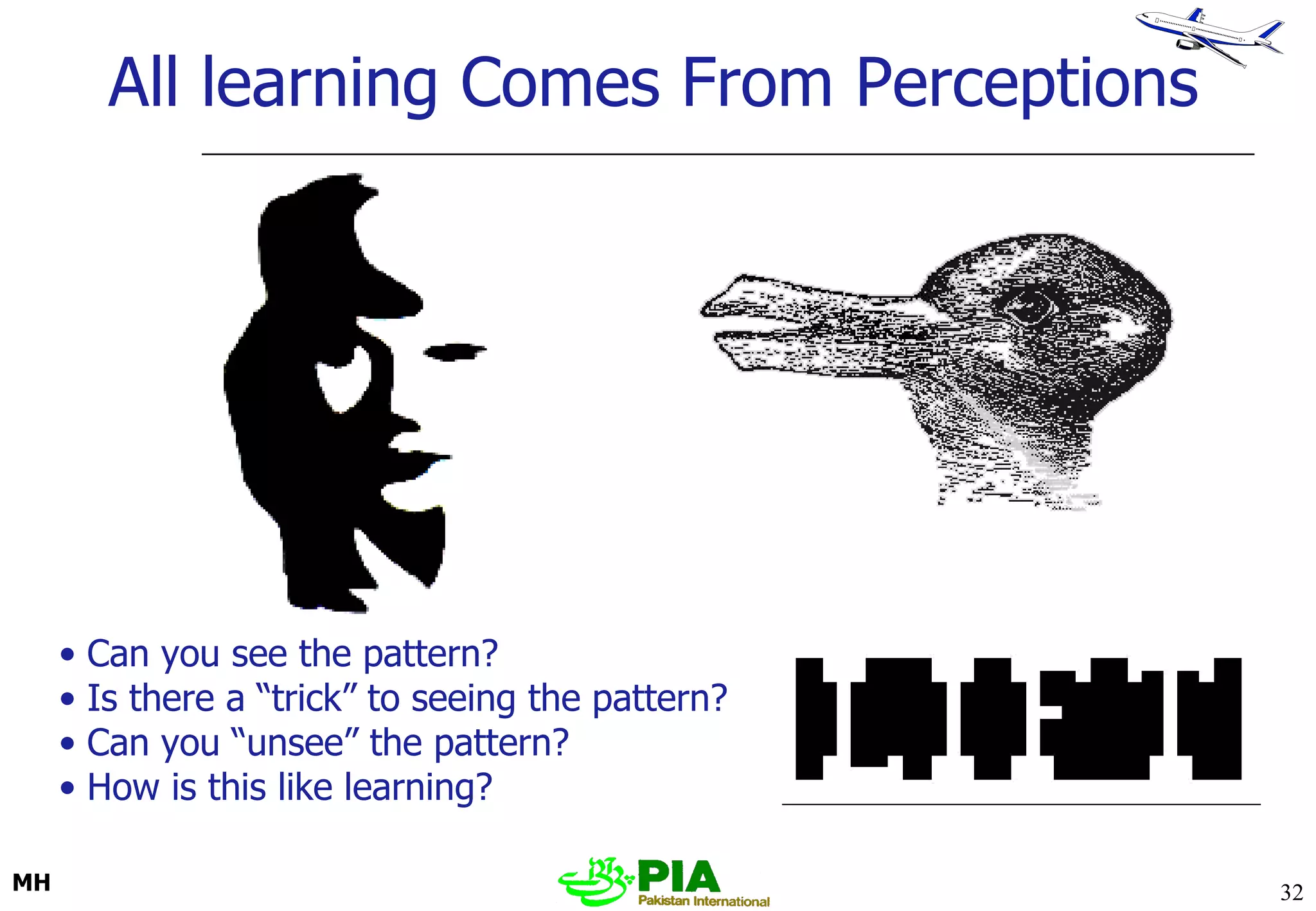
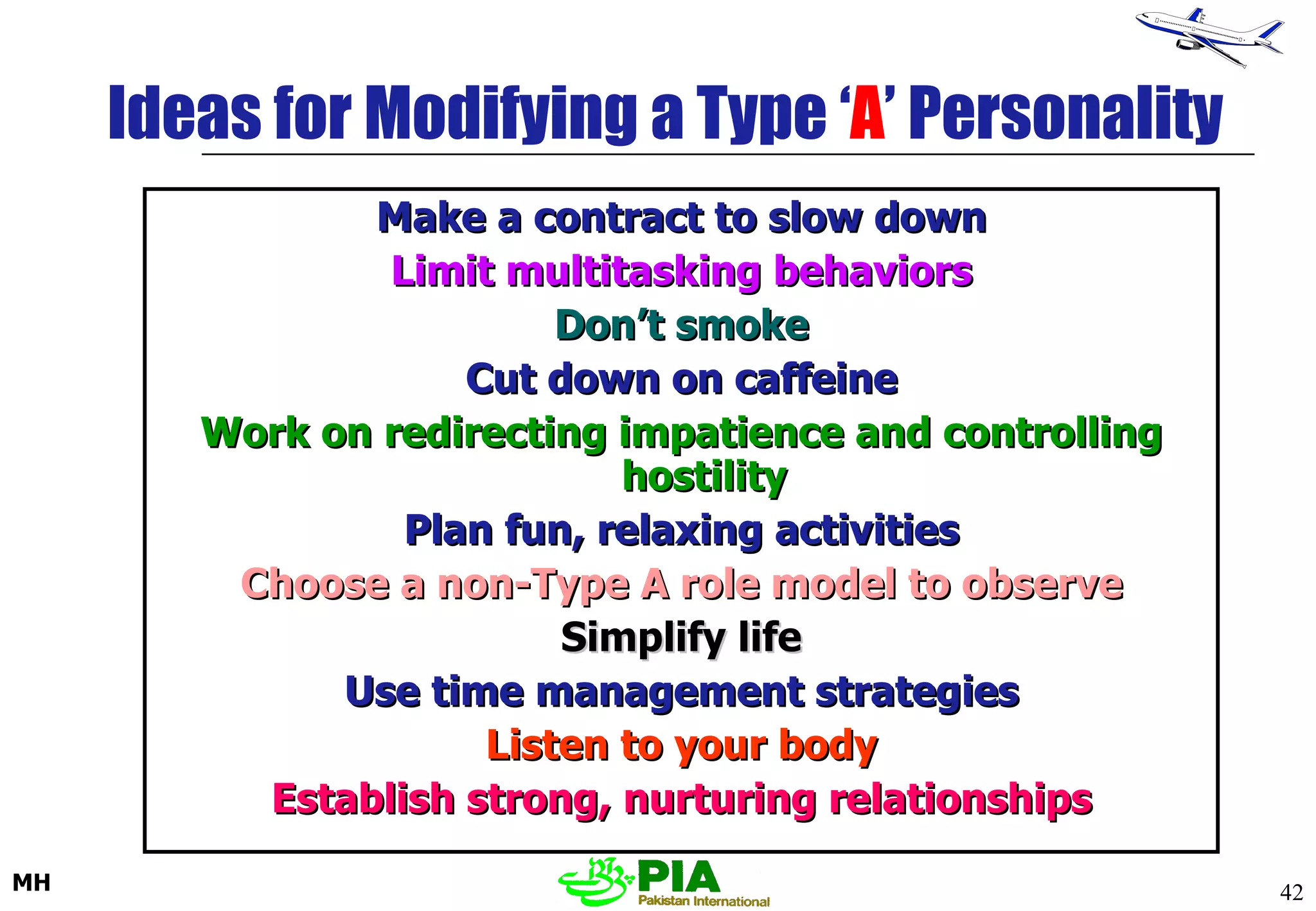
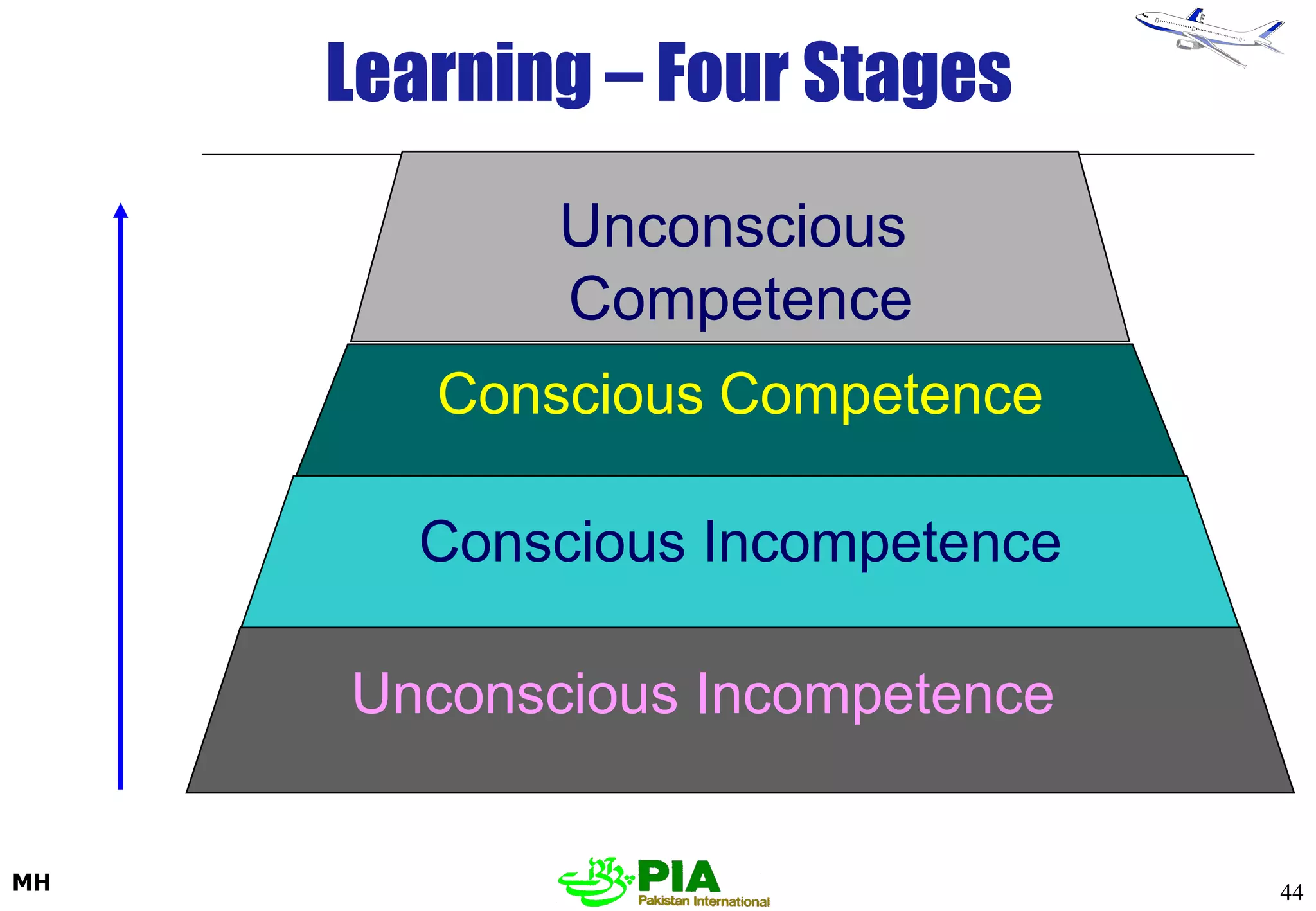
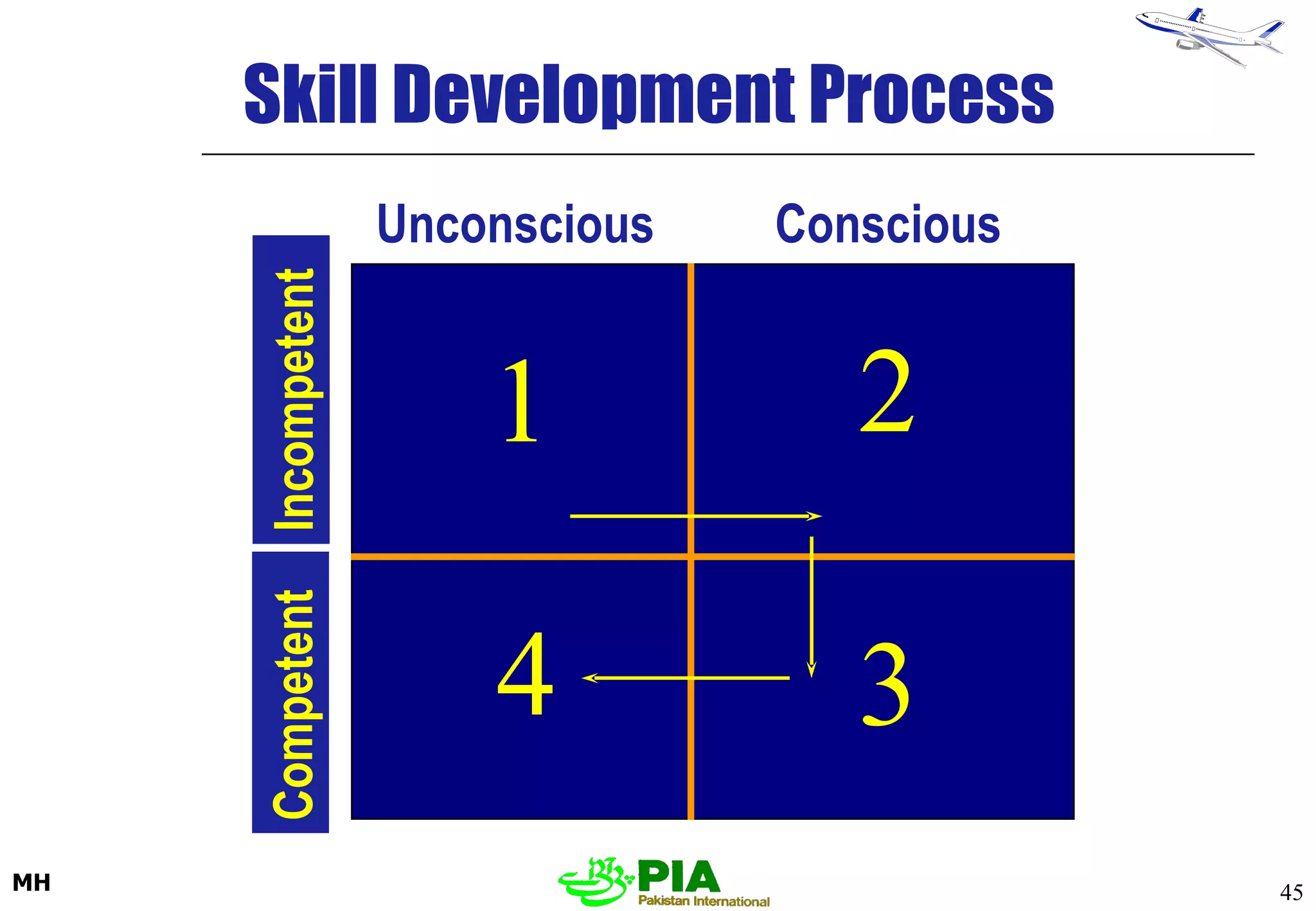
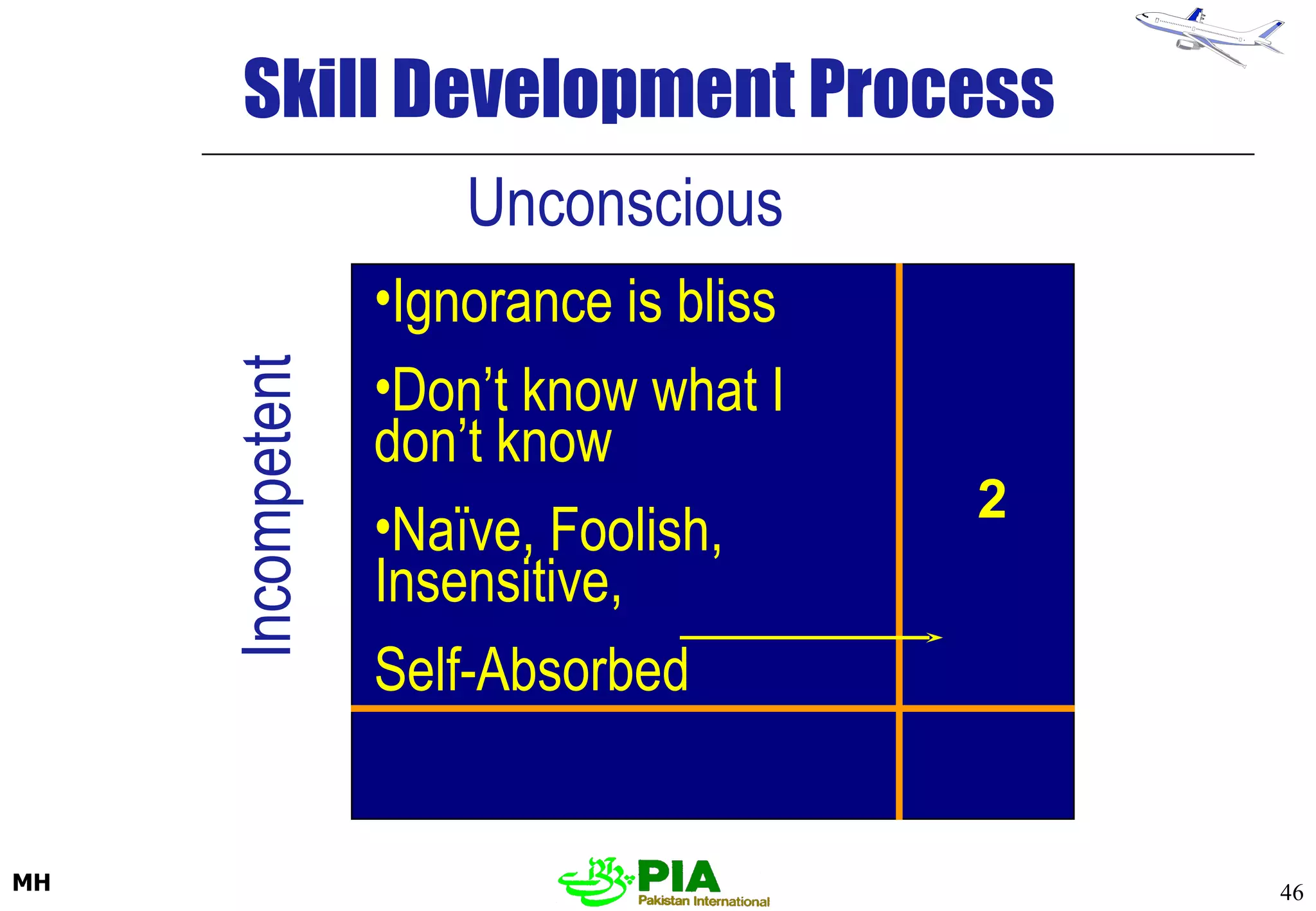
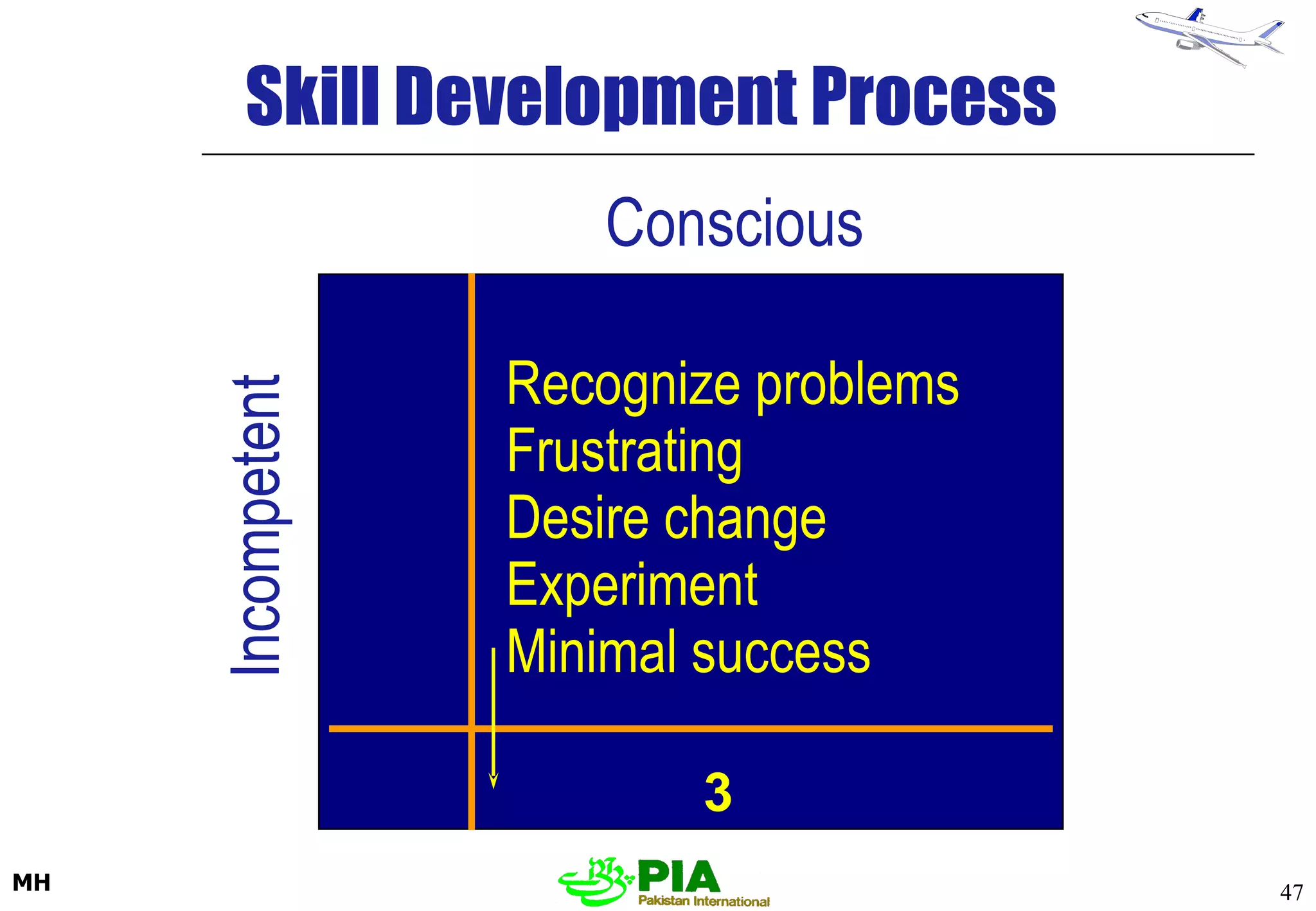
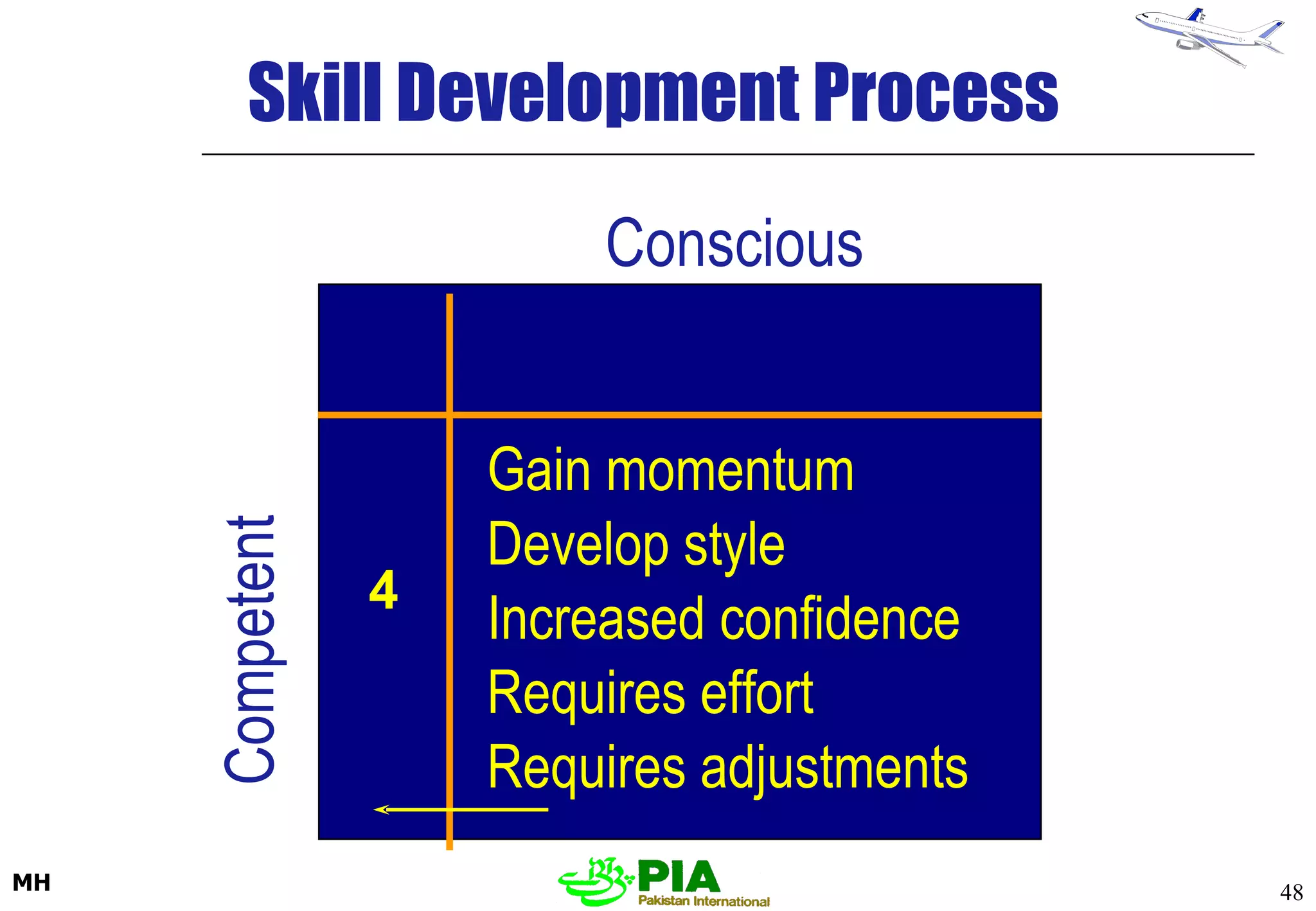
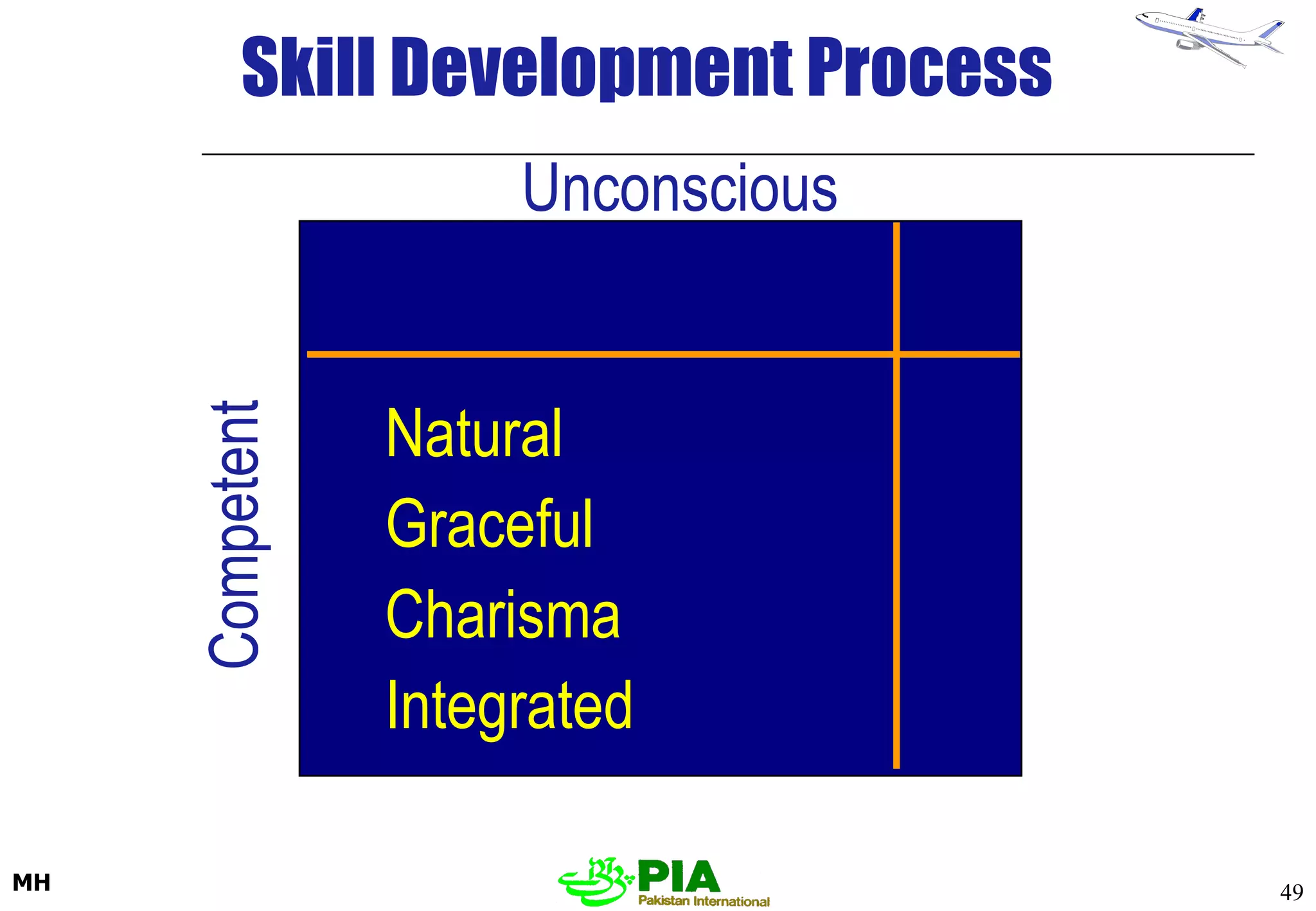
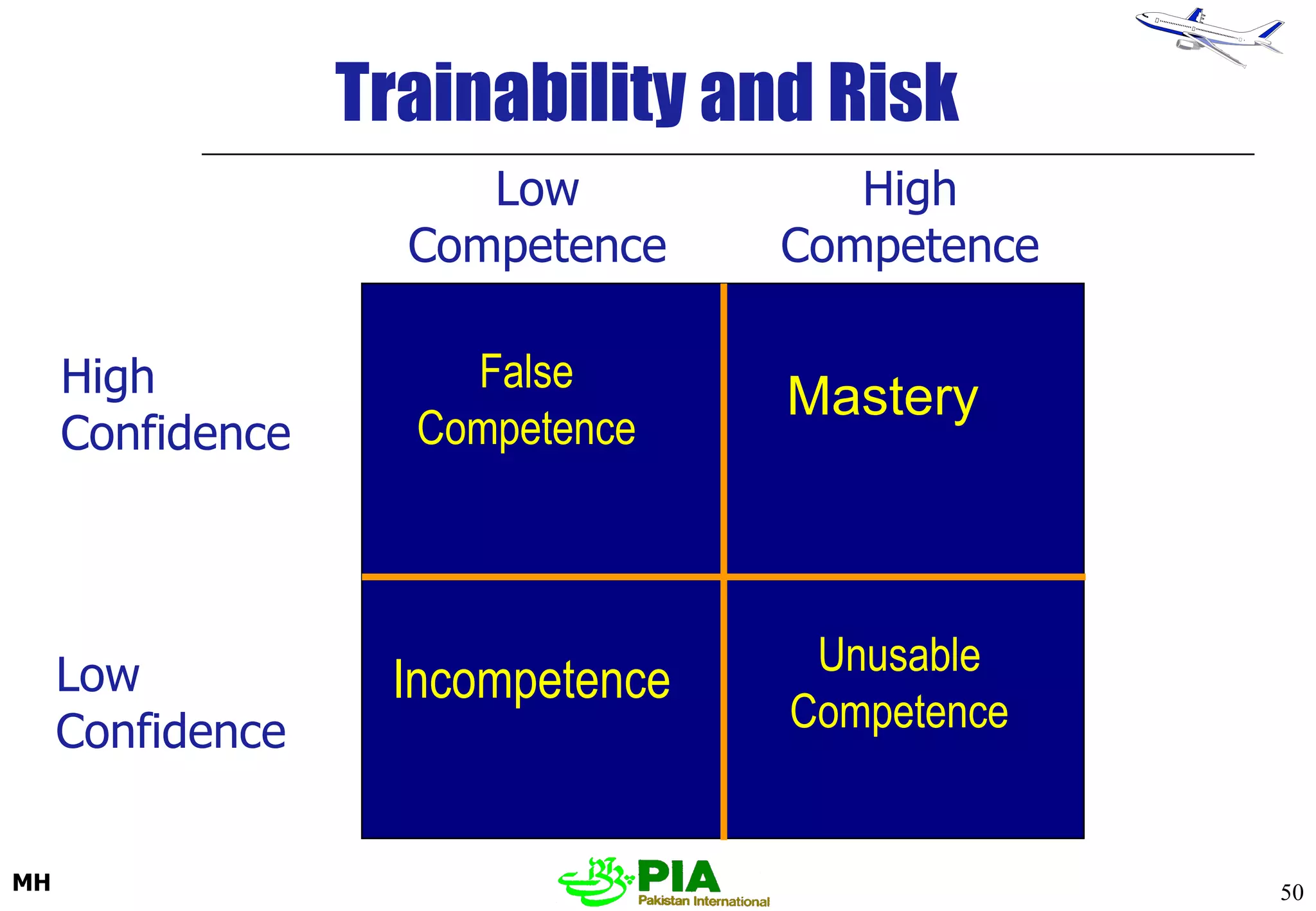
The document discusses various techniques and principles for effective instruction and learning. It covers ideas from Confucius and Lao-Tzu on learning through experience versus being told. It then defines concepts like education, training, learning and teaching. It outlines rules of learning and forgetting as well as principles like readiness, exercise, effect, primacy, intensity and recency. It discusses different learning styles, types of knowledge, skills and attitudes. It also covers the learning process, training methods, communication skills, instructional aids and evaluating learning.