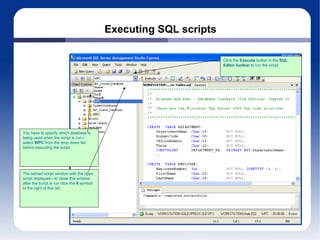
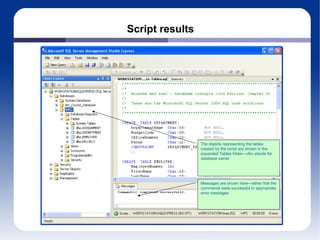
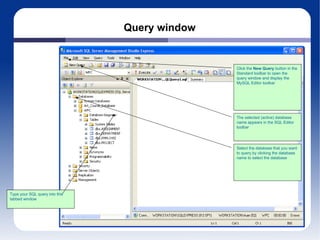
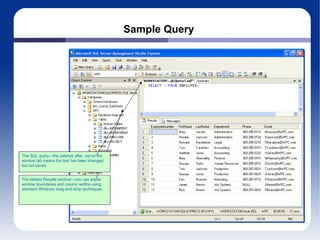
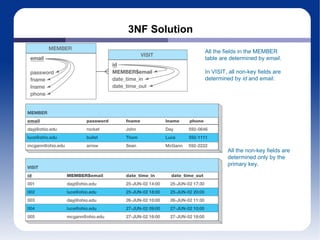
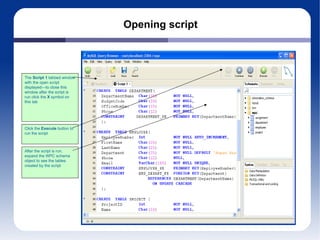
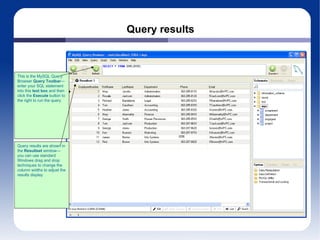
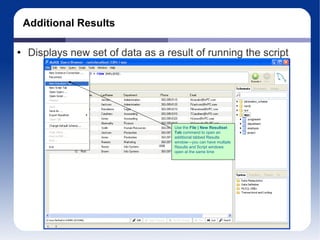
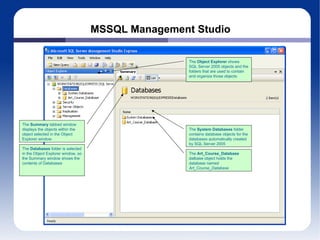
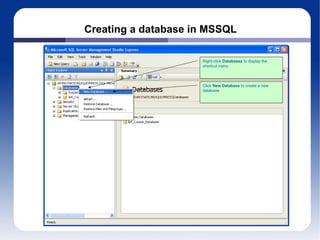
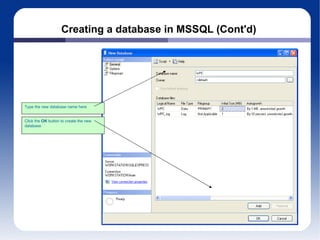
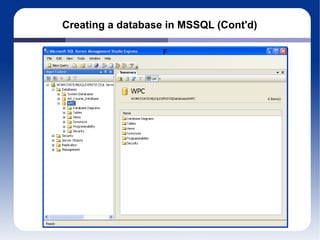
The document discusses different database management systems like Microsoft SQL Server and MySQL. It covers how to create databases, tables, and queries in both SQL Server Management Studio and MySQL Query Browser. Examples are provided of creating databases and tables using SQL scripts as well as executing queries and viewing the results in the respective management tools.


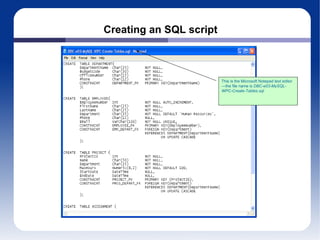
![Creating SQL Scripts This is the Microsoft Notepad text editor—the file name is DBC-e03-MSSQL-WPC-Create-Tables.sql The SQL keyword Name is enclosed in brackets as [Name] The lines that start with /* are comments—any text between the /* and the */ characters on a line is a comment and ignored by the DBMS when it runs the SQL](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/it203-classslides-unit5-110425162356-phpapp02/85/It203-class-slides-unit5-7-320.jpg)