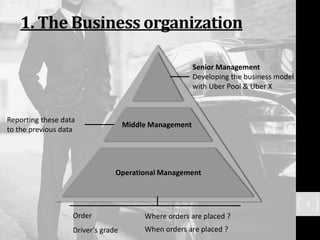
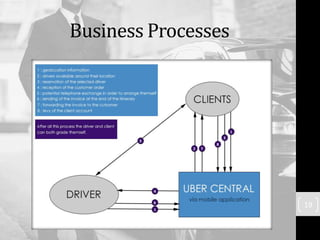
Uber has transformed the taxi industry through its use of information technology. It launched in 2009 as a mobile app that allows users to request rides from nearby drivers. Uber collects large amounts of user data through its app and has faced criticism over privacy and data security issues. While Uber has disrupted legacy taxi companies, new players may emerge using technologies like self-driving cars. Recommendations include improving customer loyalty, securing customer data, developing application controls, and informing customers clearly on data use.