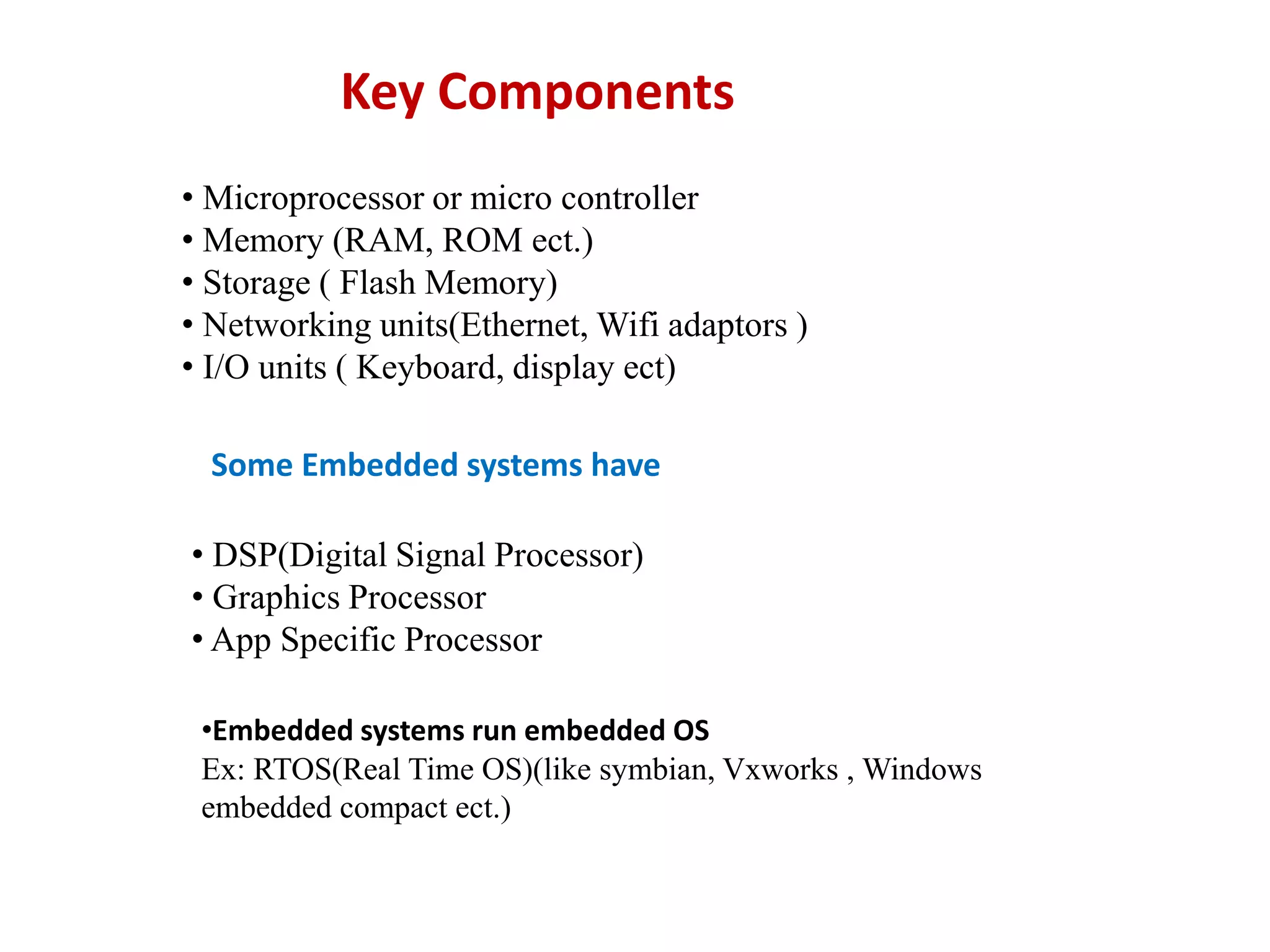
This document discusses key enabling technologies for the Internet of Things (IoT). It describes wireless sensor networks that use distributed sensor nodes to monitor environmental conditions. It also discusses cloud computing which provides on-demand computing resources and services over the Internet. Additionally, it covers big data analytics which involves collecting, processing, and analyzing large, diverse datasets. Finally, it mentions communication protocols that allow devices to exchange data over networks and embedded systems which are specialized computer systems designed to perform specific tasks.