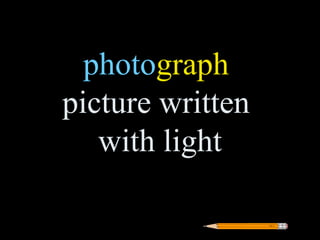
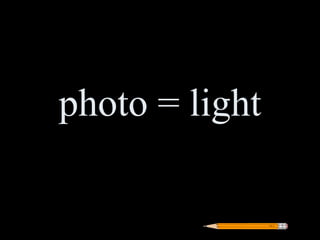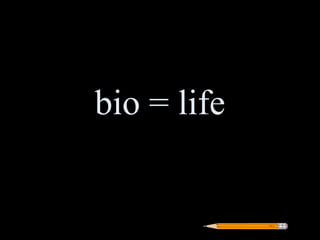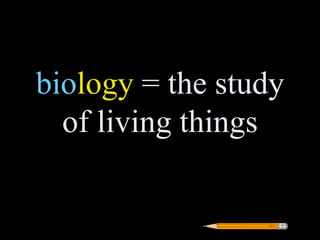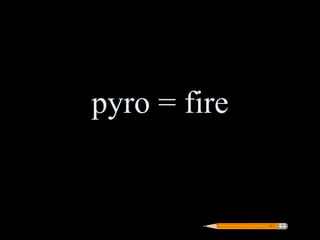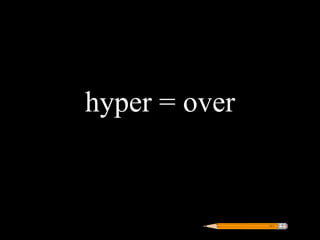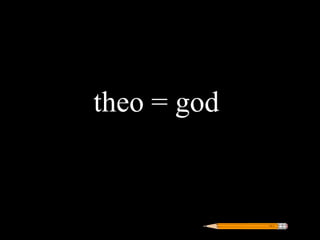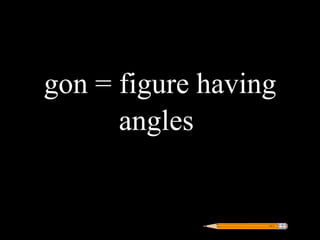Greek roots provide the meaning for thousands of English words. Many common Greek roots are used in words related to science, government, emotions, and other domains. Students are assigned an art project to illustrate the meaning of 42 common Greek roots and examples of words that contain each root.