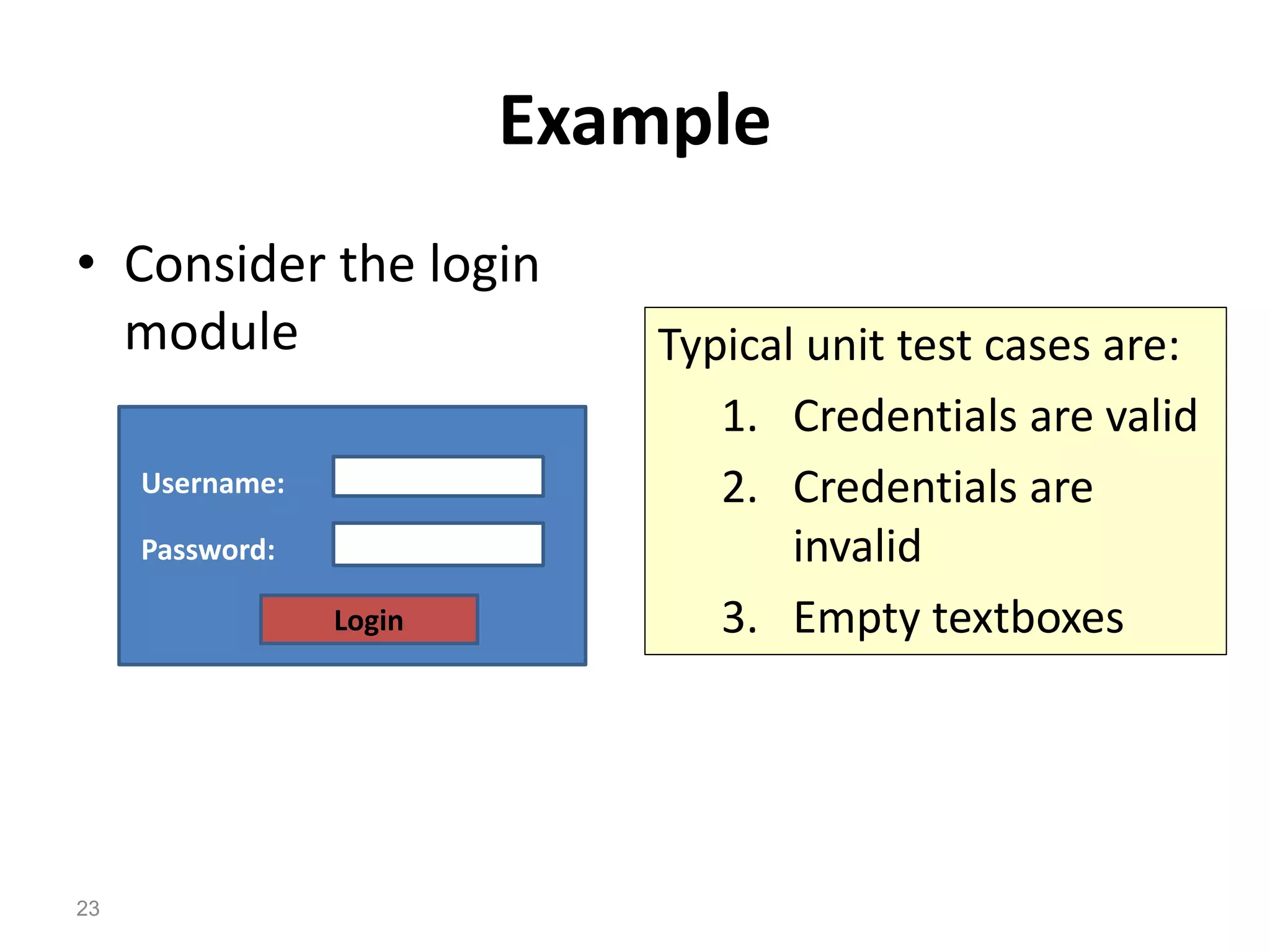
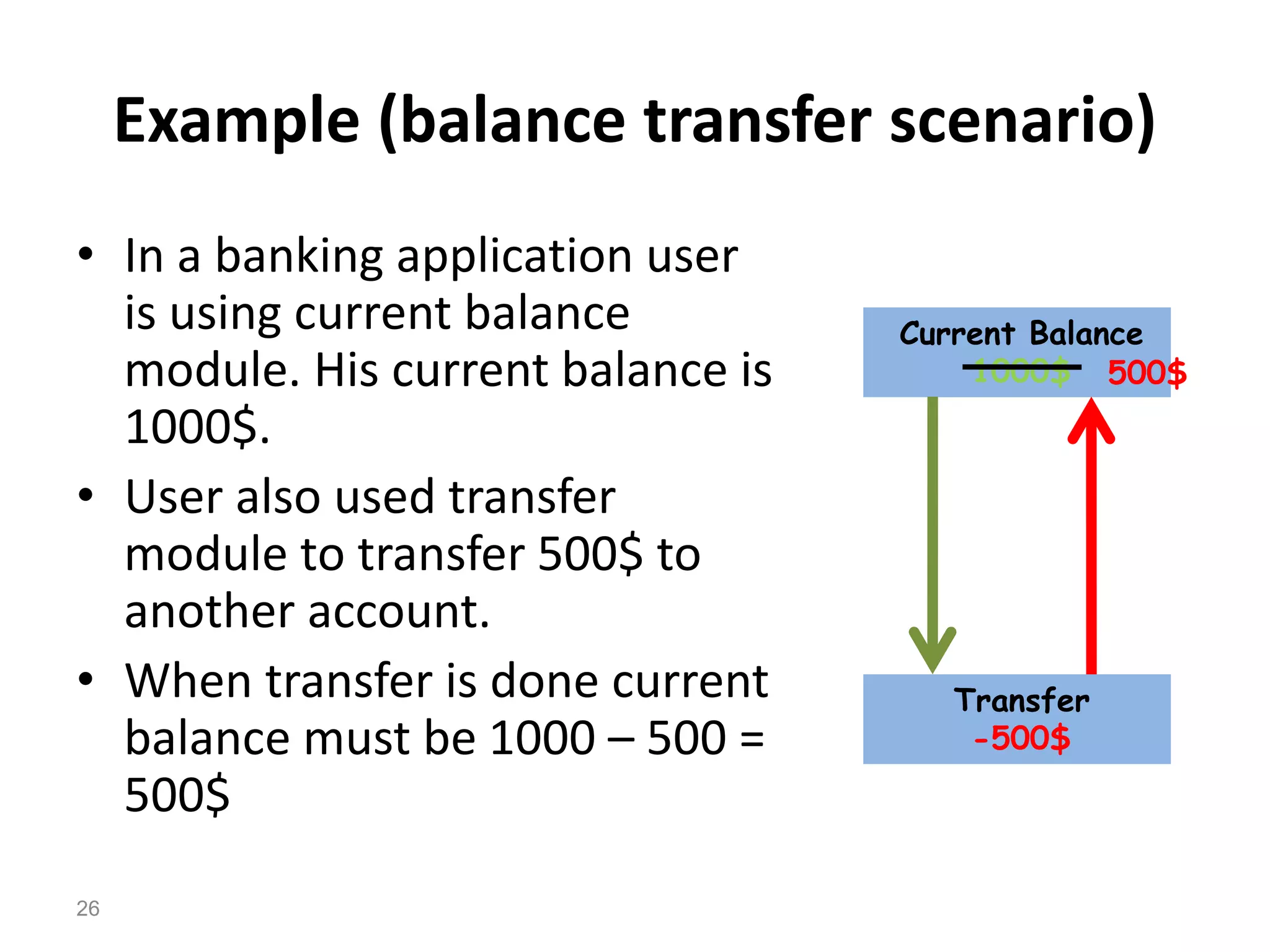
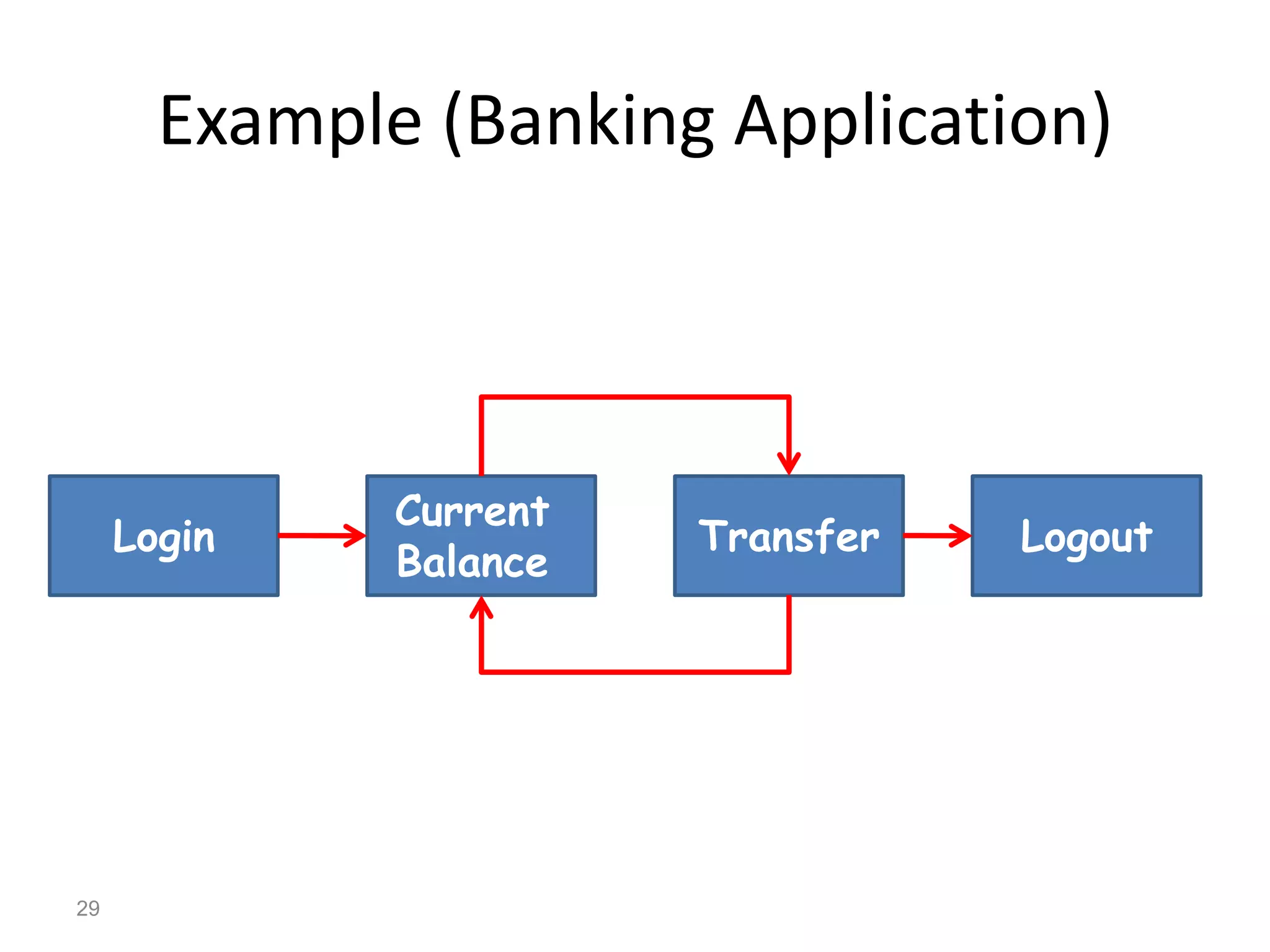
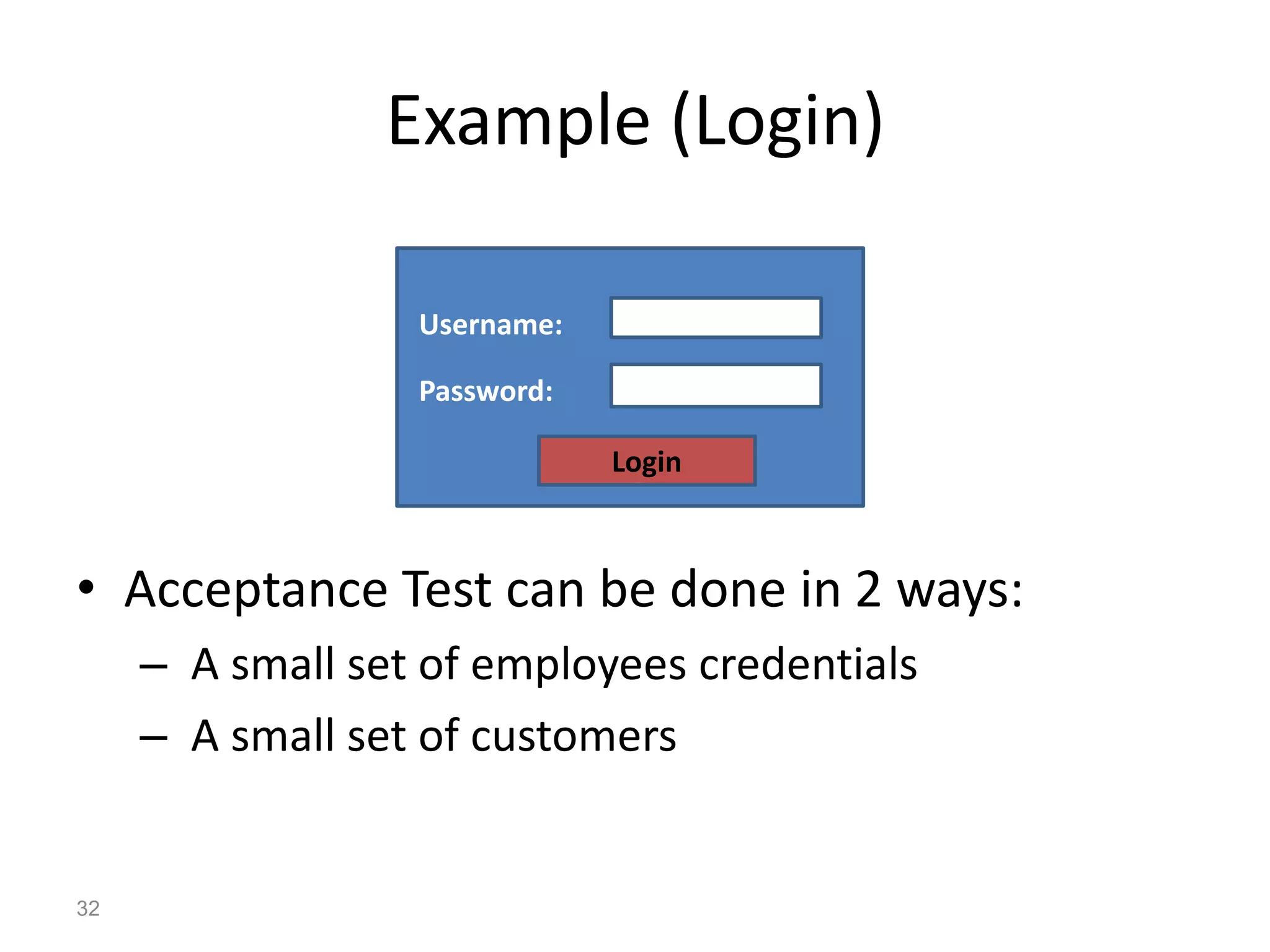
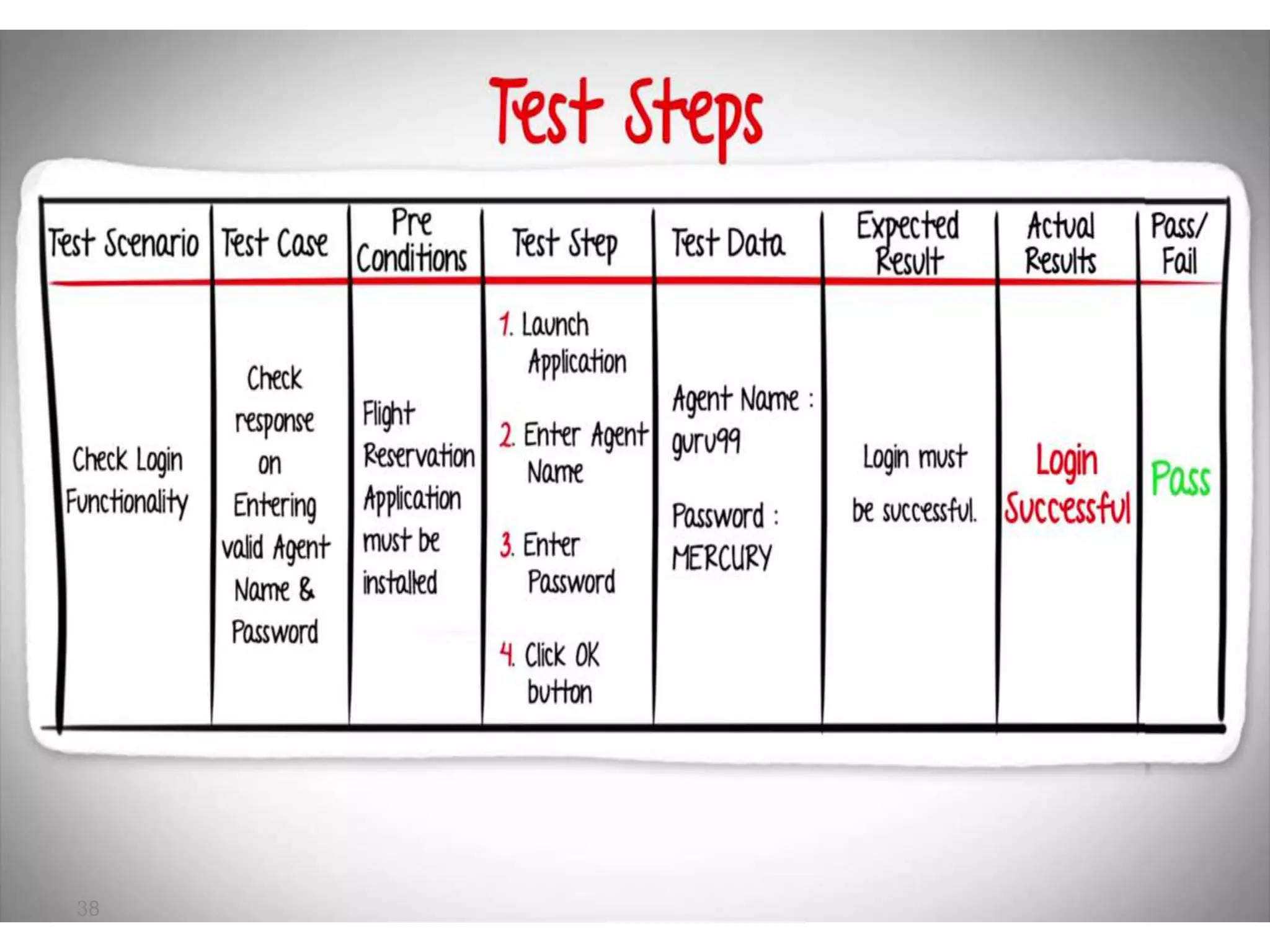
The document provides an introduction to software testing, defining it as a process to ensure software quality and identify errors before release. It covers different types of testing (white box, black box, gray box), levels of testing (unit testing, integration testing, system testing, acceptance testing), and provides guidelines on writing test cases with examples. The importance of software testing and how it contributes to the development process is emphasized throughout the document.