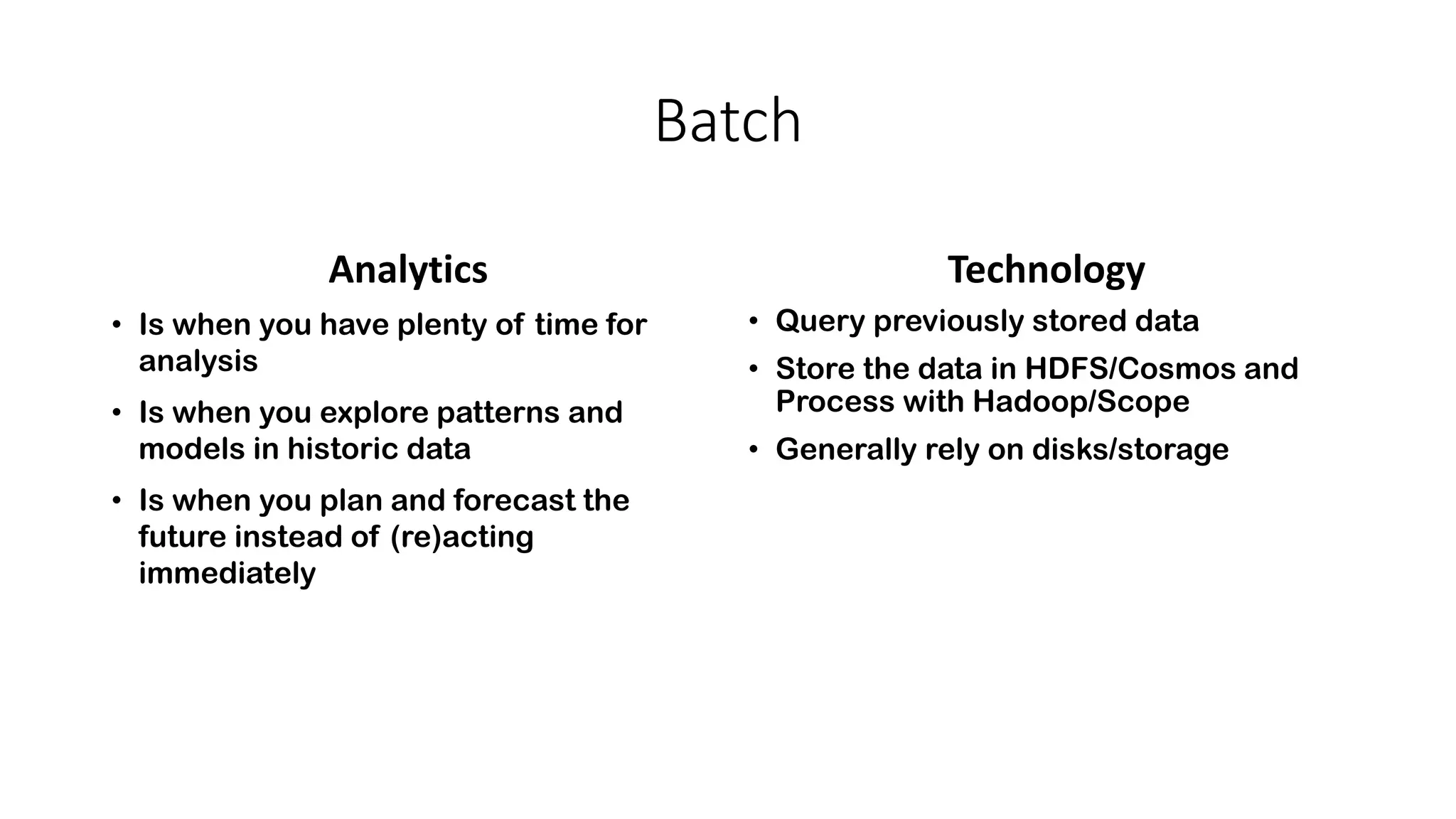
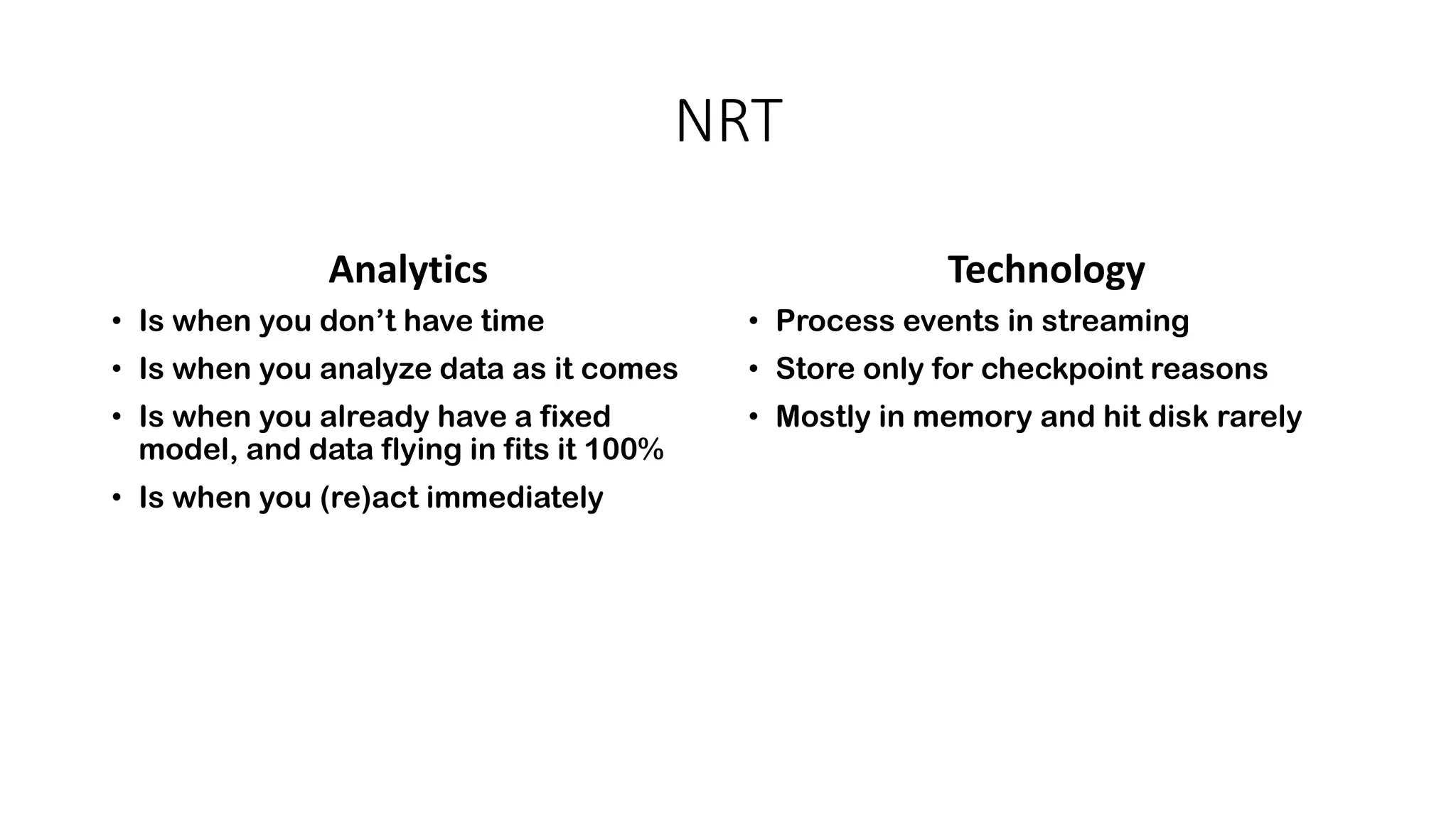
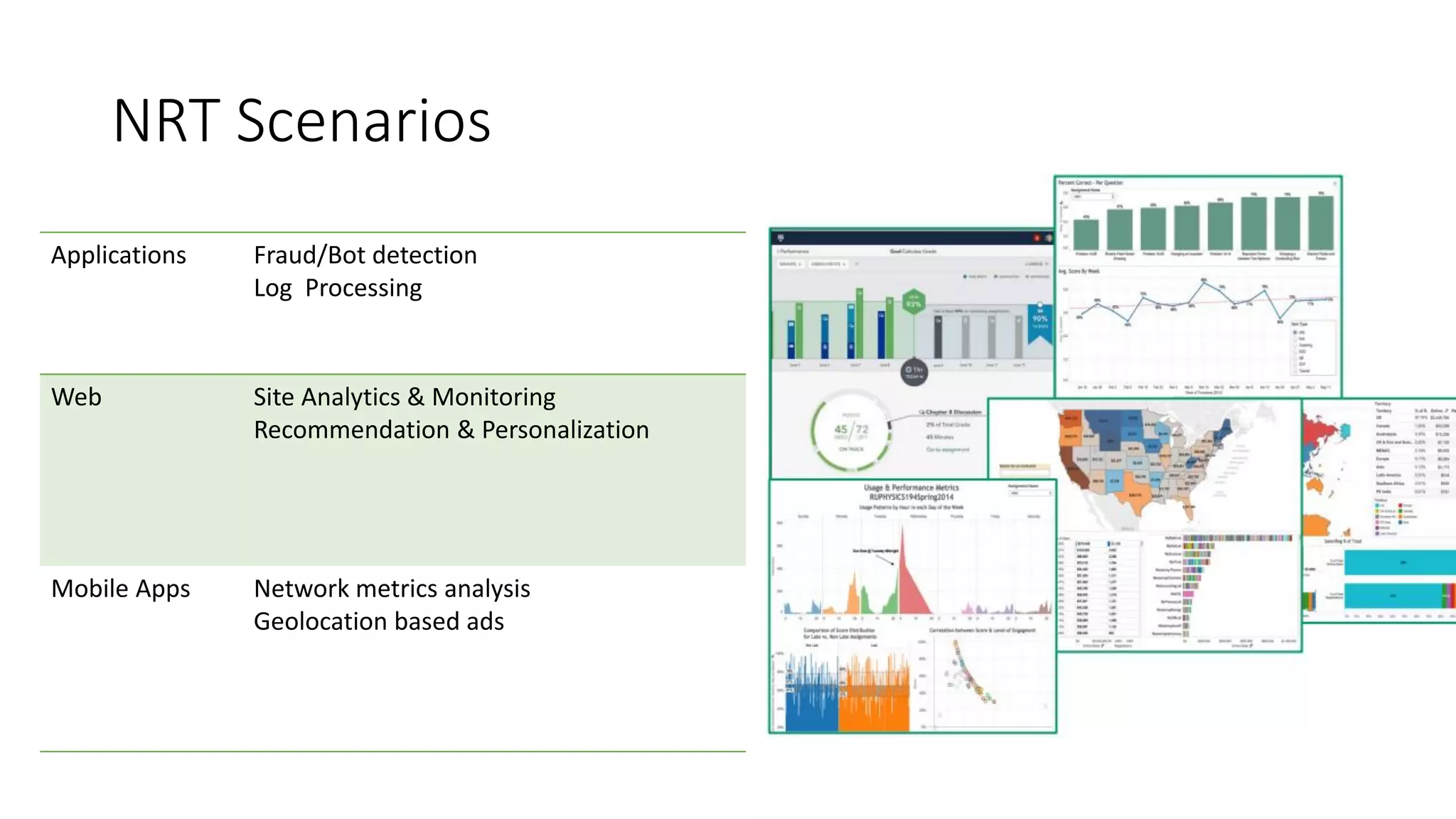
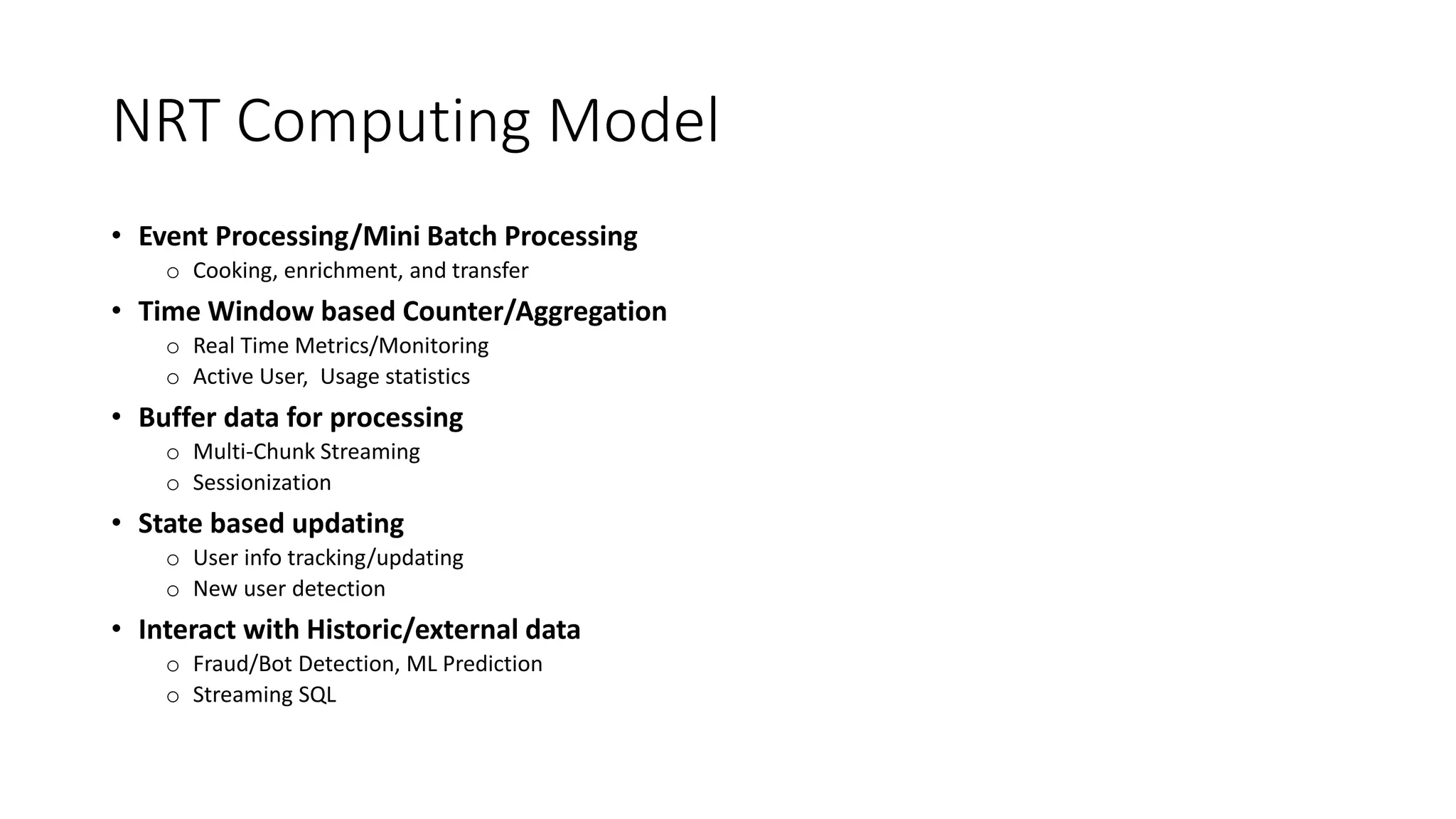
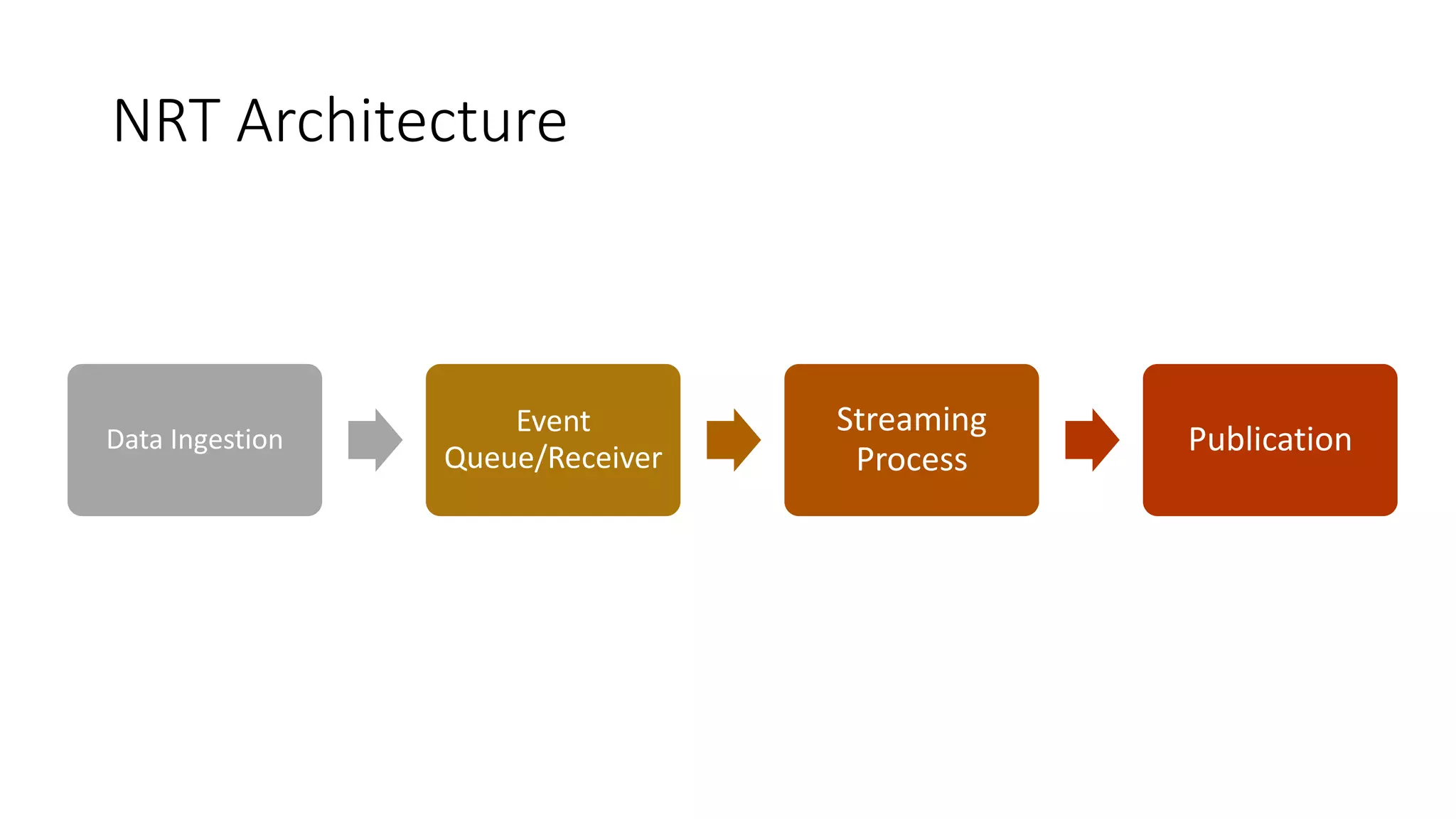
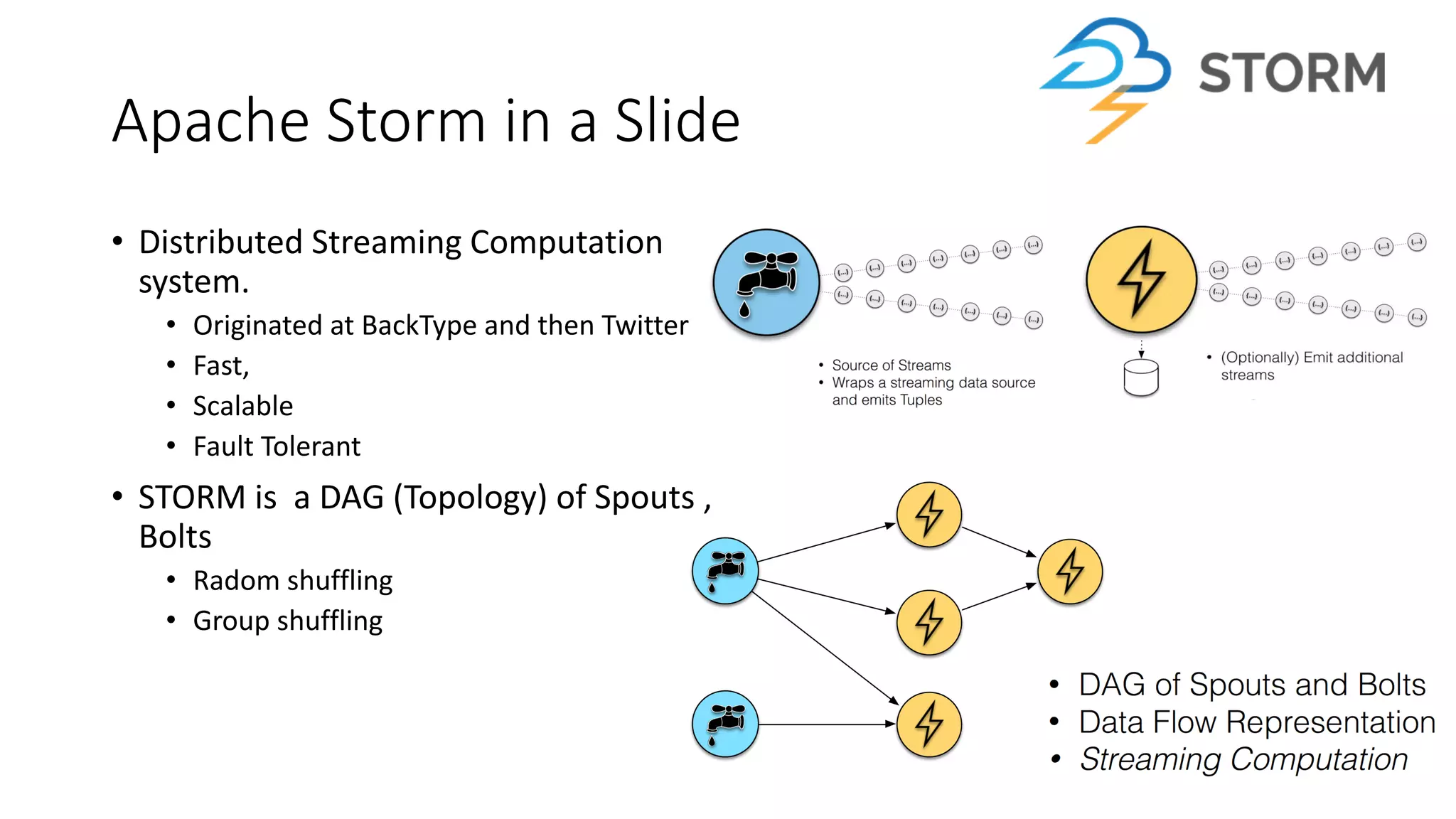
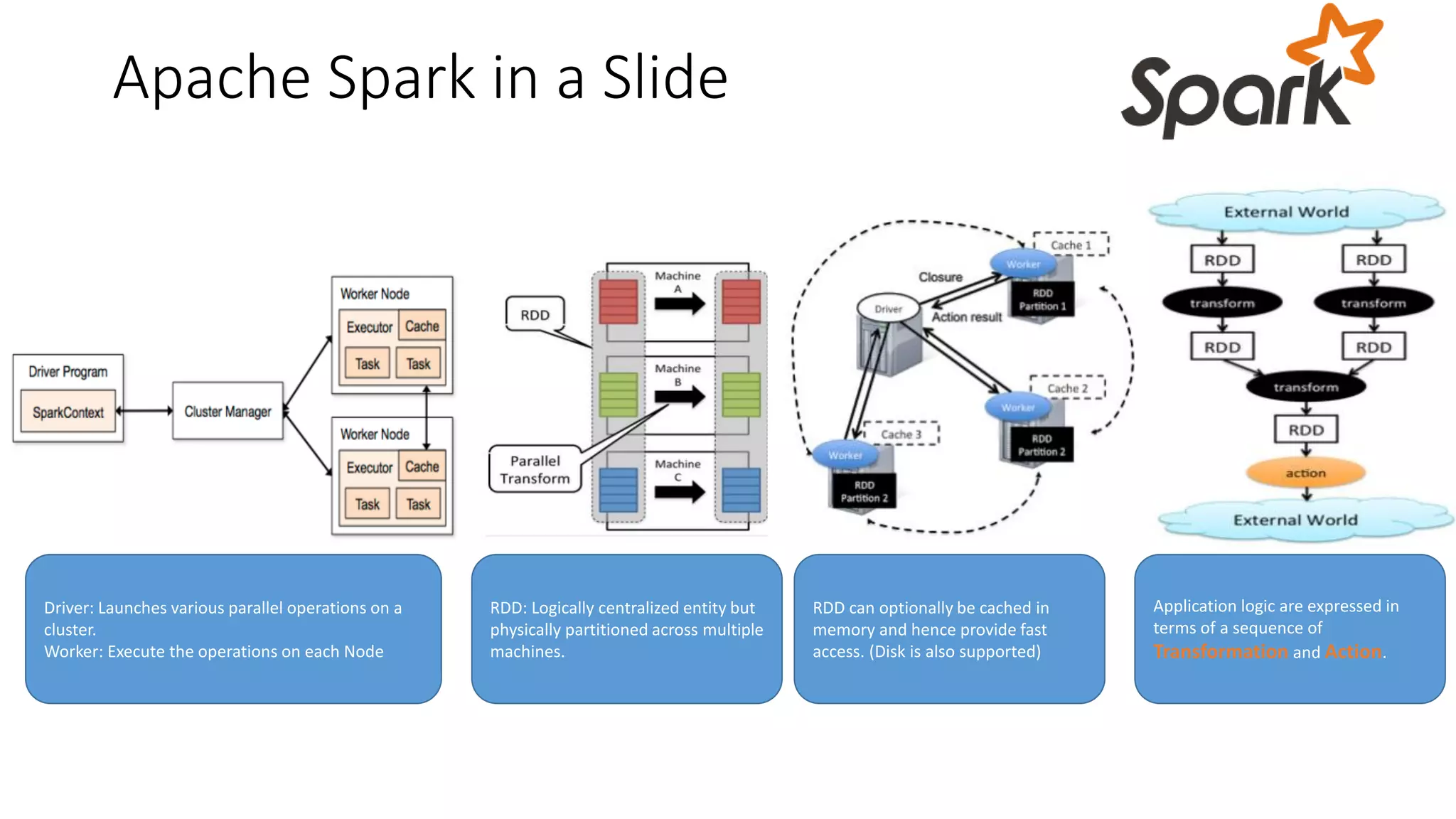
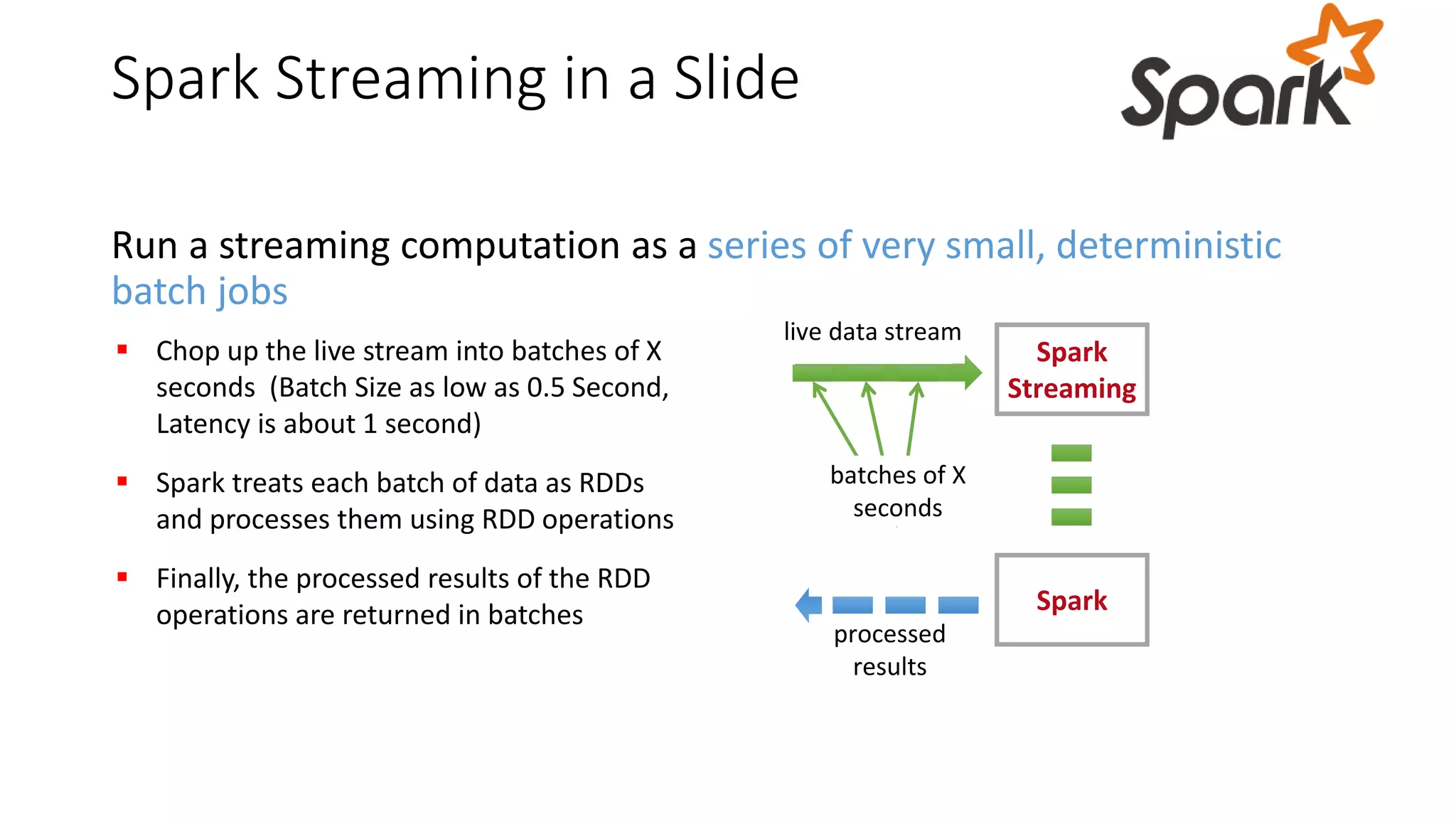
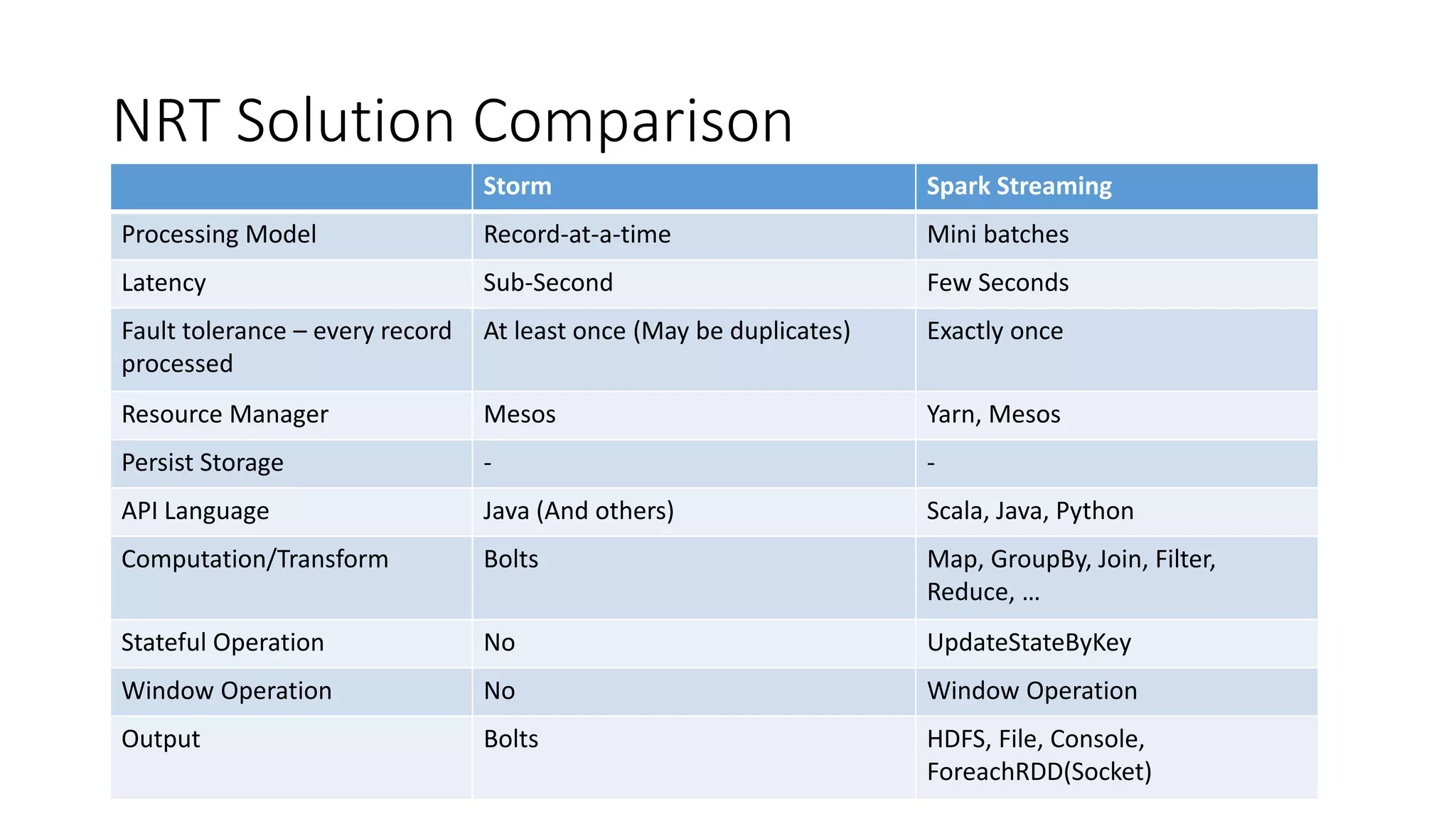
Near real-time computing processes data as it streams in within seconds, enabling immediate analytics and decisions. It is used for scenarios like fraud detection and web monitoring that require non-stop availability and processing. Near real-time systems like Storm and Spark Streaming work by processing data in micro-batches within 1-2 seconds using in-memory computation for low latency. They provide scalability, fault tolerance and support stateful operations on streaming data.