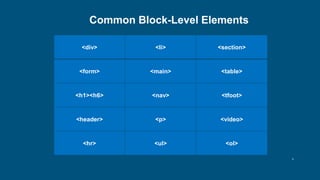
HTML (Hypertext Markup Language) is the standard markup language used to structure and present web pages. Key HTML elements include headings, paragraphs, links, images, lists, and tables. Elements are defined with start and end tags (e.g. <p>paragraph text</p>) or as empty elements without an end tag (e.g. <br> for a line break). Common block-level elements like <div> and <p> occupy the full width of the page, while inline elements like <a> and <b> sit within surrounding content. Attributes provide additional information about elements, such as the href attribute specifying a link URL for <a> elements.