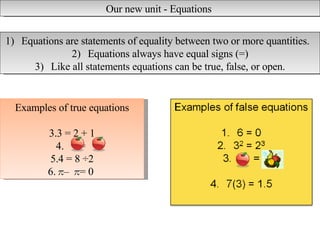
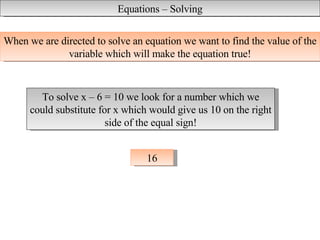
The document discusses equations and solving equations. It defines an equation as a statement of equality between two or more quantities that always includes an equal sign. Equations can be true, false, or open. To solve an equation means to find the value of the variable that makes the statement true. The document provides examples of different types of equations and introduces the cover-up method for solving equations.