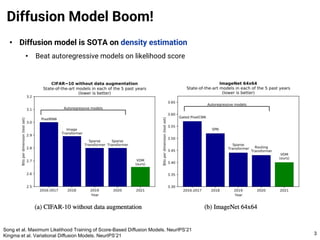
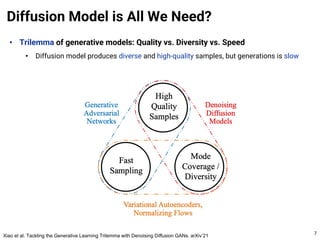
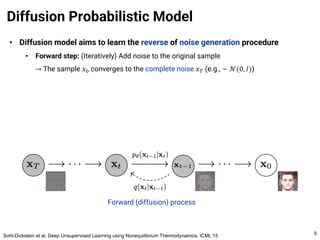
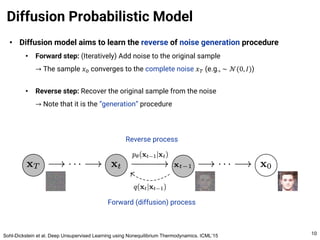
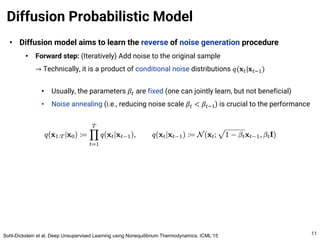
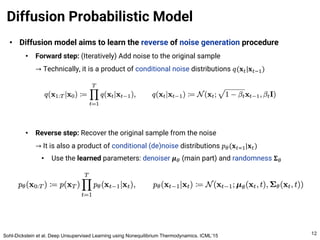
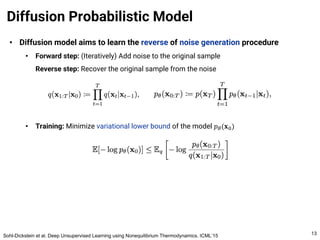
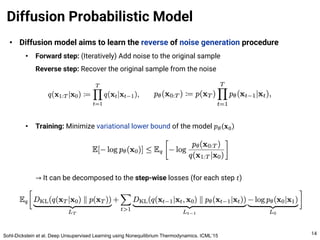
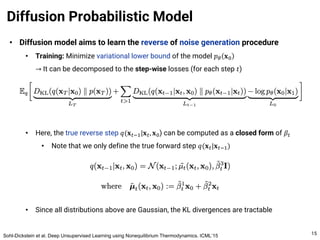
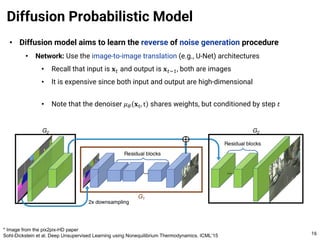
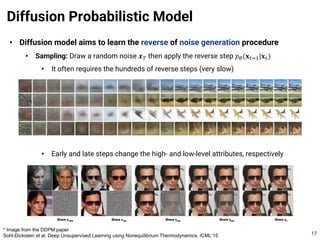
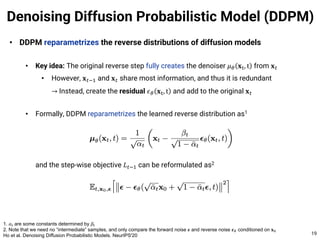
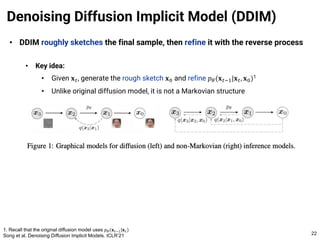
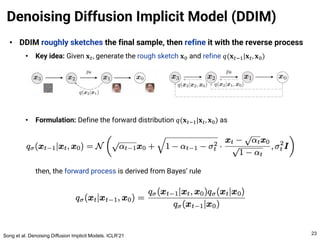
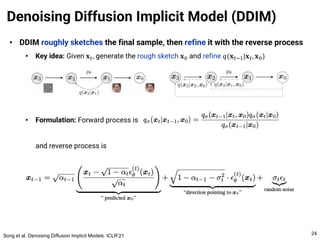
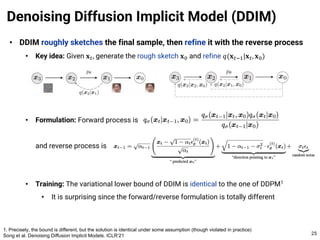
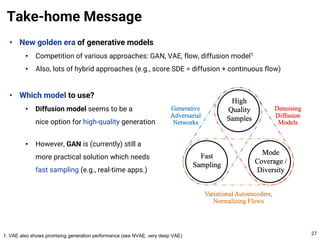
The document provides an introduction to diffusion models. It discusses that diffusion models have achieved state-of-the-art performance in image generation, density estimation, and image editing. Specifically, it covers the Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Model (DDPM) which reparametrizes the reverse distributions of diffusion models to be more efficient. It also discusses the Denoising Diffusion Implicit Model (DDIM) which generates rough sketches of images and then refines them, significantly reducing the number of sampling steps needed compared to DDPM. In summary, diffusion models have emerged as a highly effective approach for generative modeling tasks.