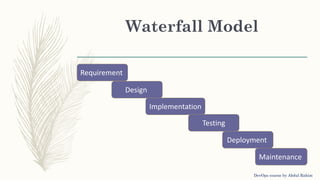
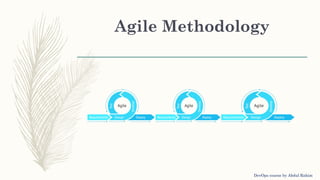
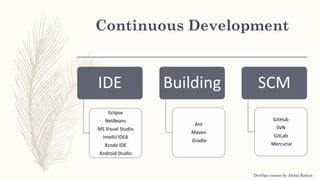
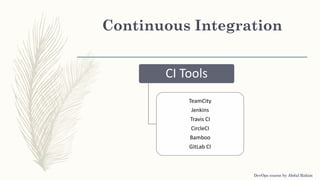
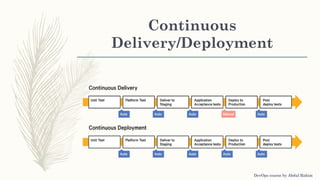
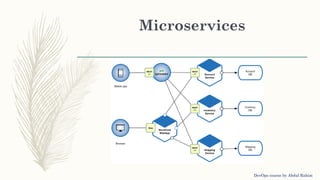
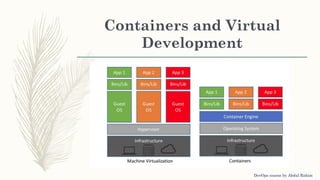
The document outlines a DevOps course by Abdul Rahim, detailing DevOps as a cultural shift improving collaboration between development and operations for faster, more reliable software delivery. It includes a history of DevOps, key objectives, best practices, and covers various methodologies such as continuous integration, continuous delivery, microservices, and infrastructure as code. Additionally, it addresses the importance of monitoring, communication, container development, and cluster management tools in the DevOps lifecycle.