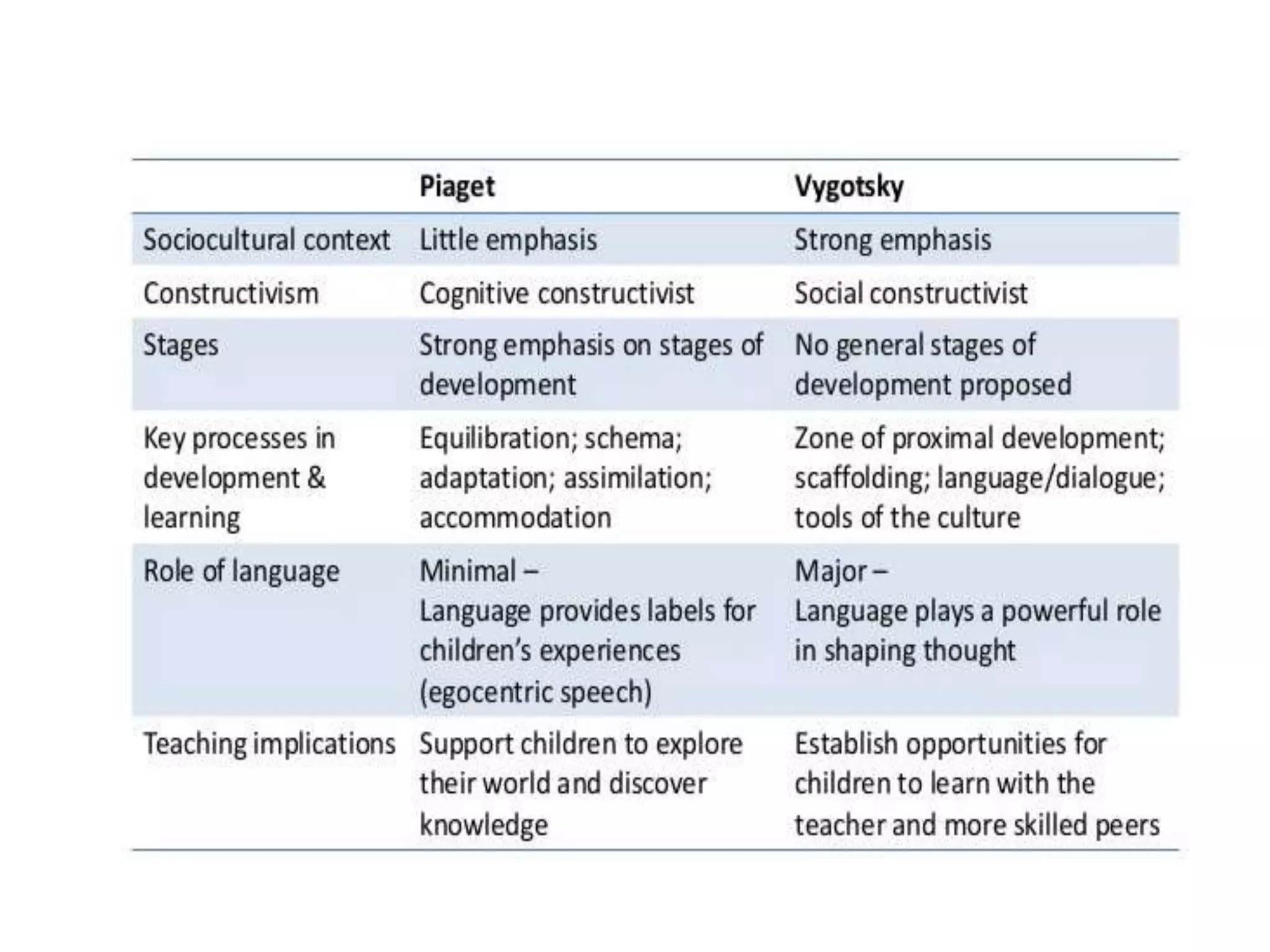
The document introduces constructivist learning theories, which posit that learners construct knowledge through experiences rather than passively receiving information. Key principles of constructivism are that learning is social and embedded within contexts, and the goal of teaching is to design experiences that facilitate student-led knowledge construction. Examples of constructivist classroom activities provided are inquiry-based learning, problem-based learning, cooperative learning, and reciprocal teaching. Vygotsky's social cultural theory and Piaget's theory of cognitive development are also summarized in relation to their influences on constructivist perspectives.