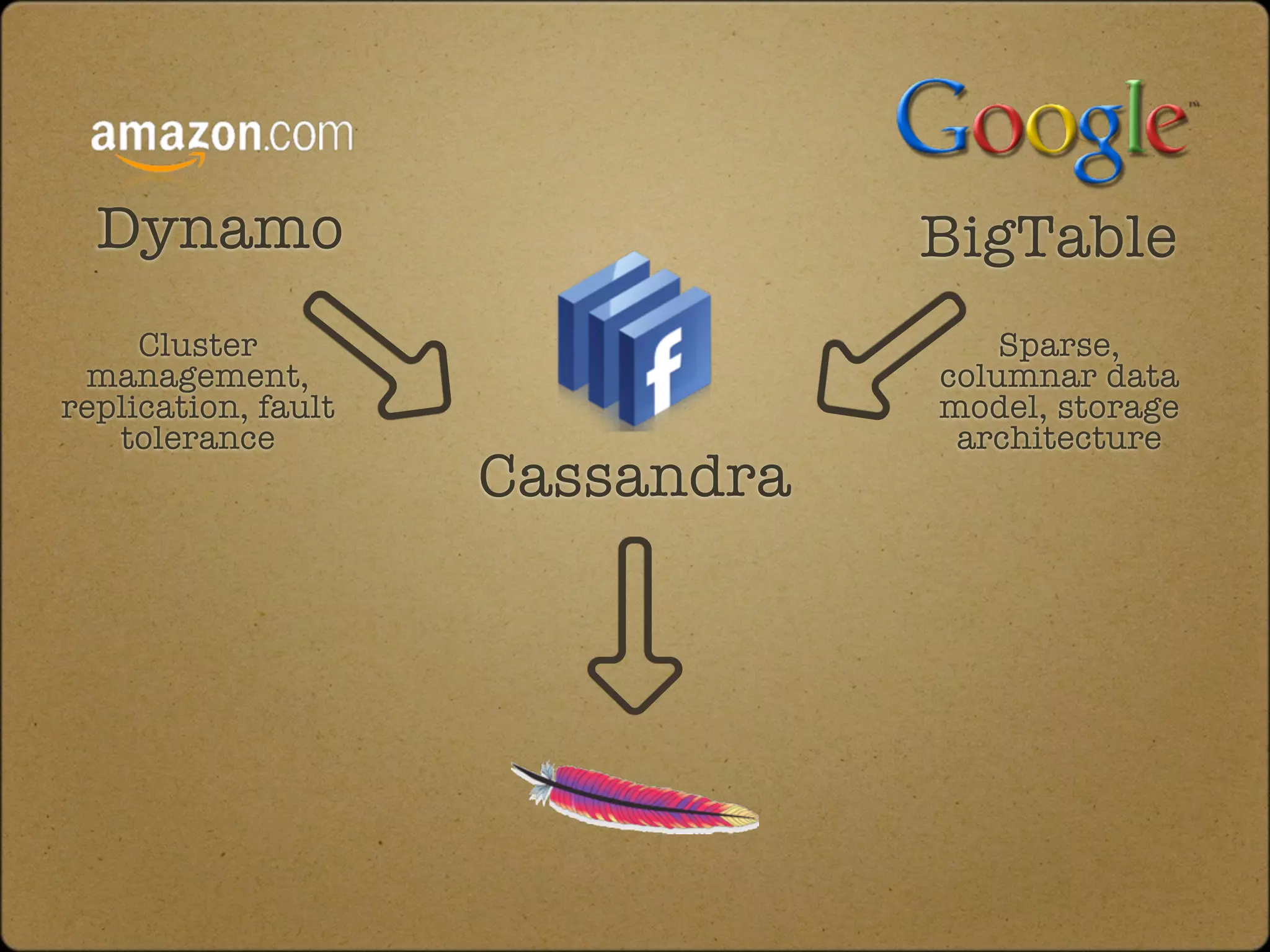
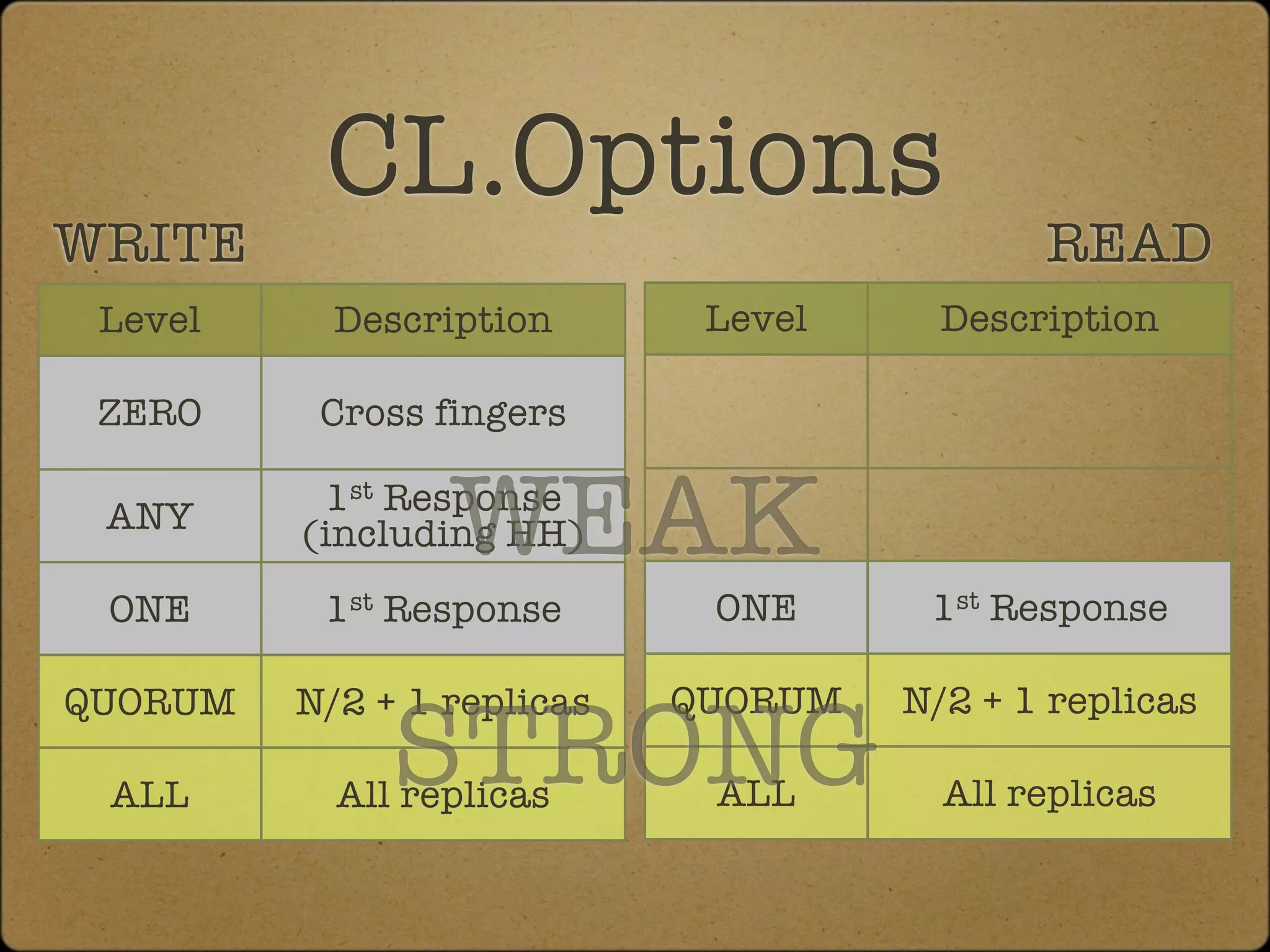
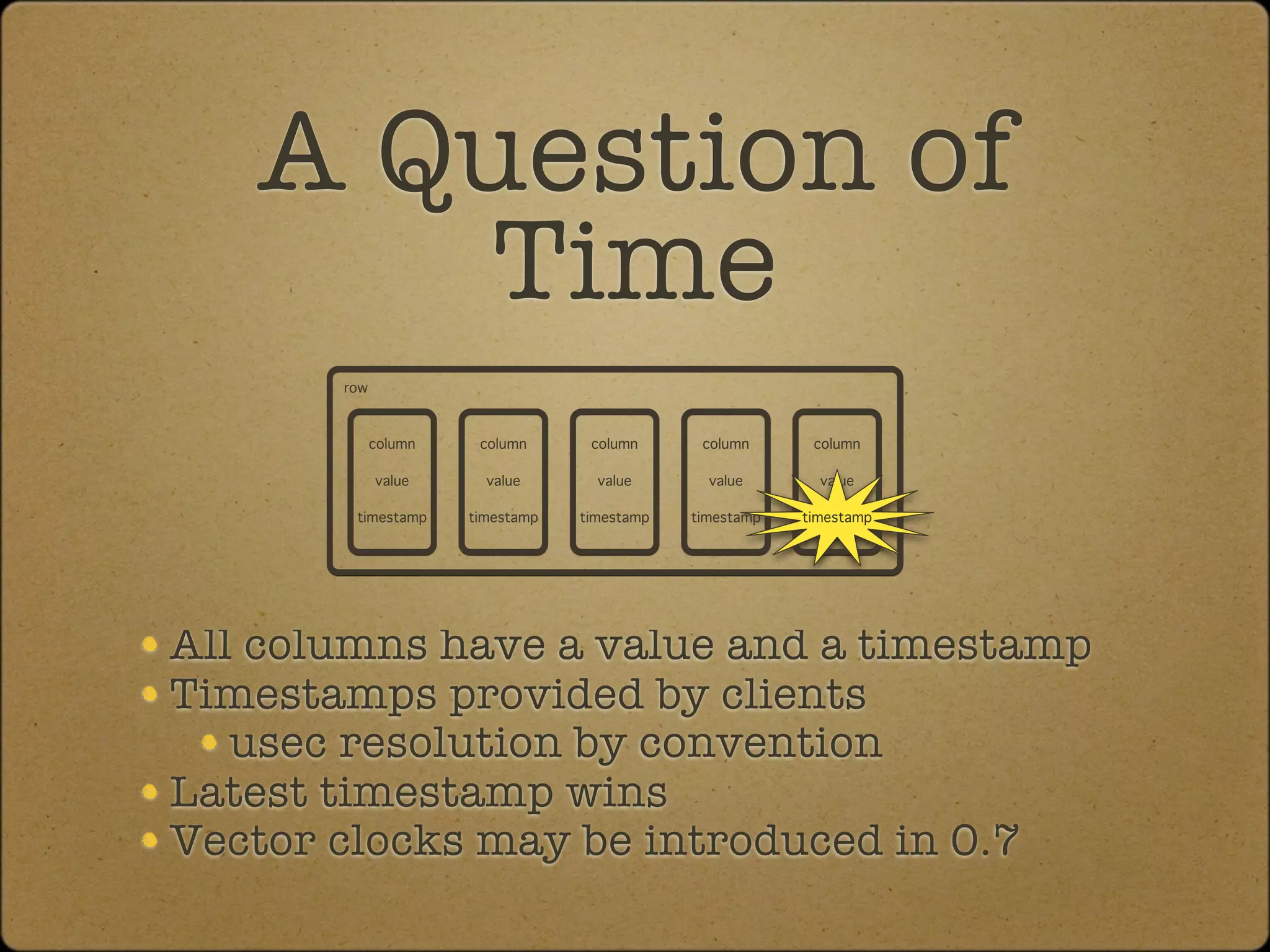
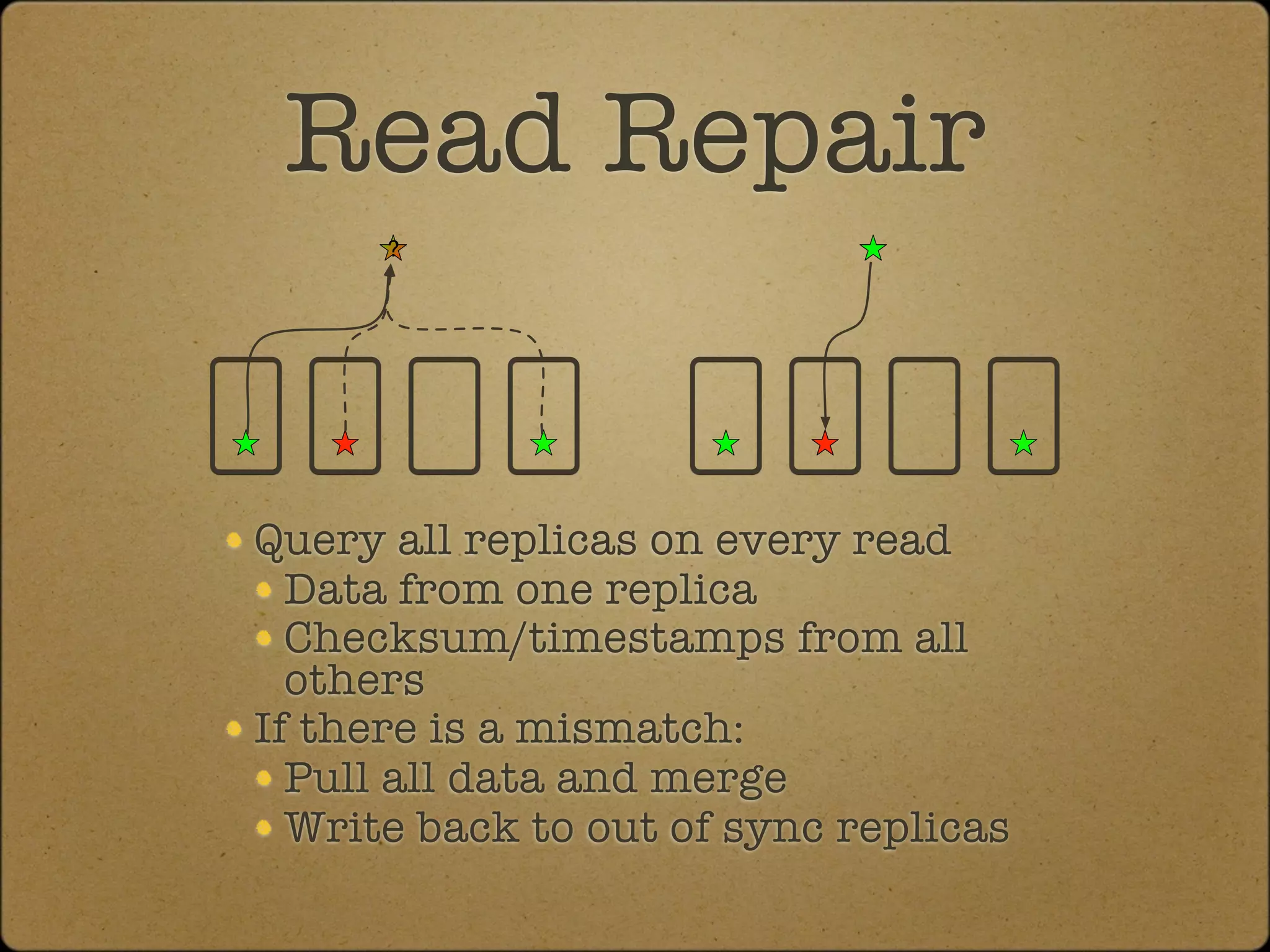
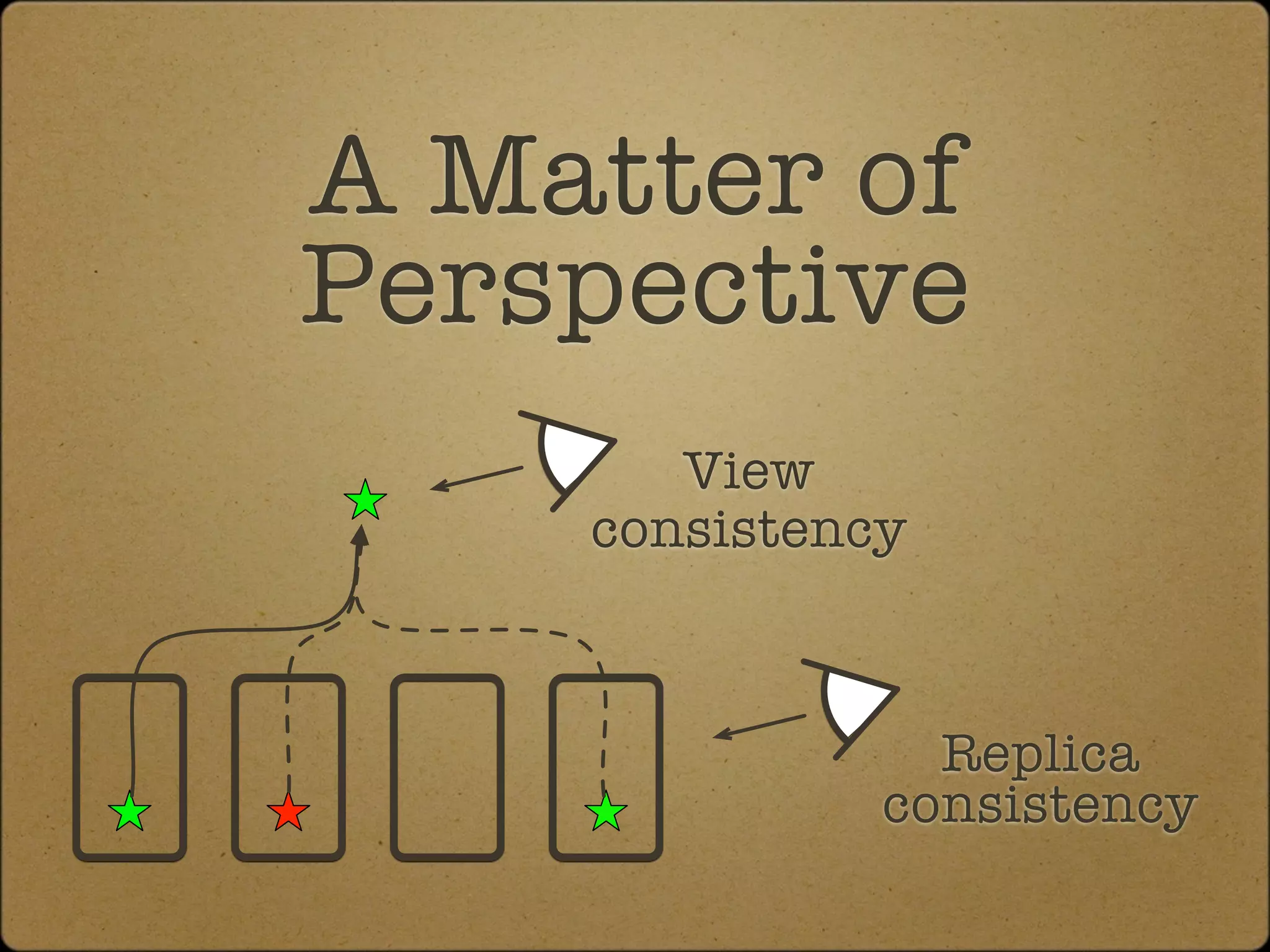
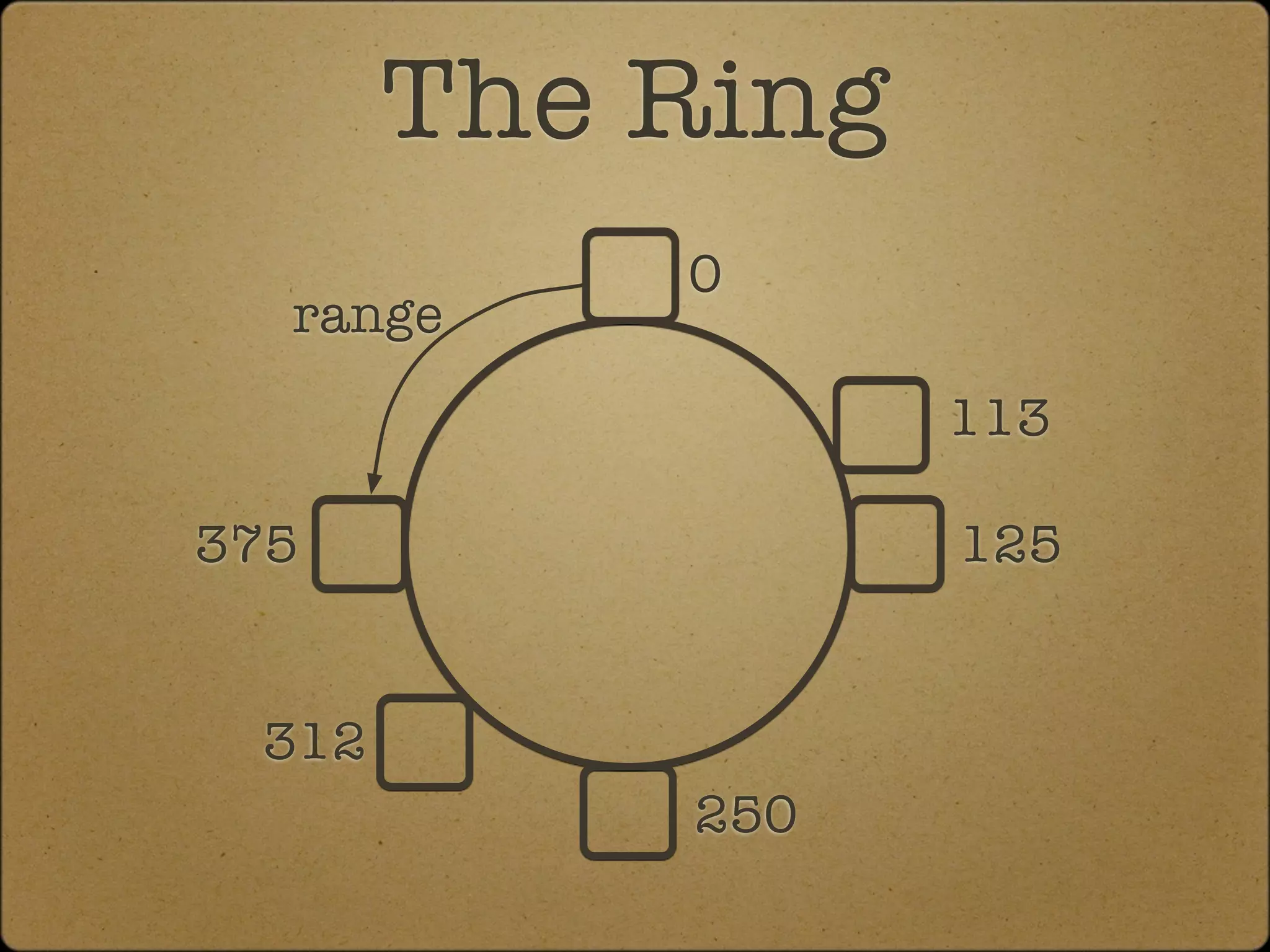
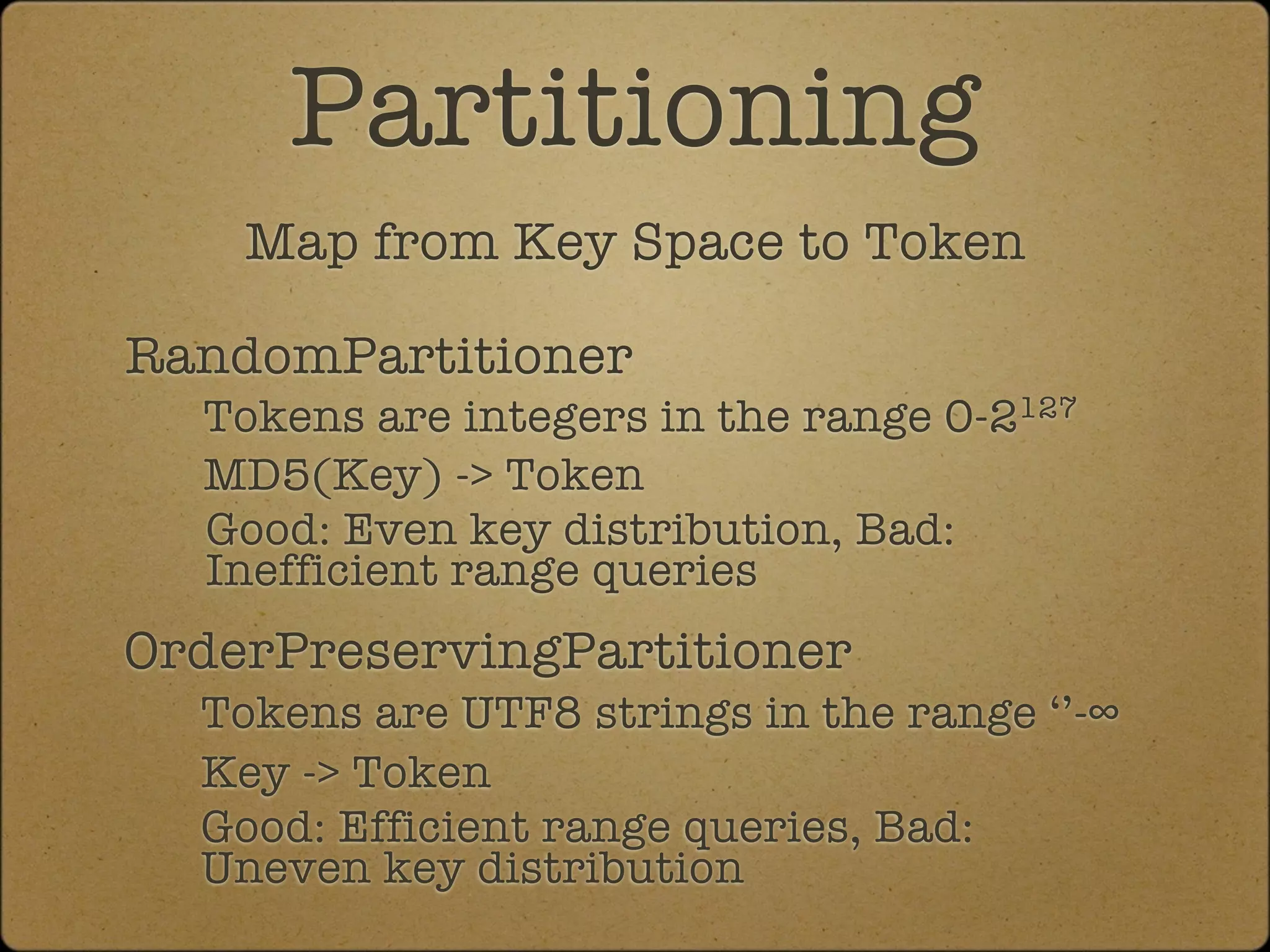
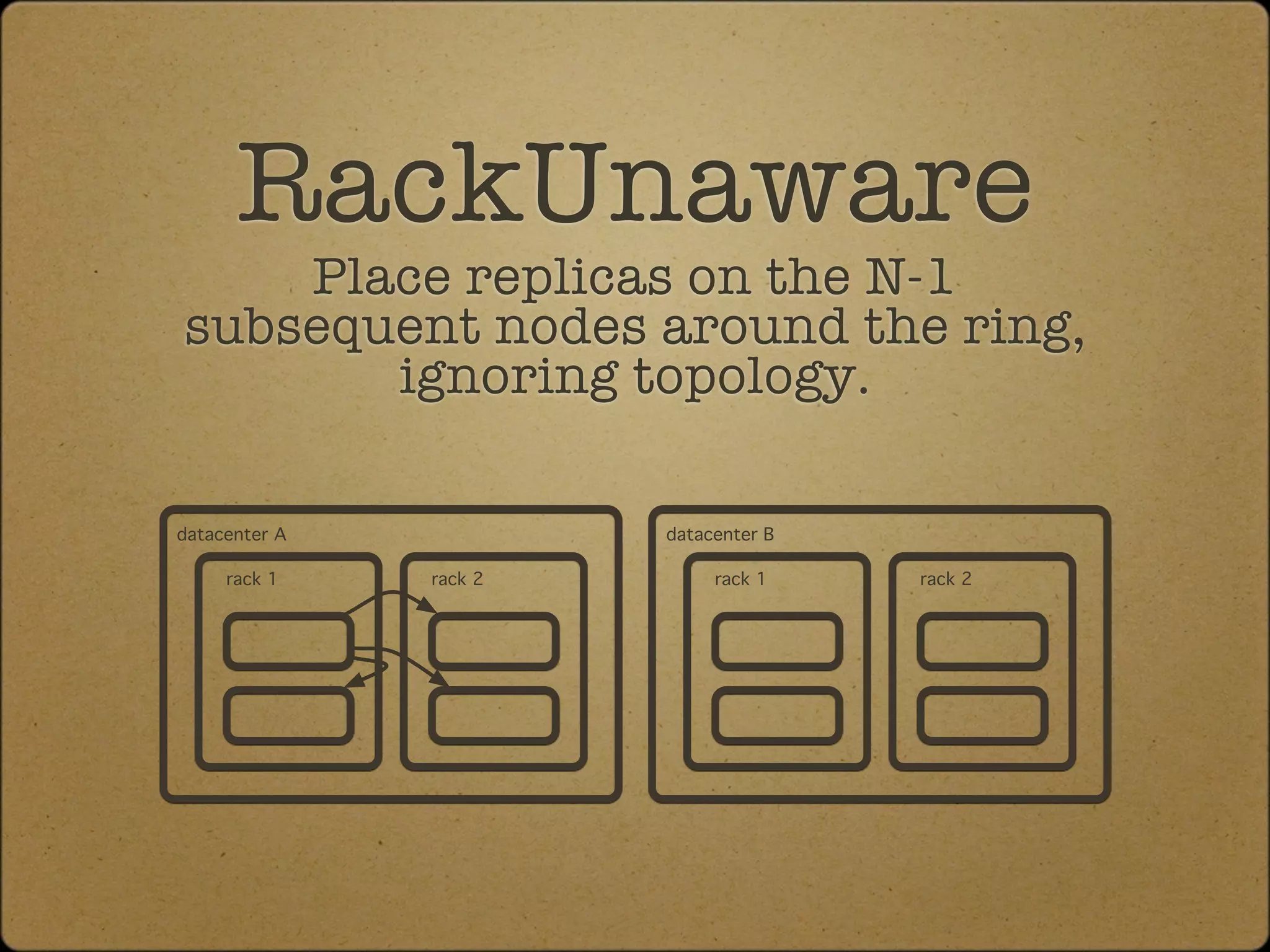
The document discusses the replication and consistency features of Cassandra, highlighting its dynamo-like and bigtable-like architectures. It covers critical concepts such as the number of data copies, consistency levels, and data placement strategies in a distributed hash table system. Additional topics include partitioning and the importance of timestamps in managing data consistency.




![[1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cassandra2010-04-27-100429121250-phpapp02/75/Introduction-to-Cassandra-Replication-and-Consistency-6-2048.jpg)






![[2]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cassandra2010-04-27-100429121250-phpapp02/75/Introduction-to-Cassandra-Replication-and-Consistency-17-2048.jpg)






![[fin]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cassandra2010-04-27-100429121250-phpapp02/75/Introduction-to-Cassandra-Replication-and-Consistency-27-2048.jpg)


