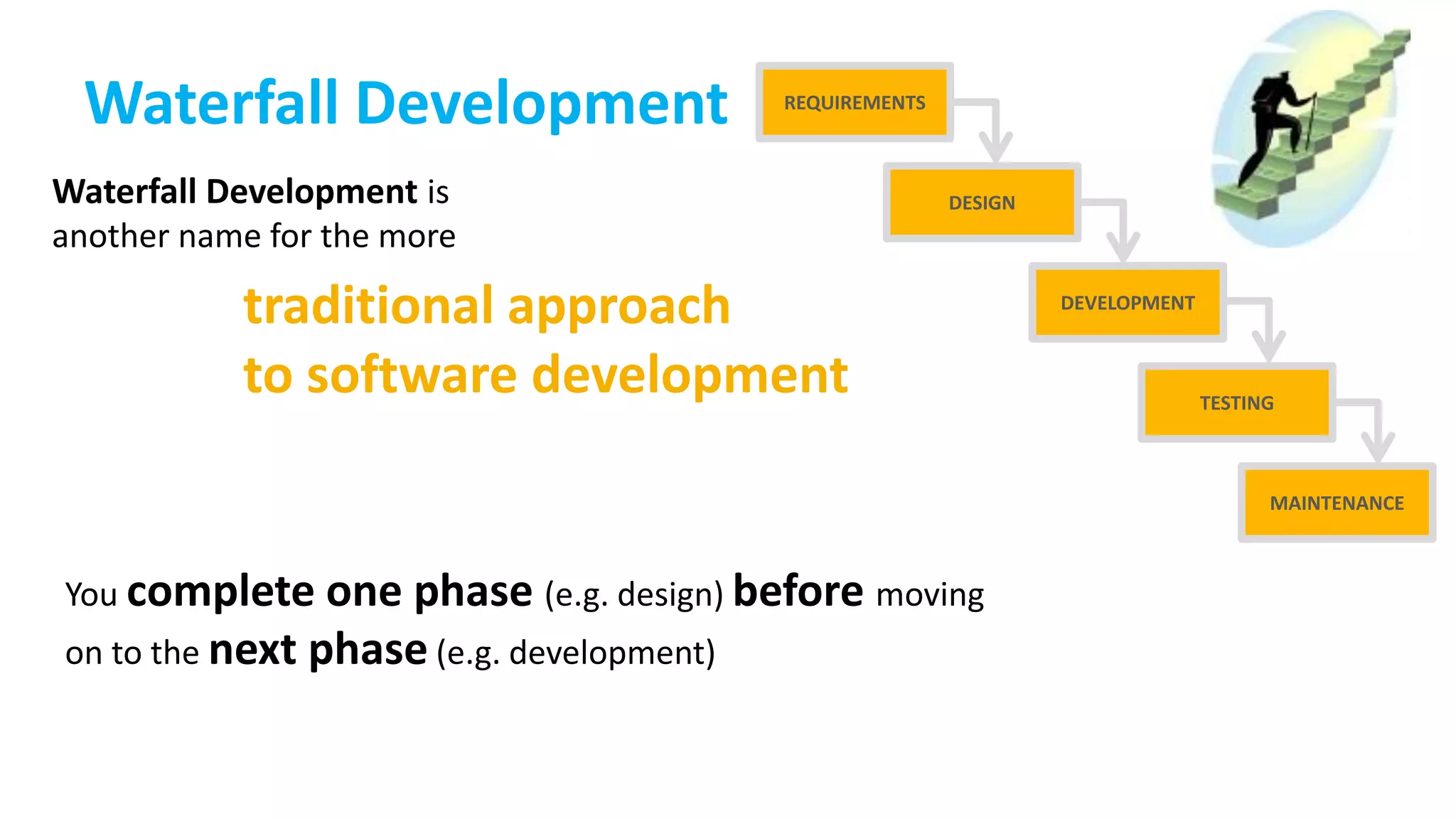
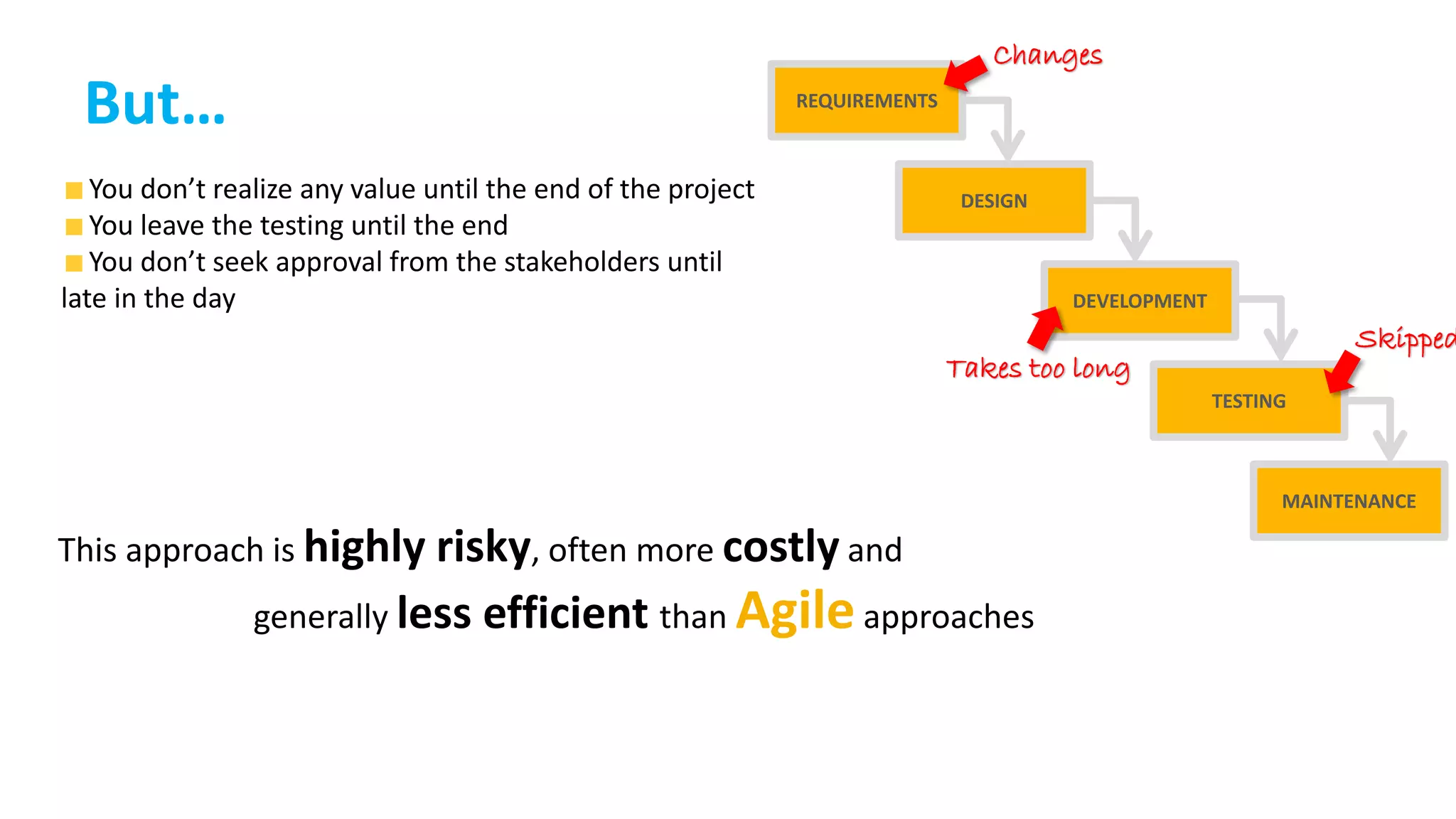
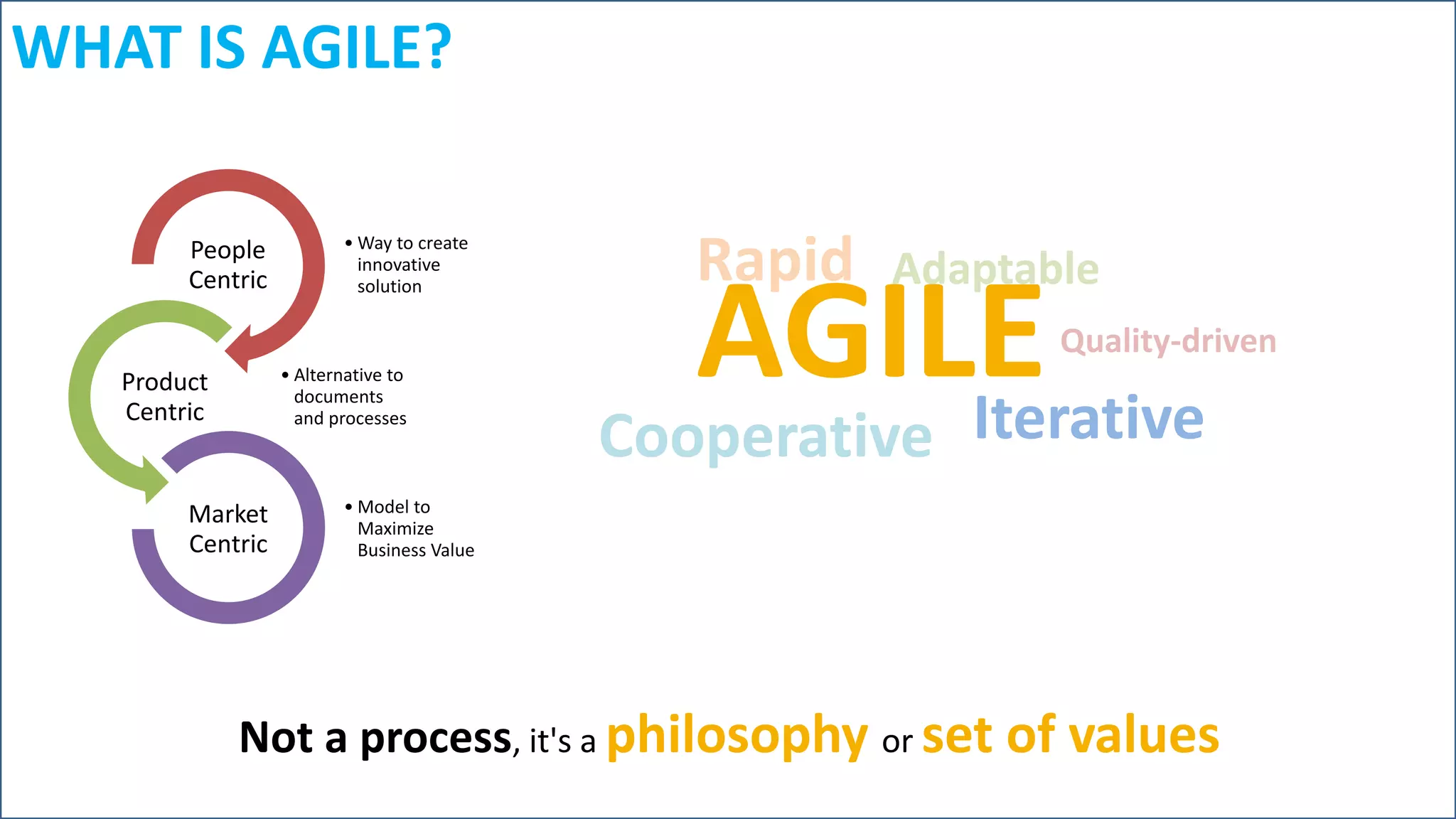
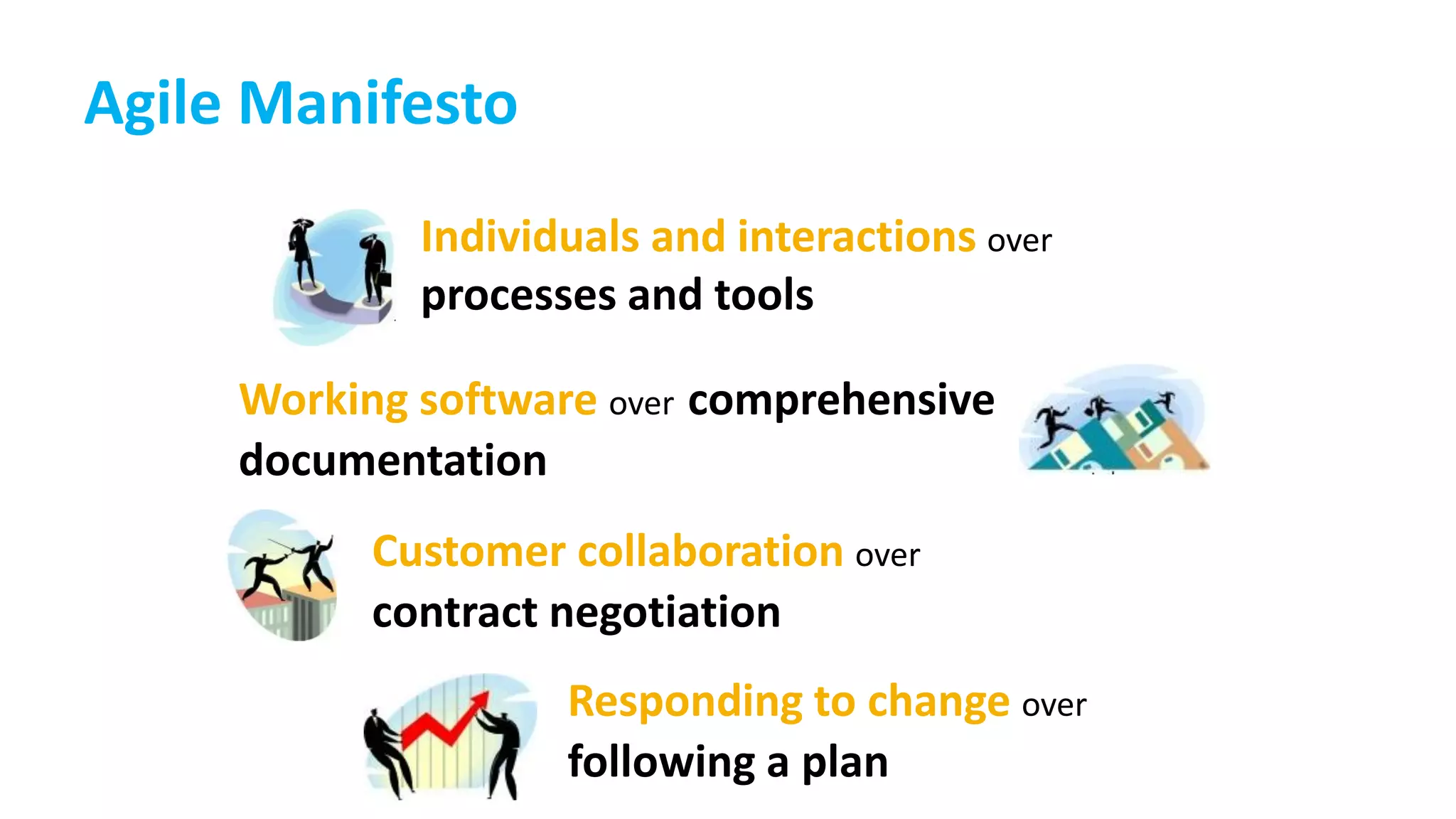
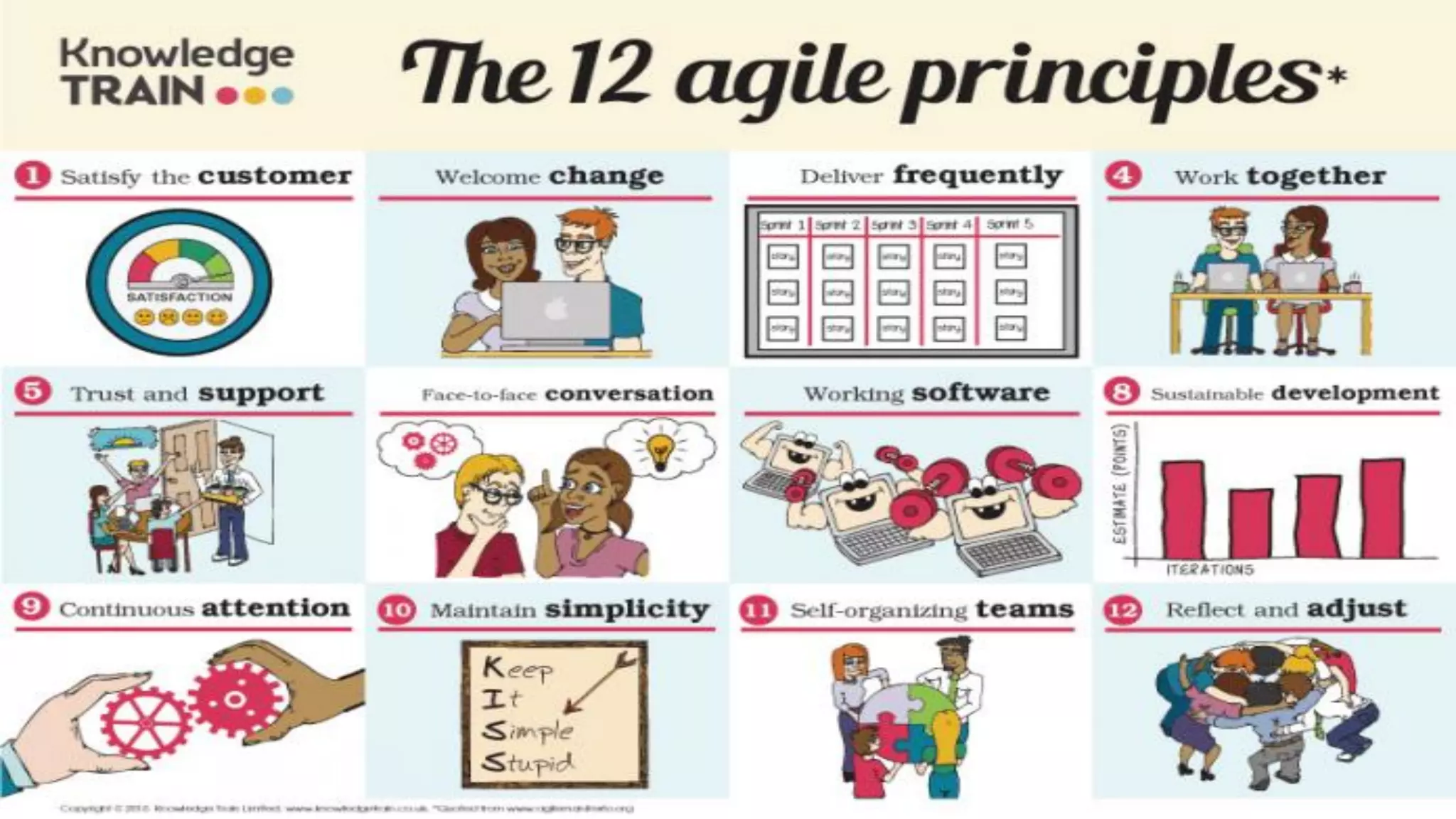
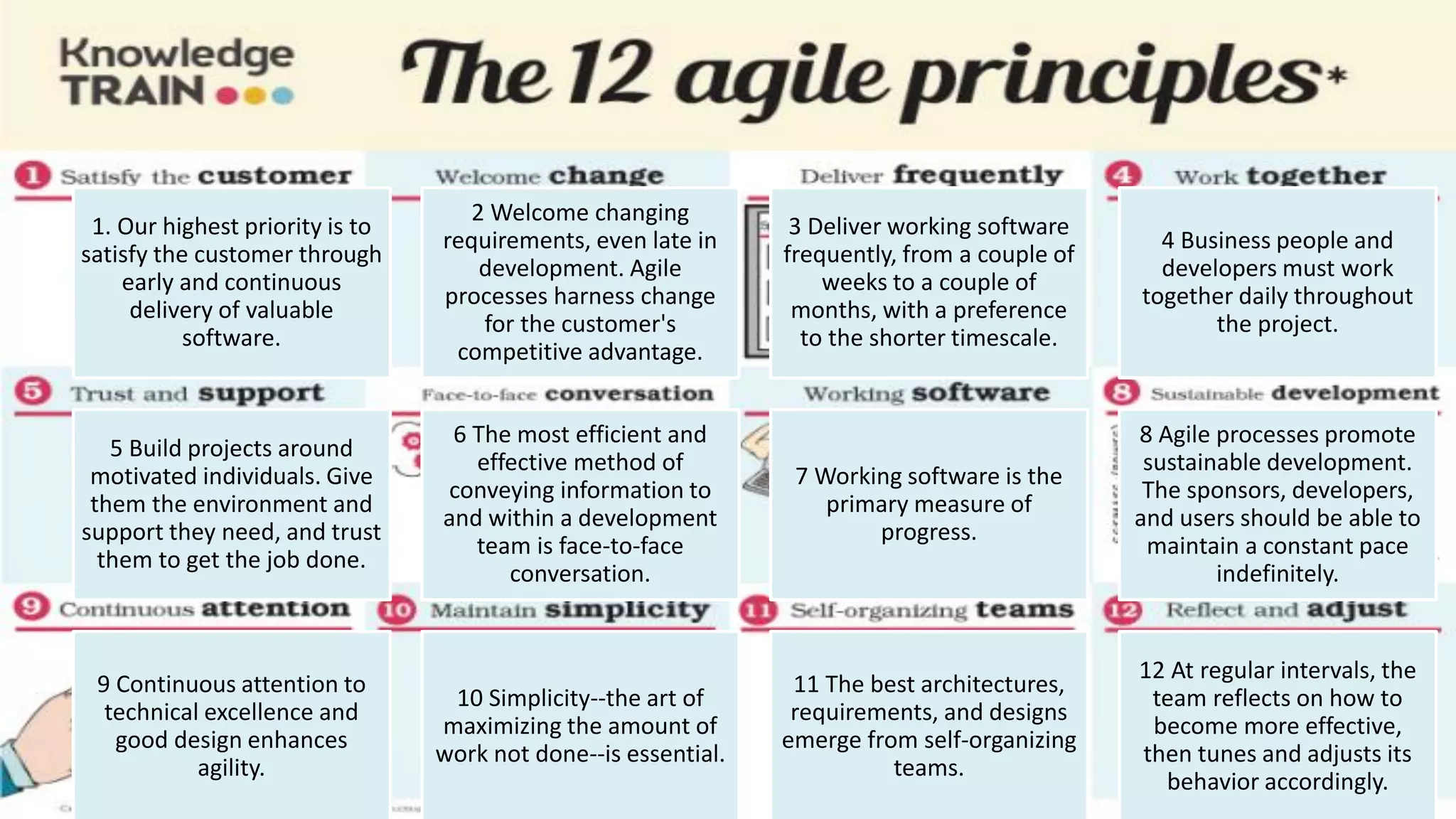
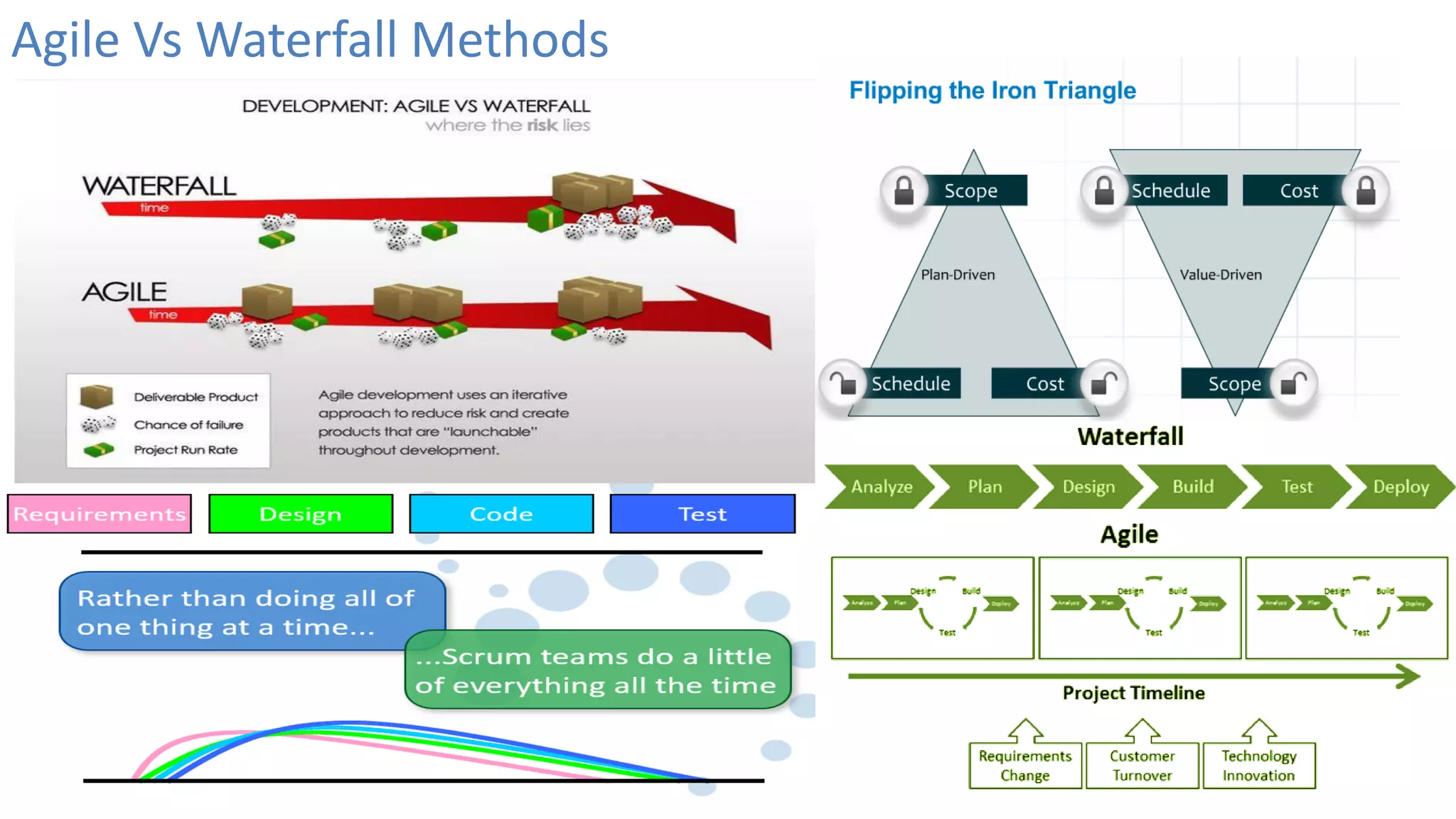
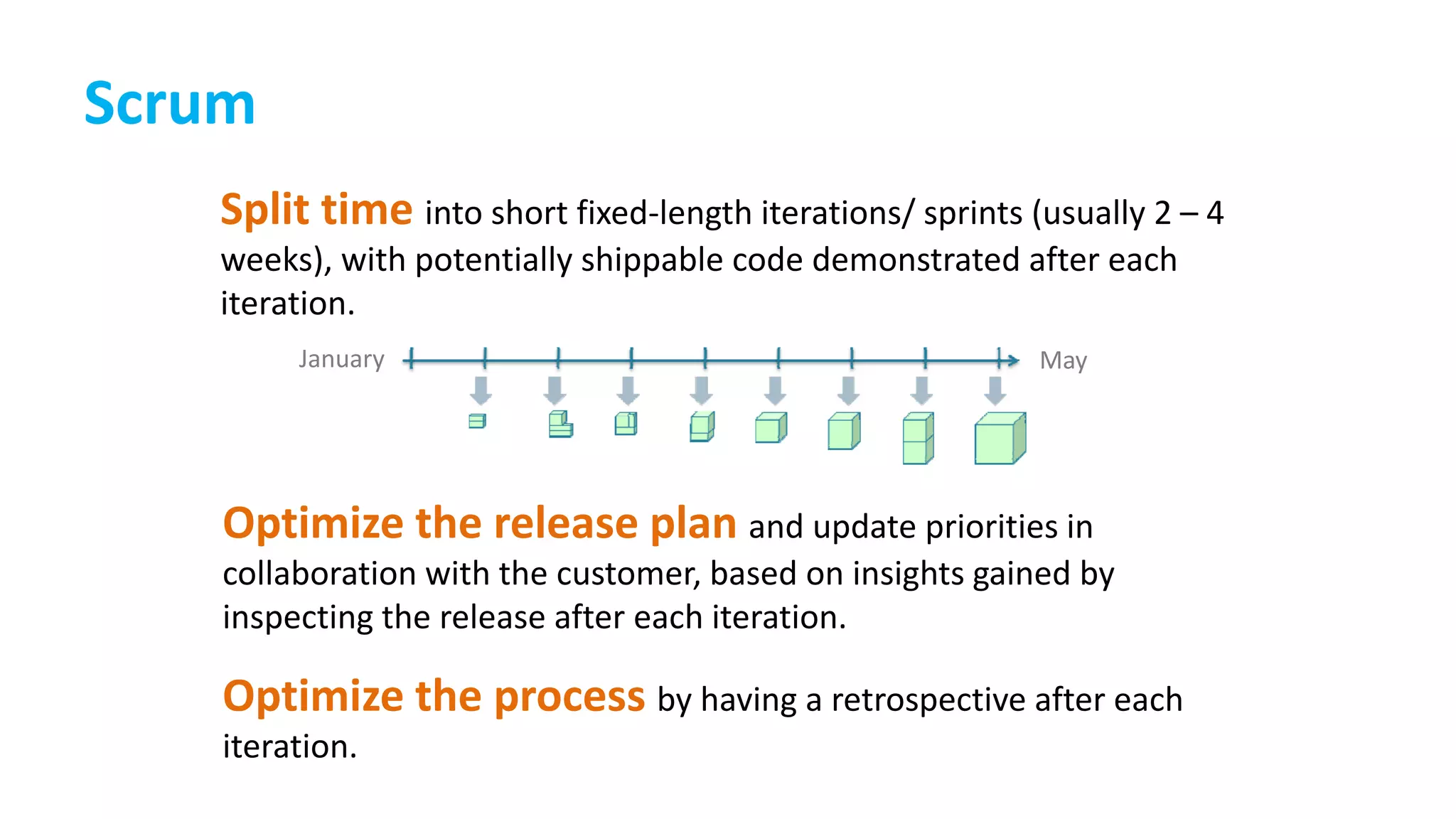
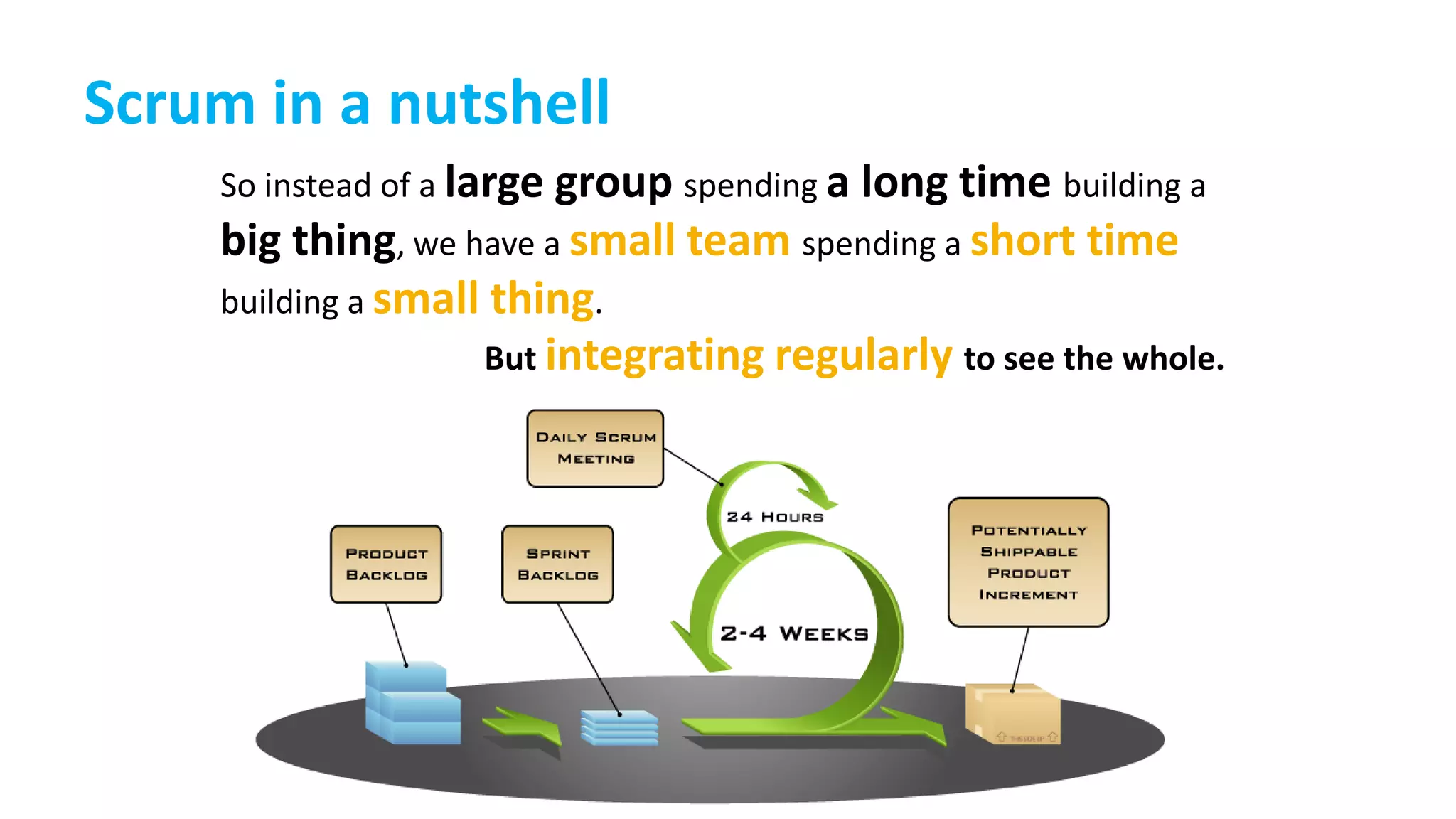
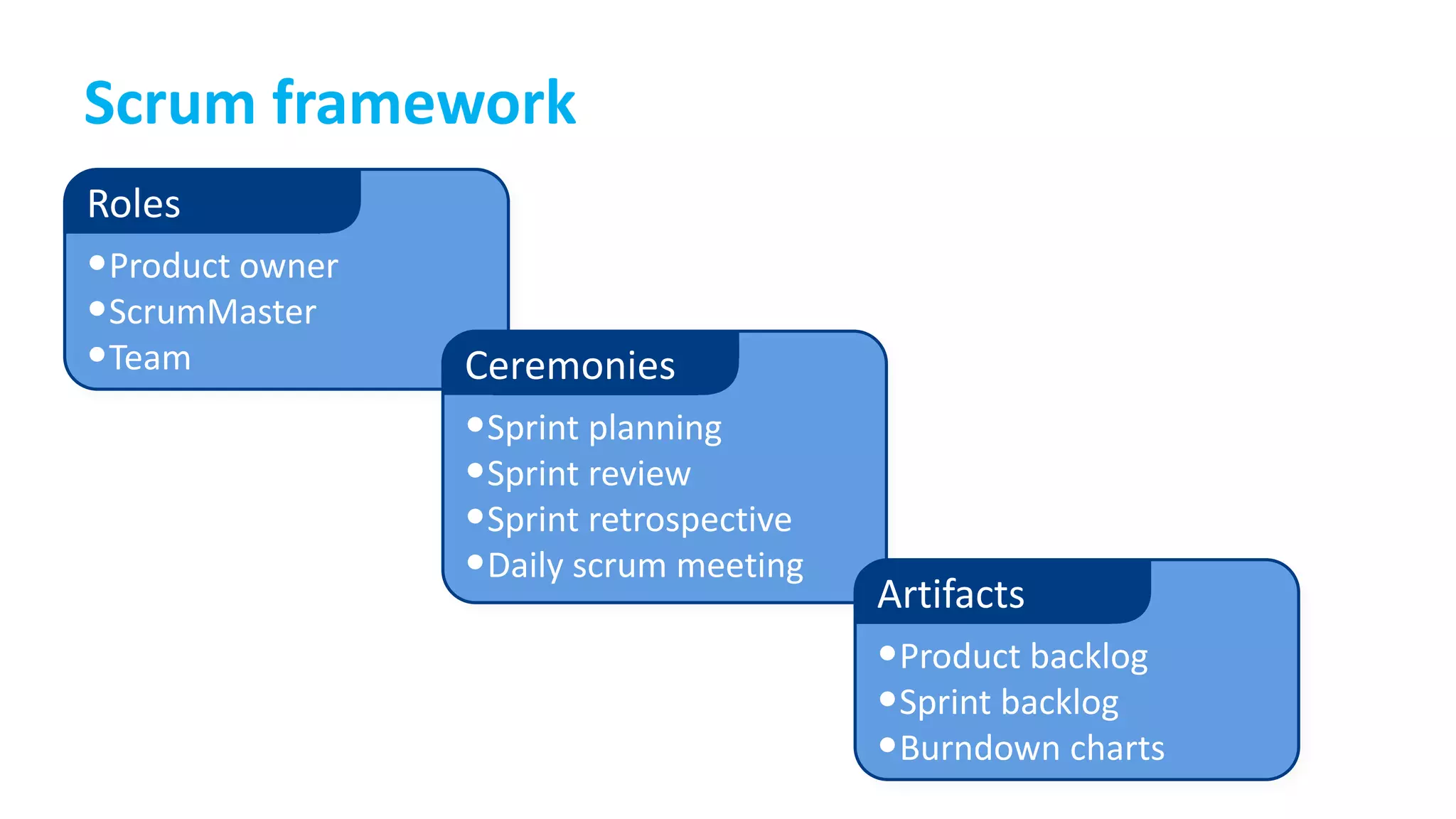
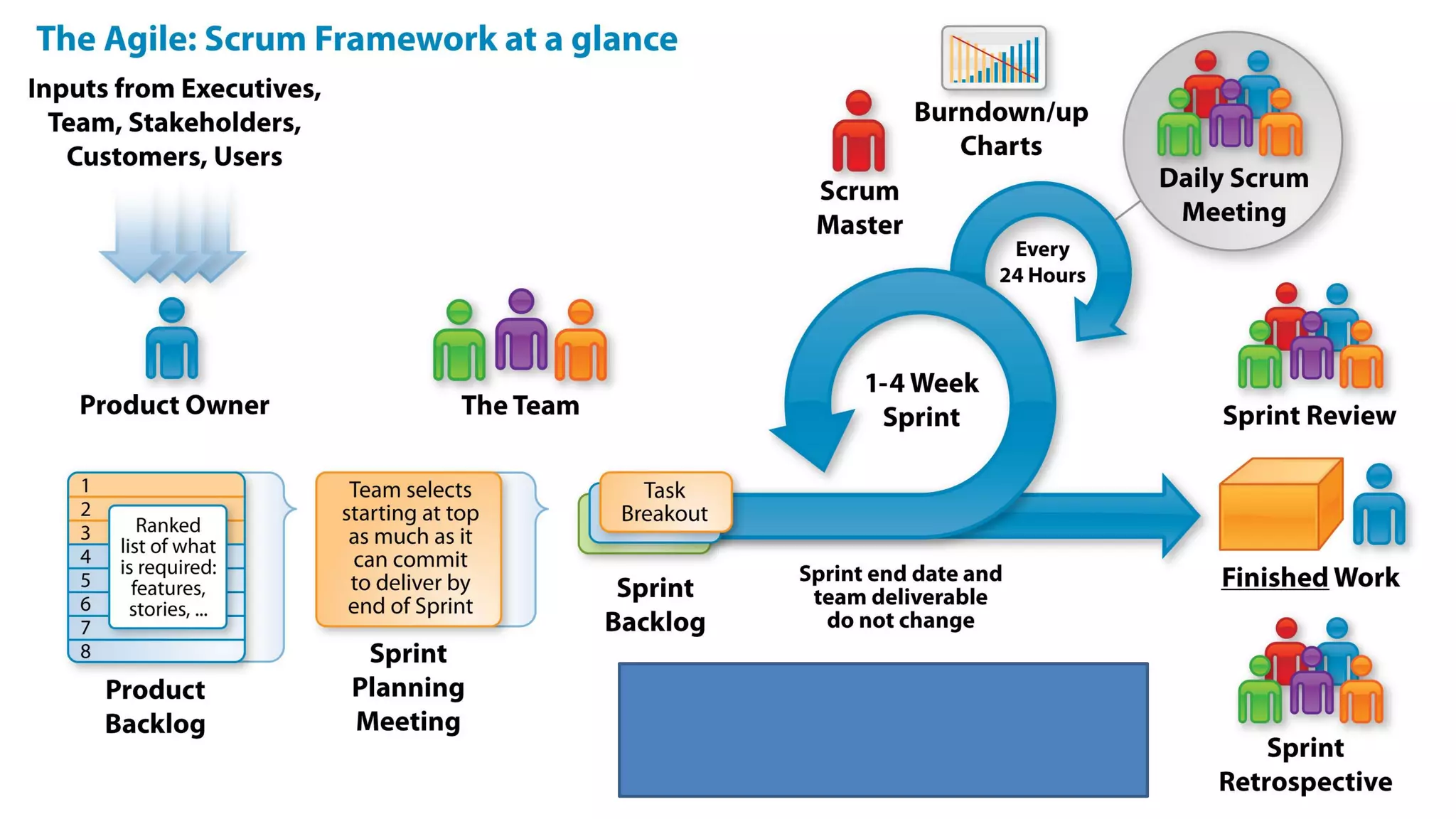
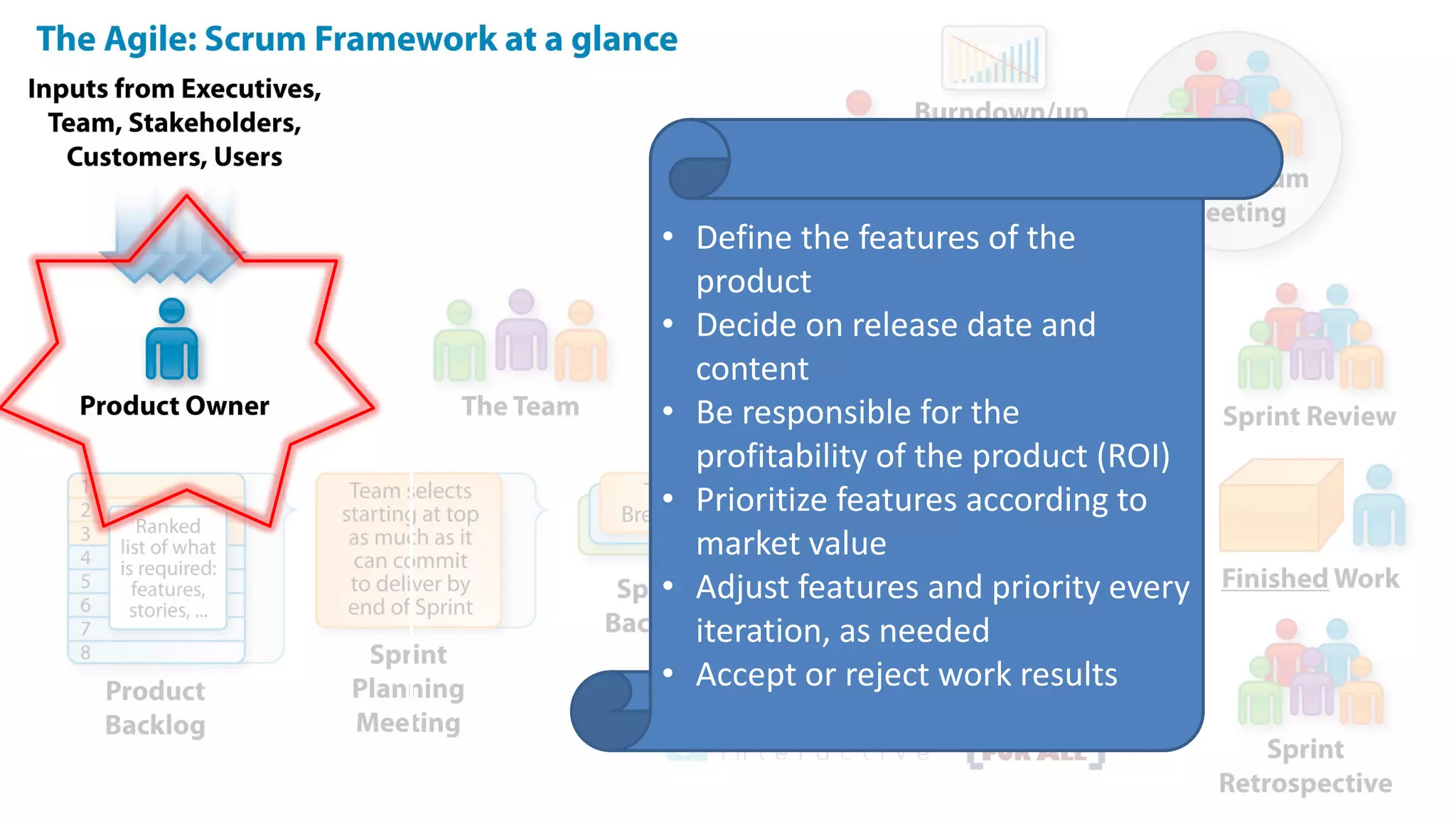
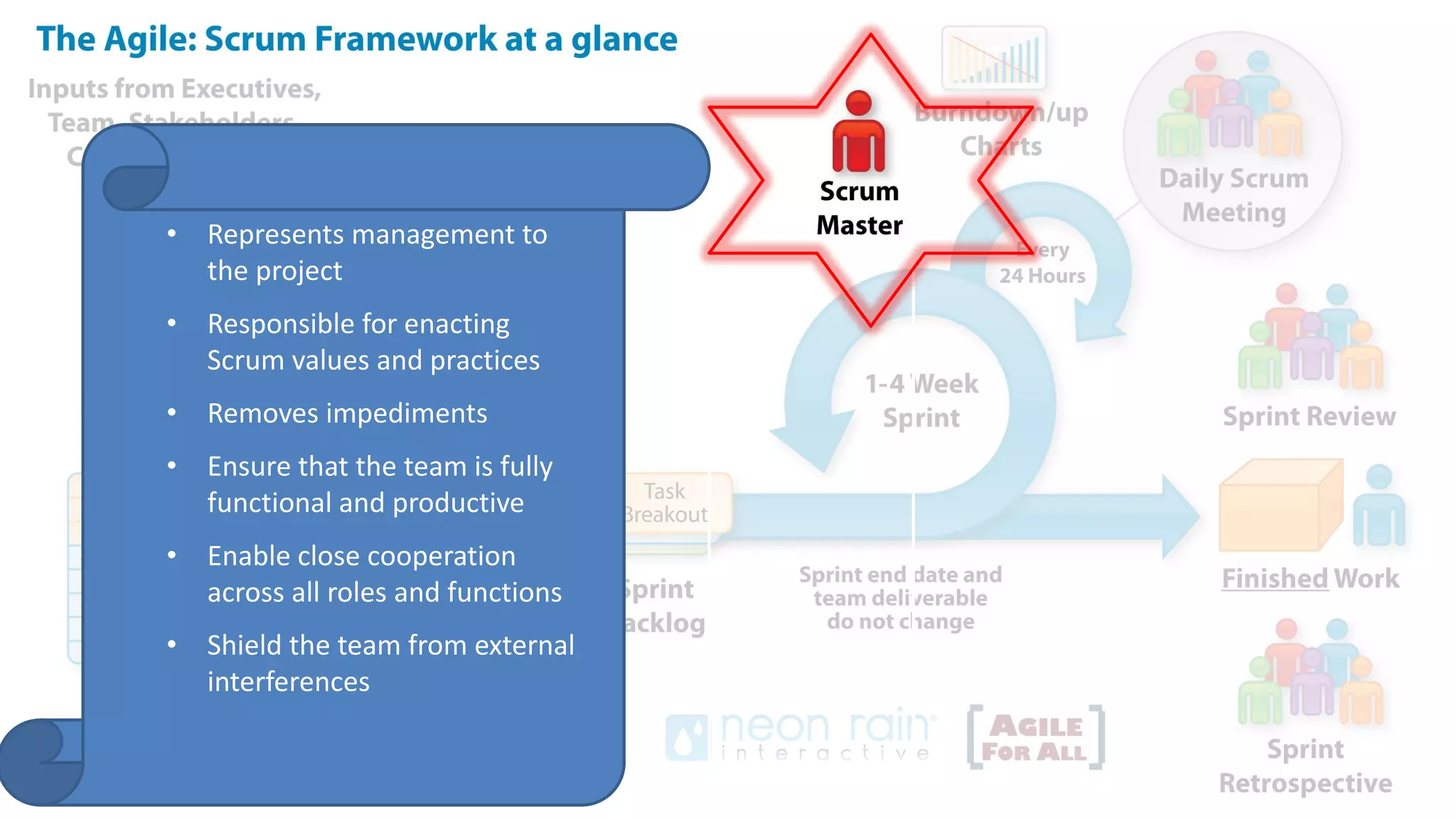
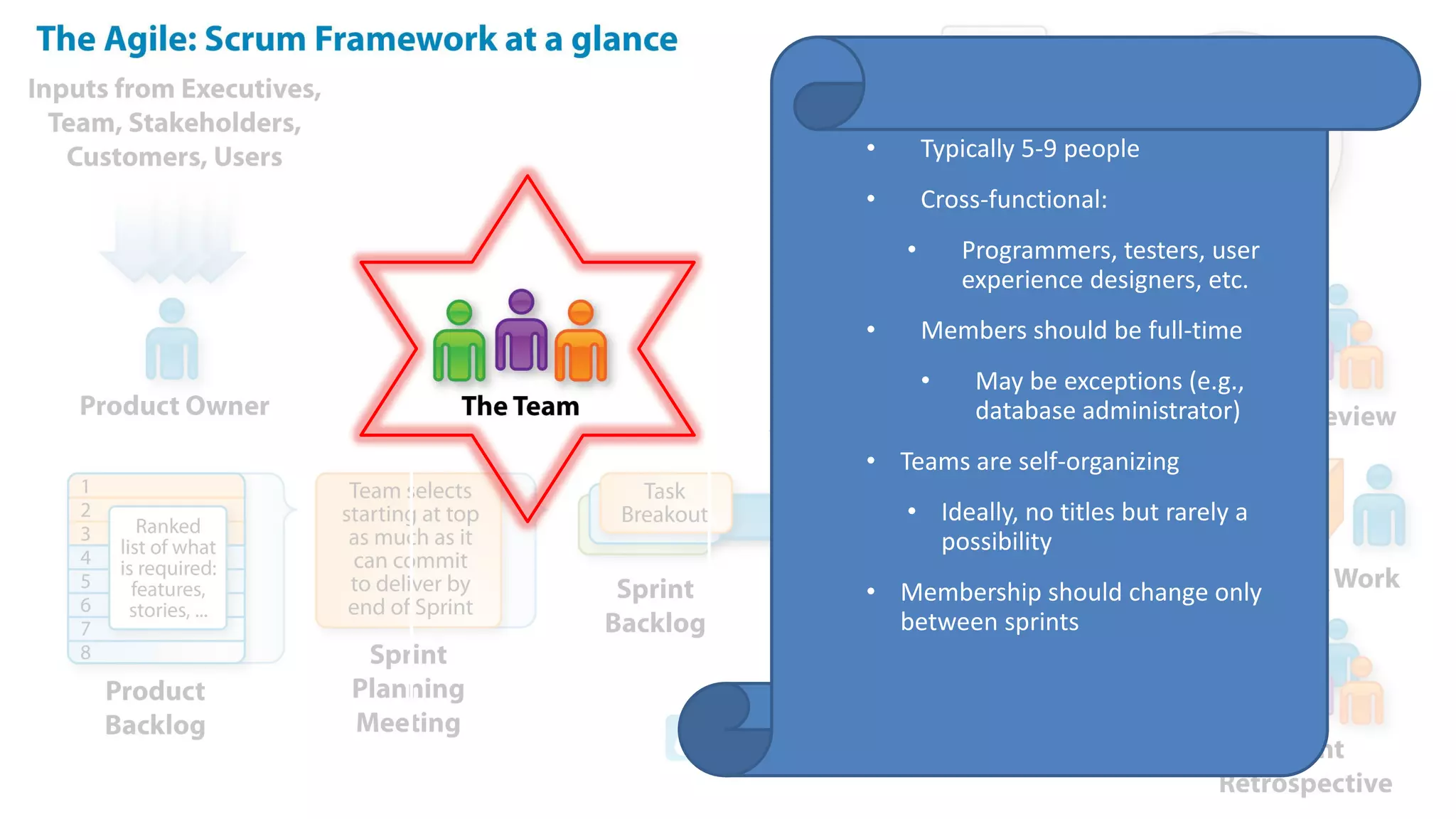
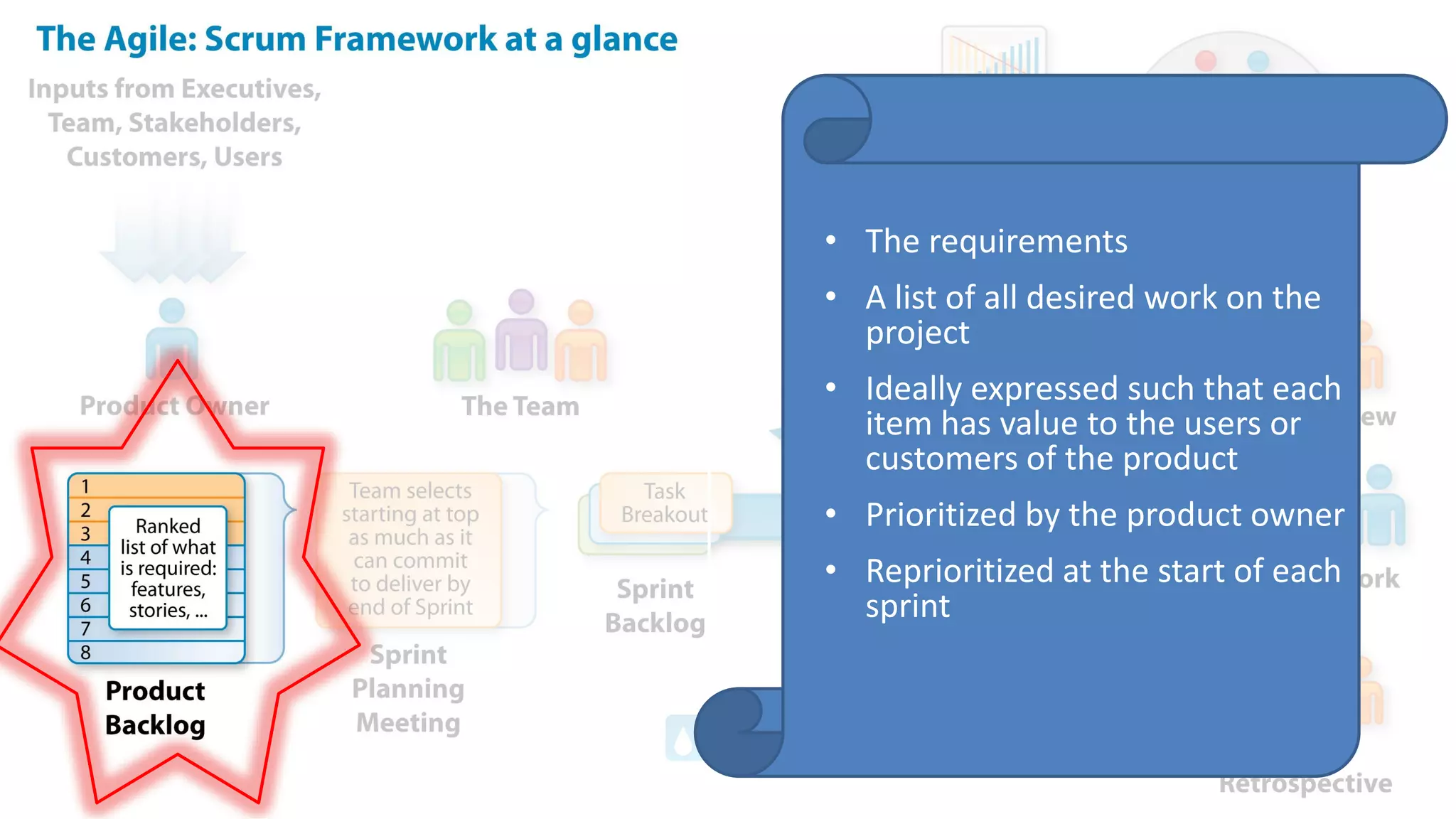
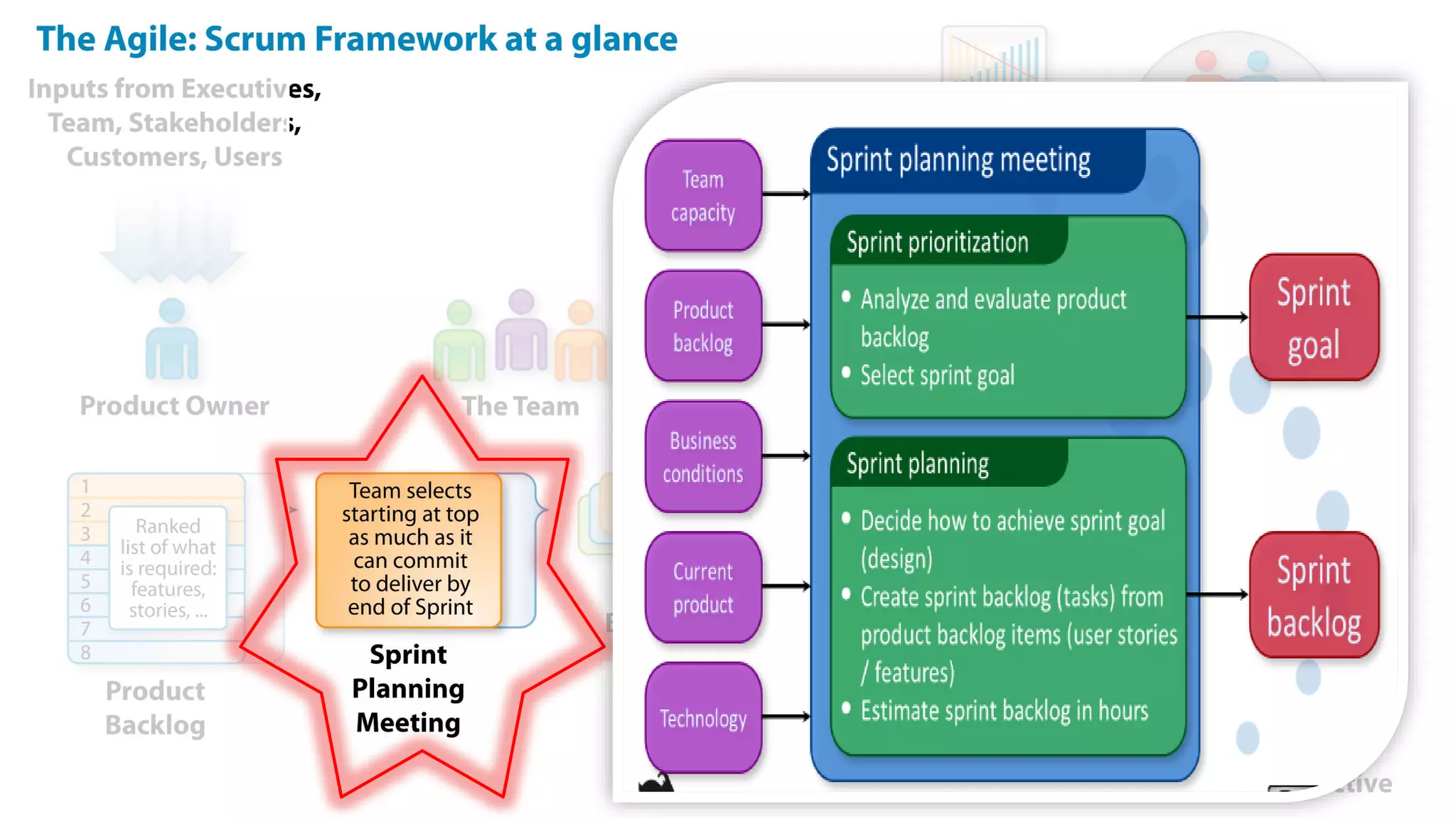
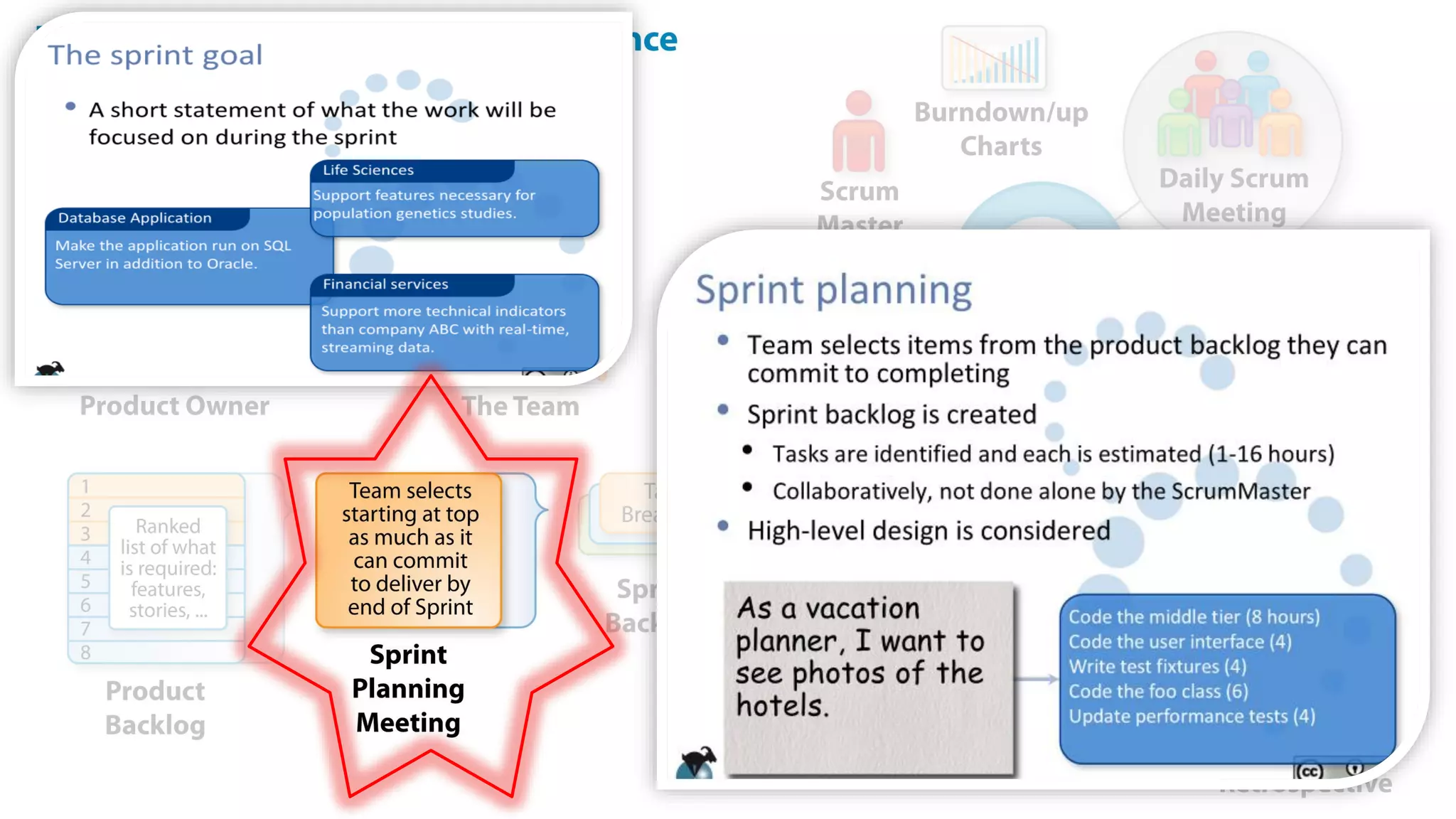
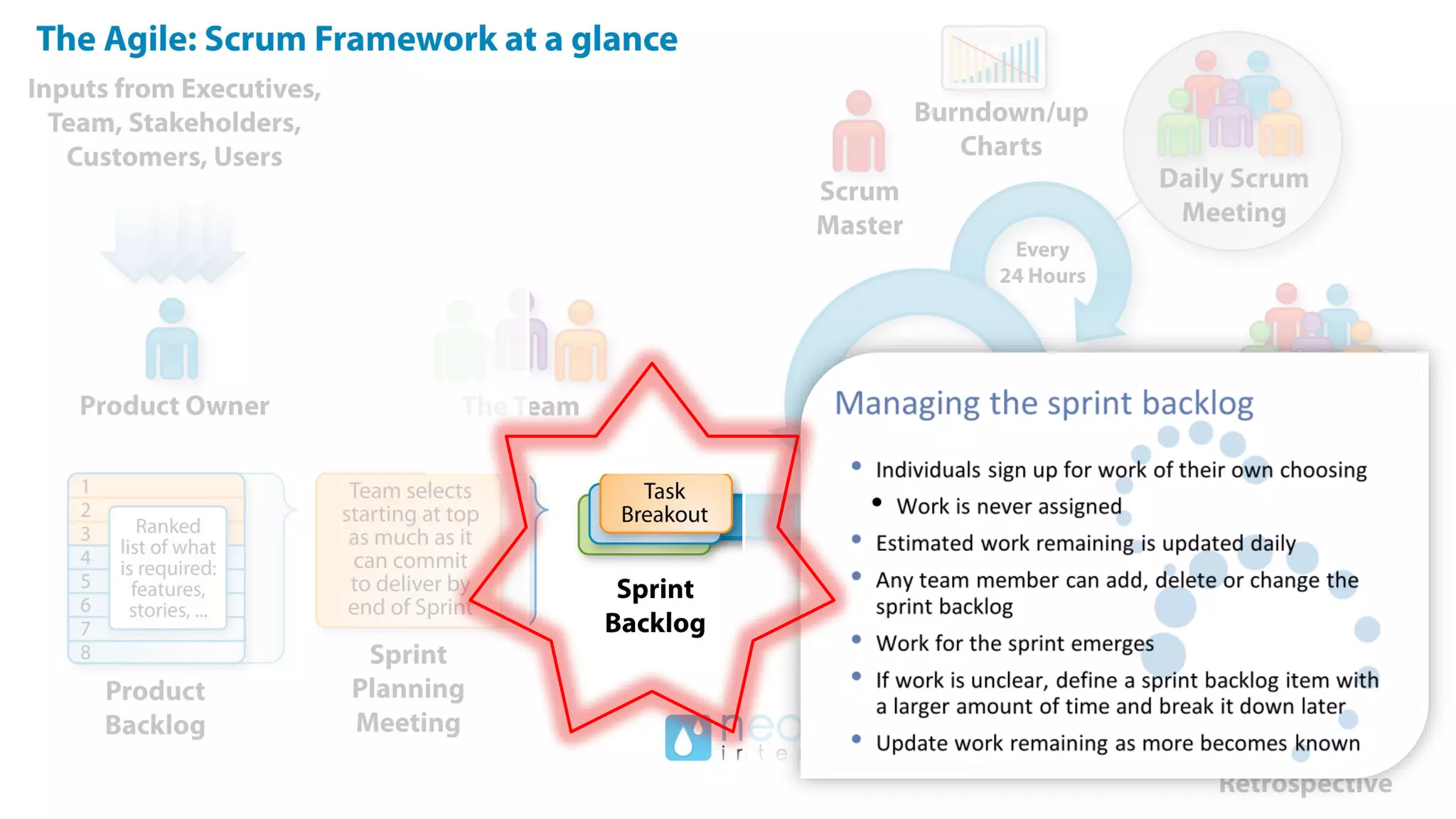
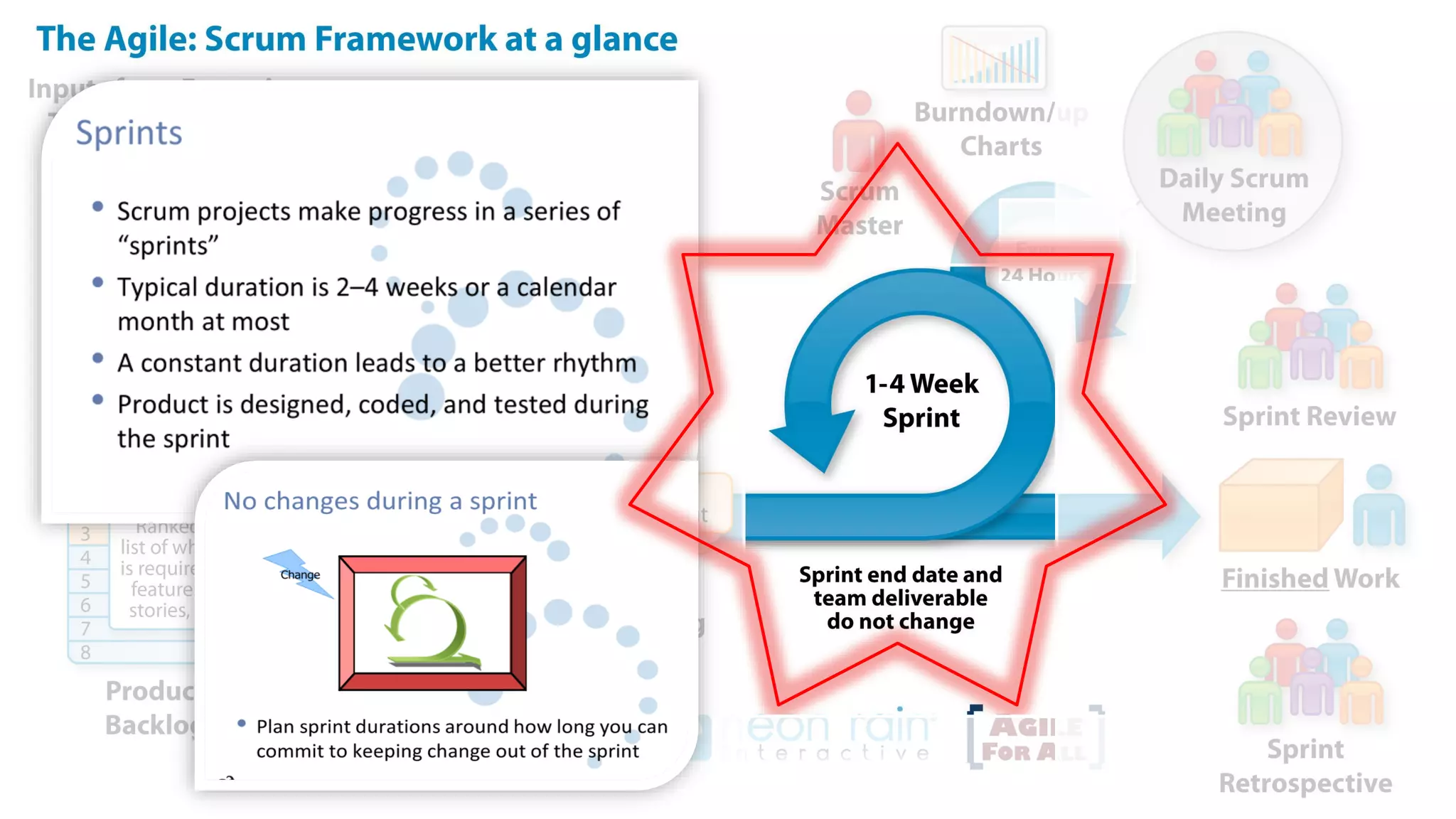
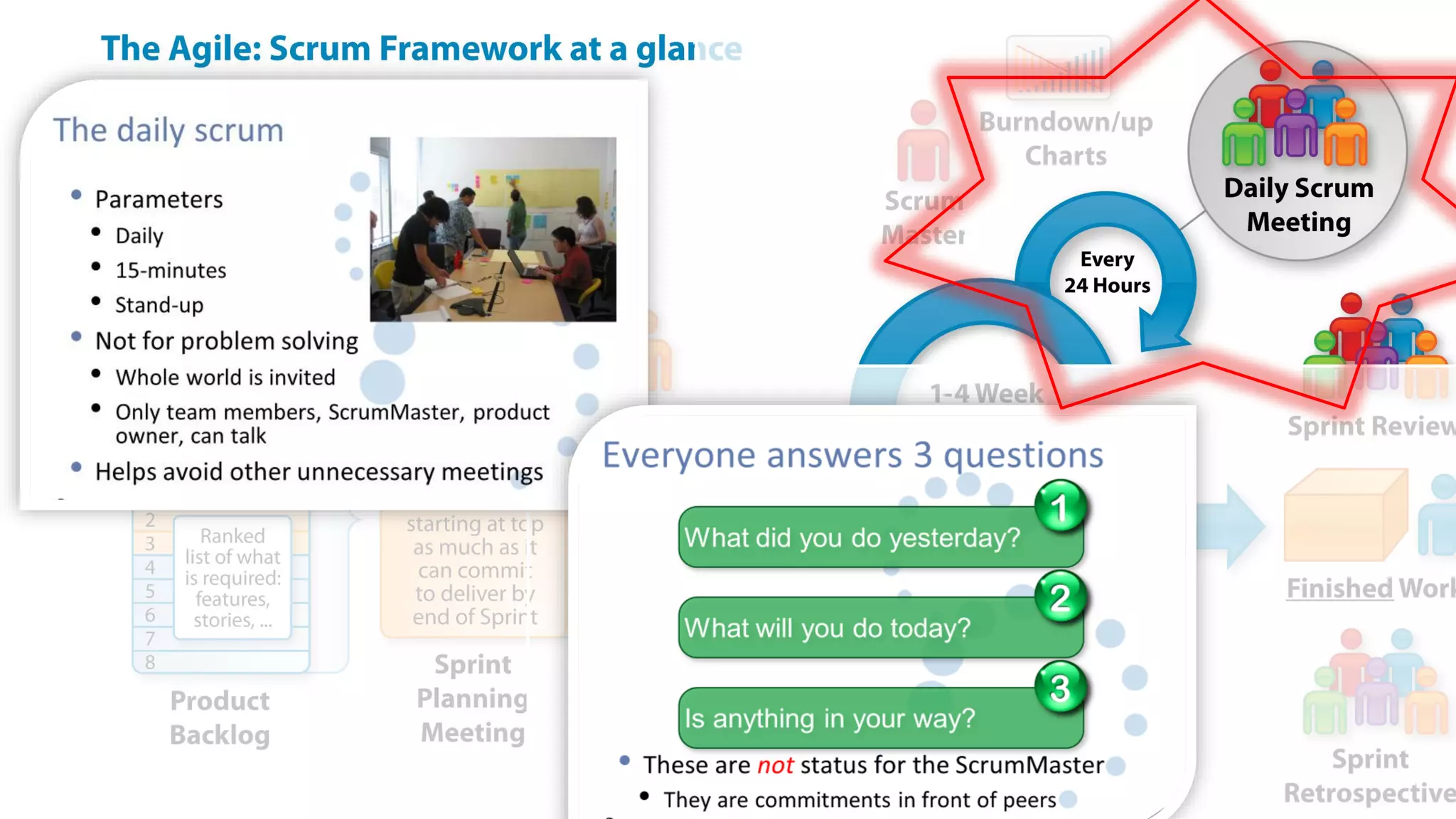
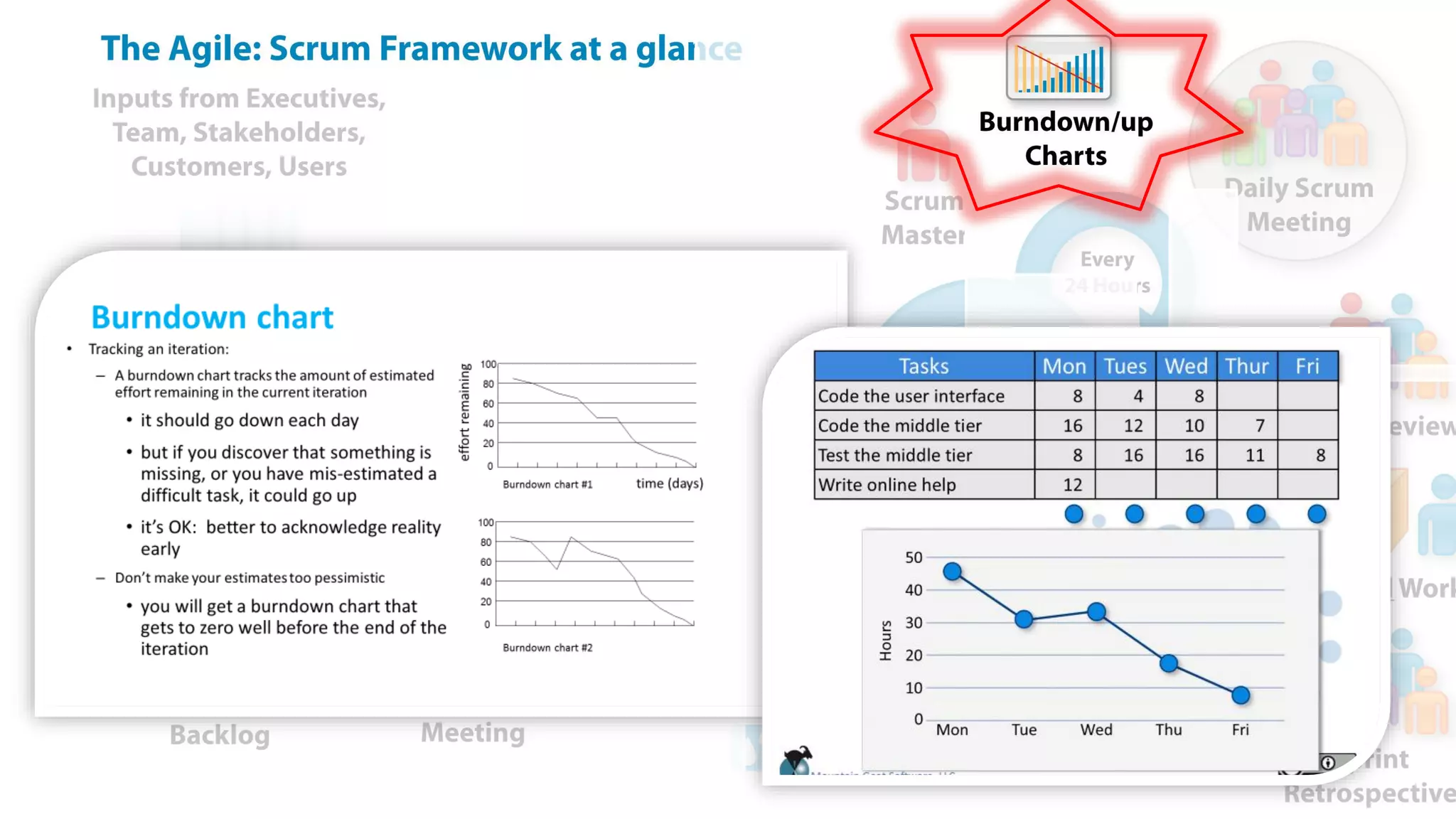
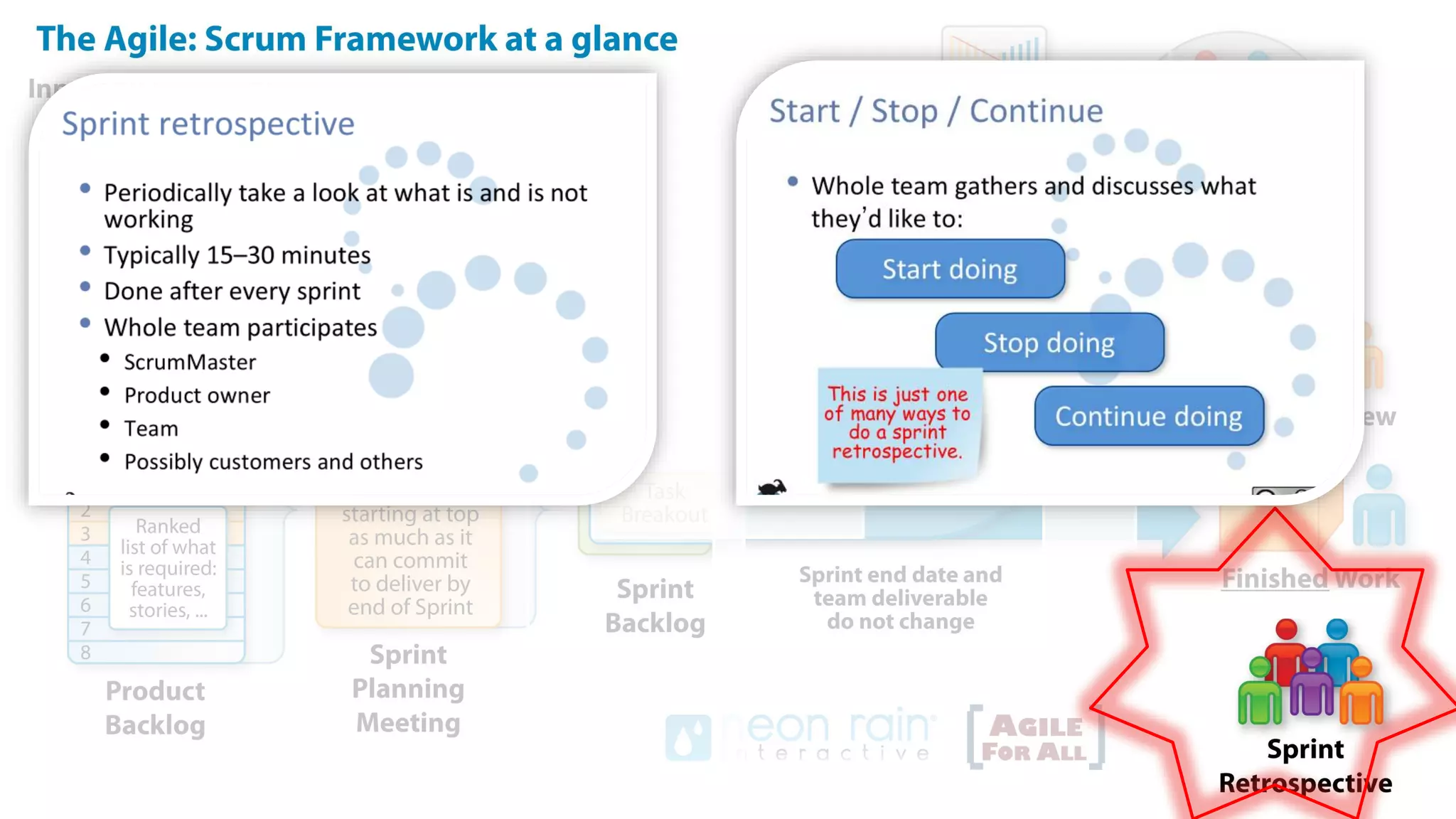
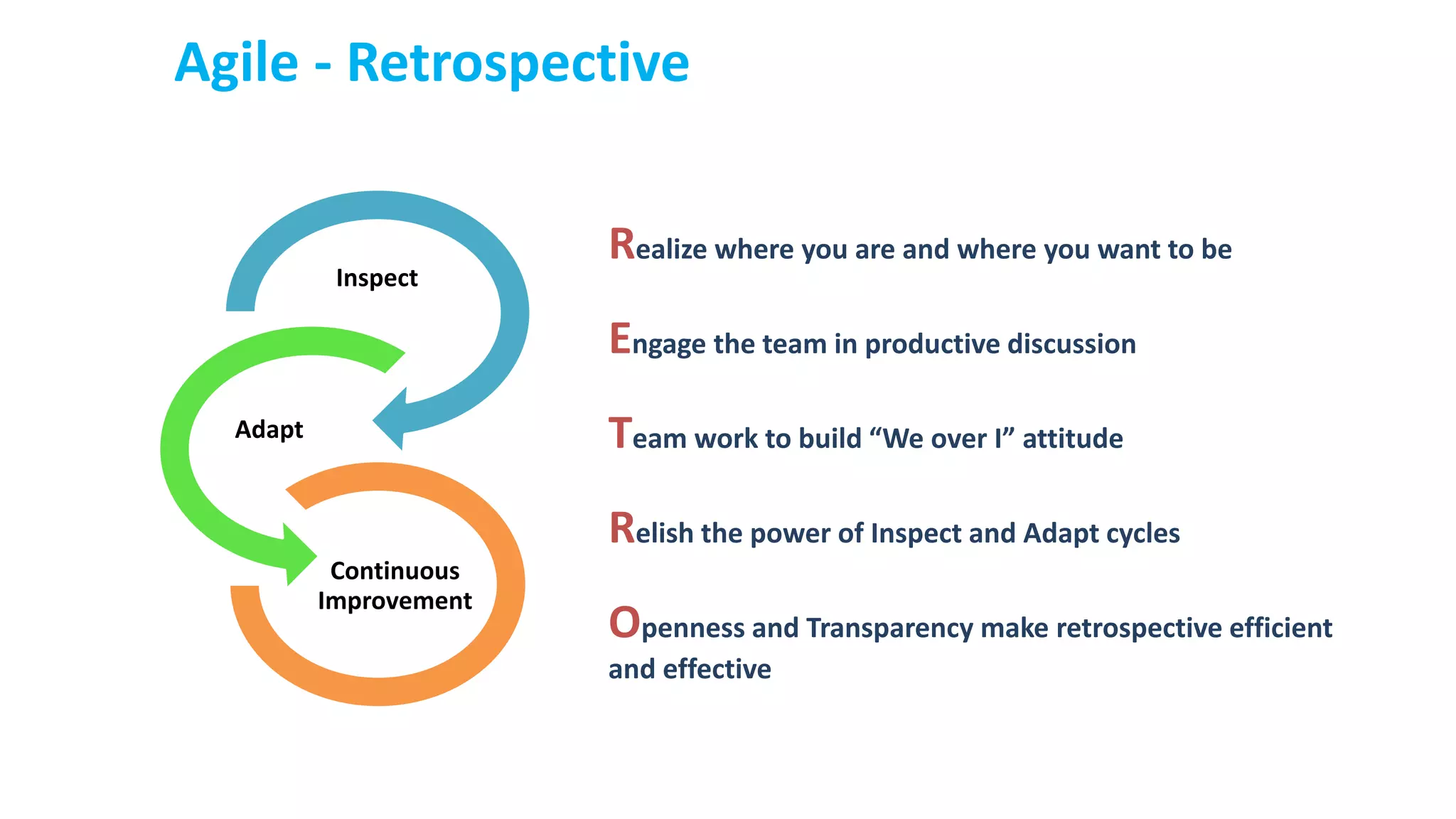
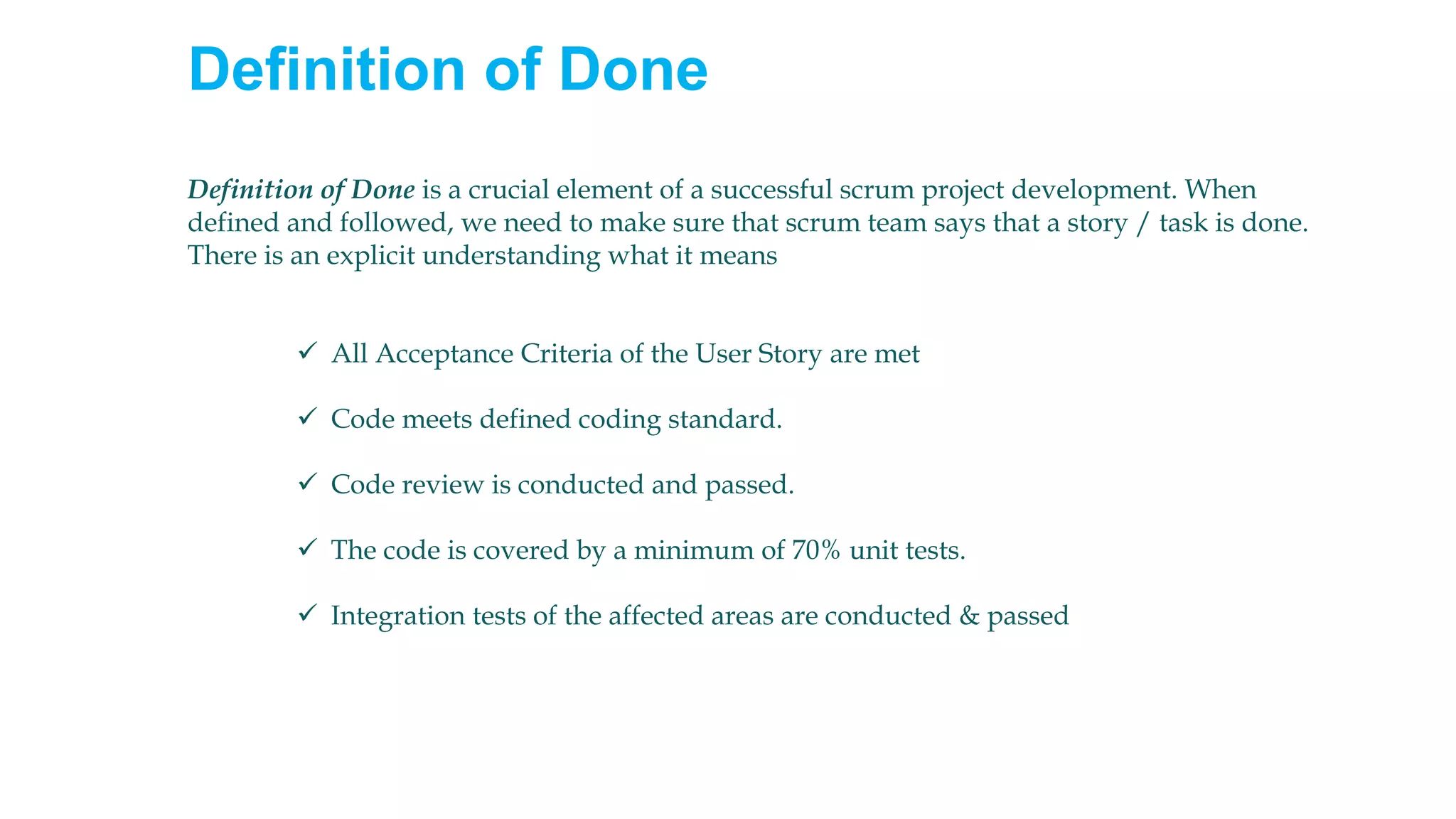
This document provides an introduction to Agile and Scrum methodologies. It begins with an overview of the presenter and their experience. It then contrasts the traditional waterfall approach with Agile, noting that Agile values individuals, collaboration, working software and responding to change. The Agile manifesto principles are outlined. Scrum is introduced as an Agile framework, describing its roles, ceremonies and artifacts like sprints and product backlogs. Key Scrum concepts like user stories, estimation, and definitions of done are defined. The document concludes by noting that simply doing Agile iterations is not enough and that teams must embrace Agile values like collaboration and continual improvement.