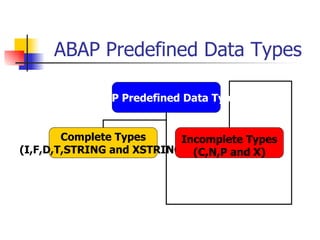
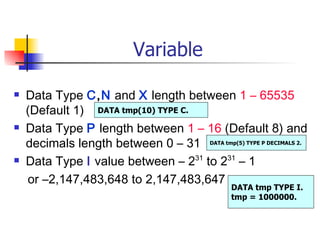
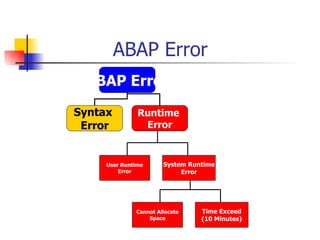
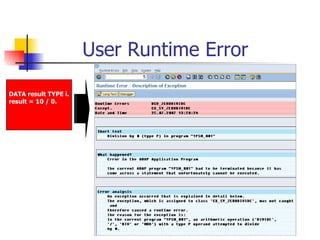
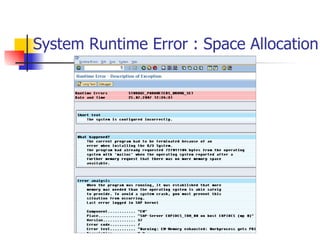
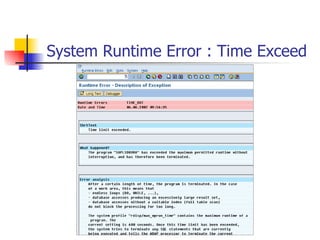
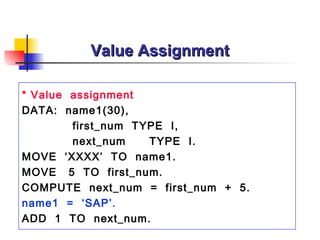
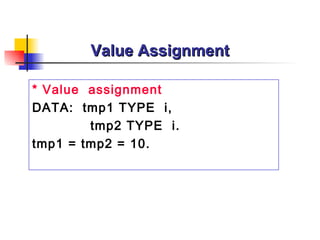
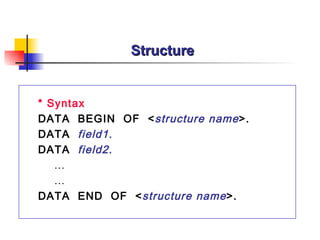
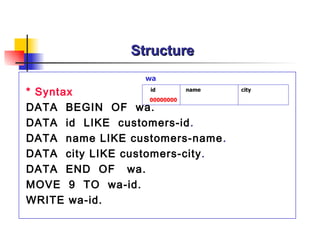
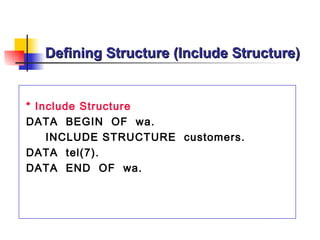
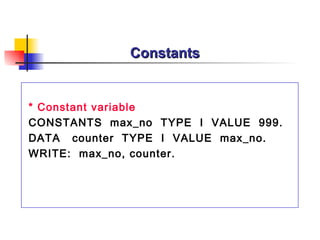
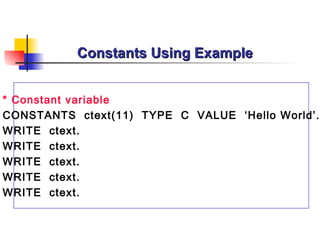
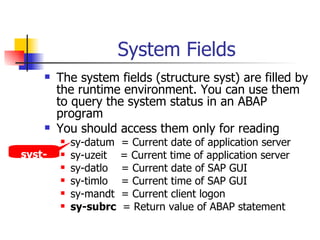
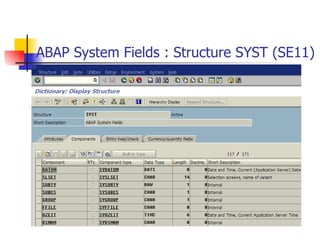
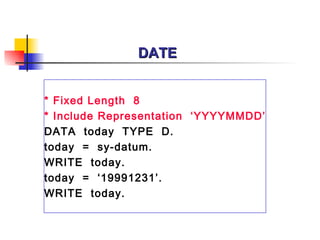
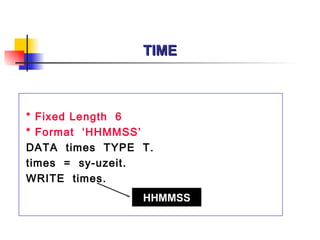
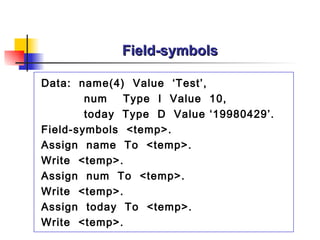
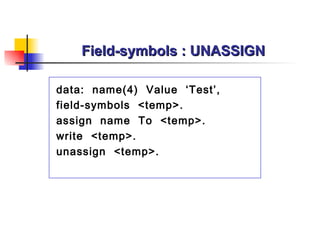
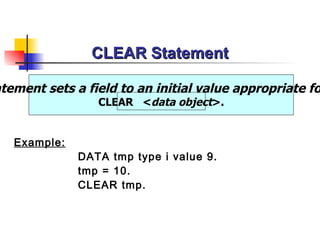
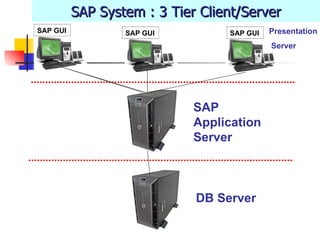
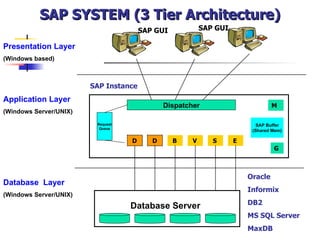
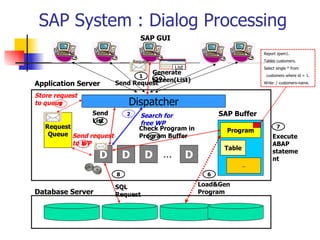
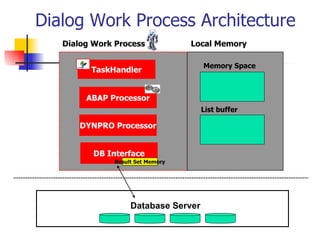
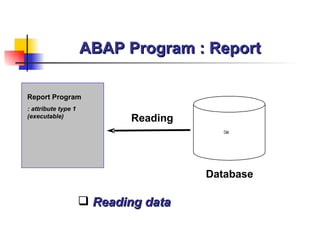
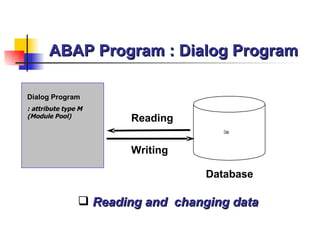
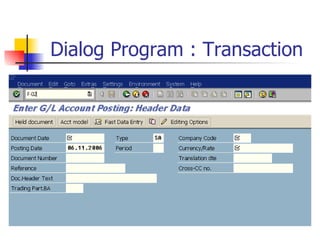
The document provides an overview of ABAP programming and outlines 6 chapters that will be covered, including introduction to ABAP, list processing, open SQL, event-driven programming, modularization, and debugging. It also describes the basic structure of an ABAP program and shows examples of ABAP statements, data types, and system fields.























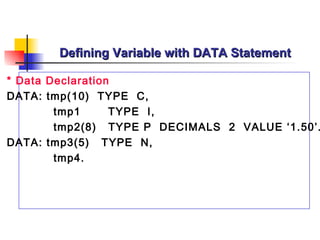
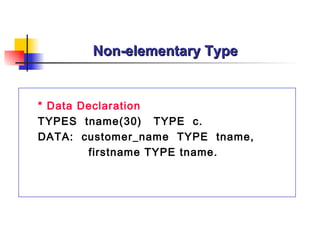
![Defining Variable with DATA Statement
* Syntax
DATA var[( length )] [Type type ] [Decimals number ].
DATA var LIKE Table-Field [VALUE initial value ].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/abapprogrammingoverview-090715081305-phpapp02/85/Introduction-to-ABAP-37-320.jpg)