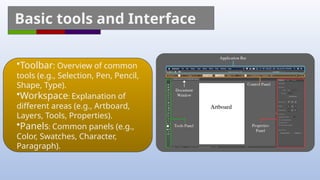
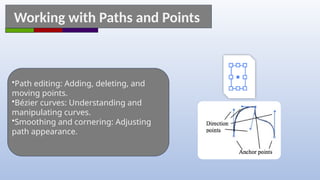
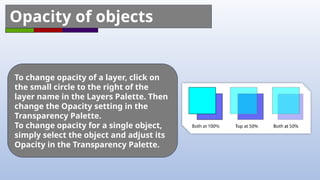
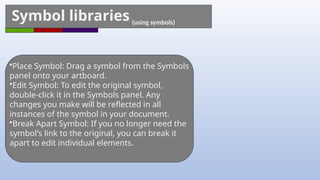
Adobe Illustrator is a vector graphics software primarily used for creating and editing illustrations, logos, and typography. Key features include scalable vector graphics, various drawing and color tools, and the ability to manage layers and symbols for efficient design. The document provides an overview of essential tools, techniques, and tips for effectively using Illustrator.