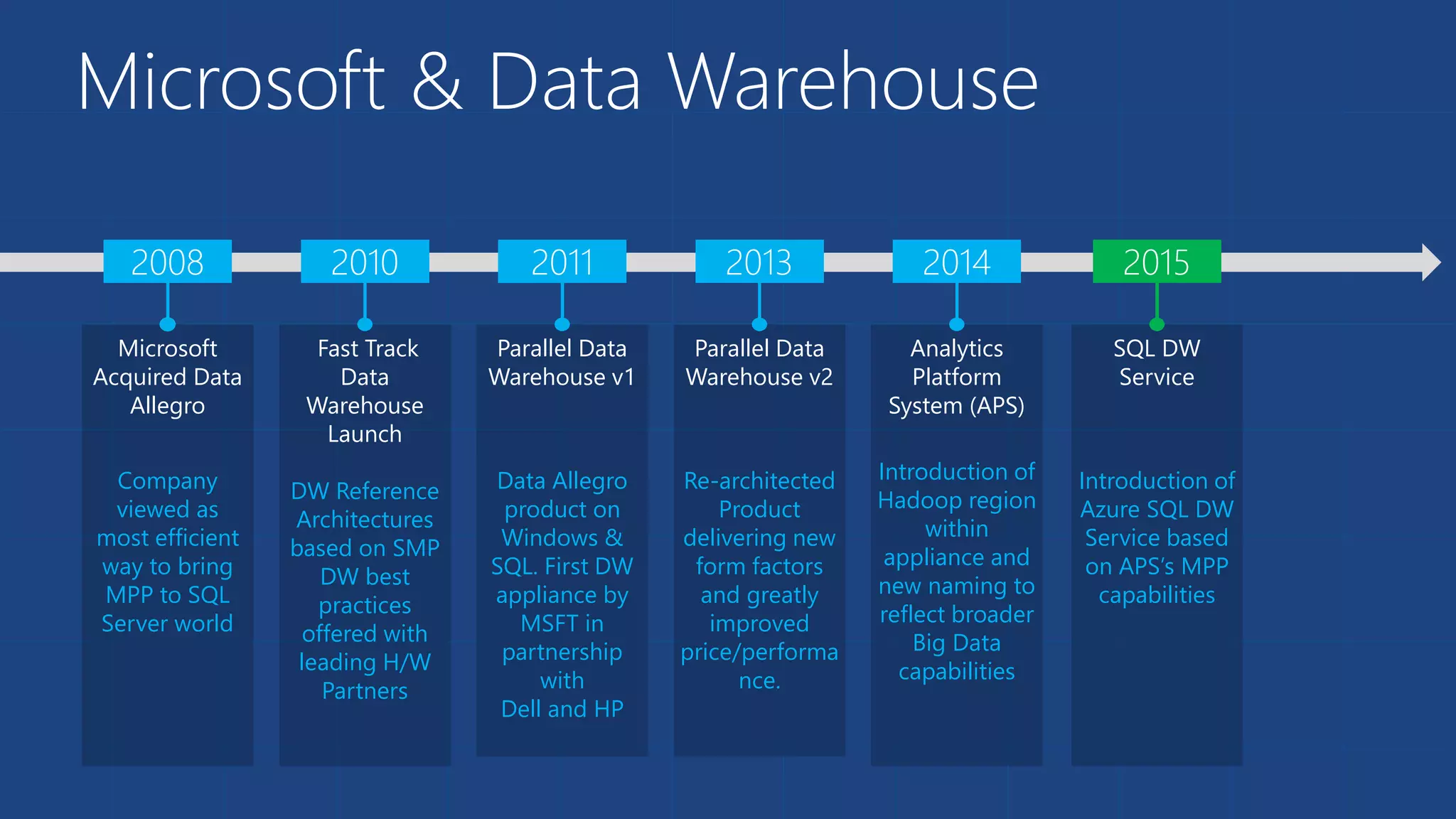
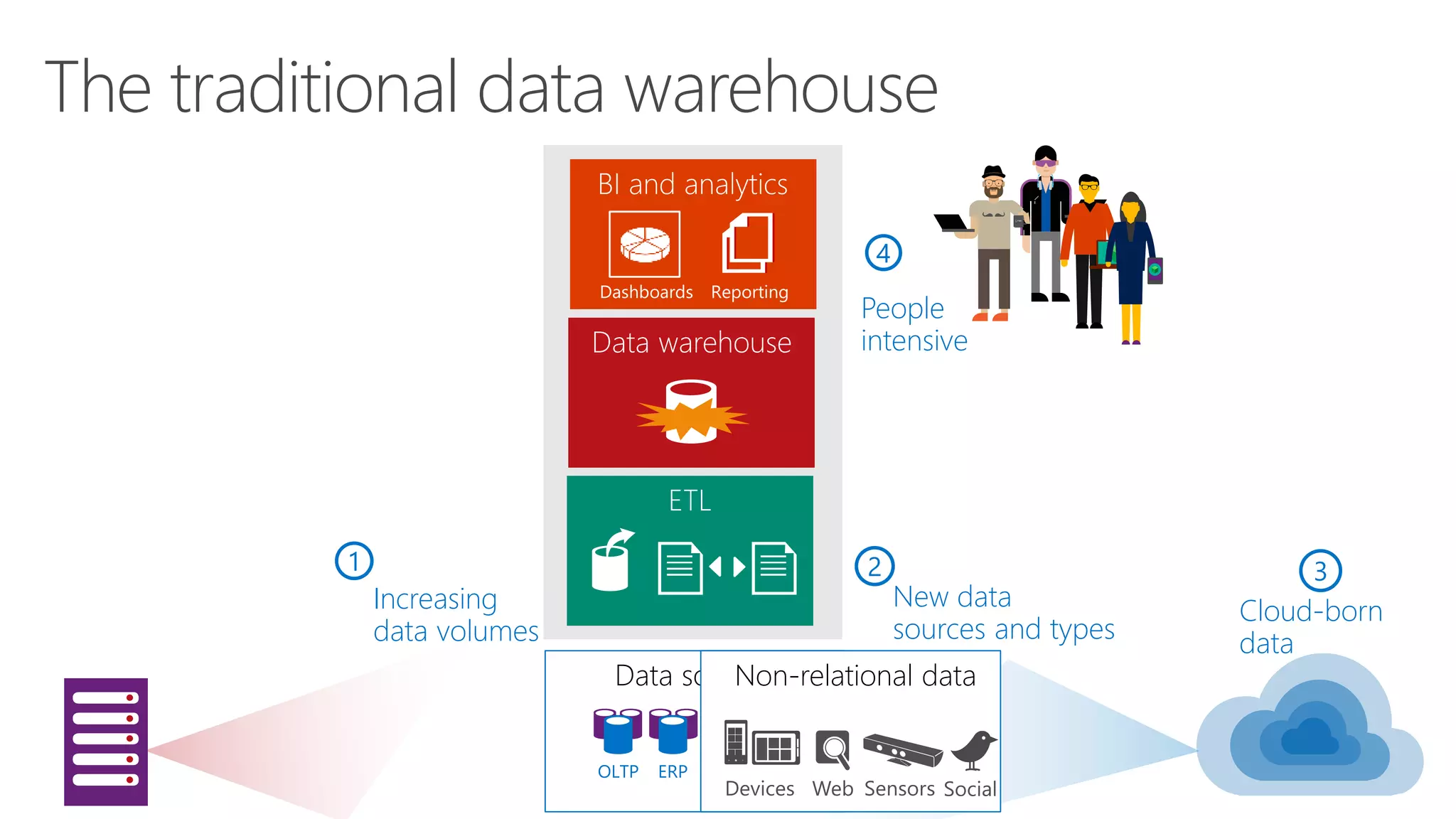
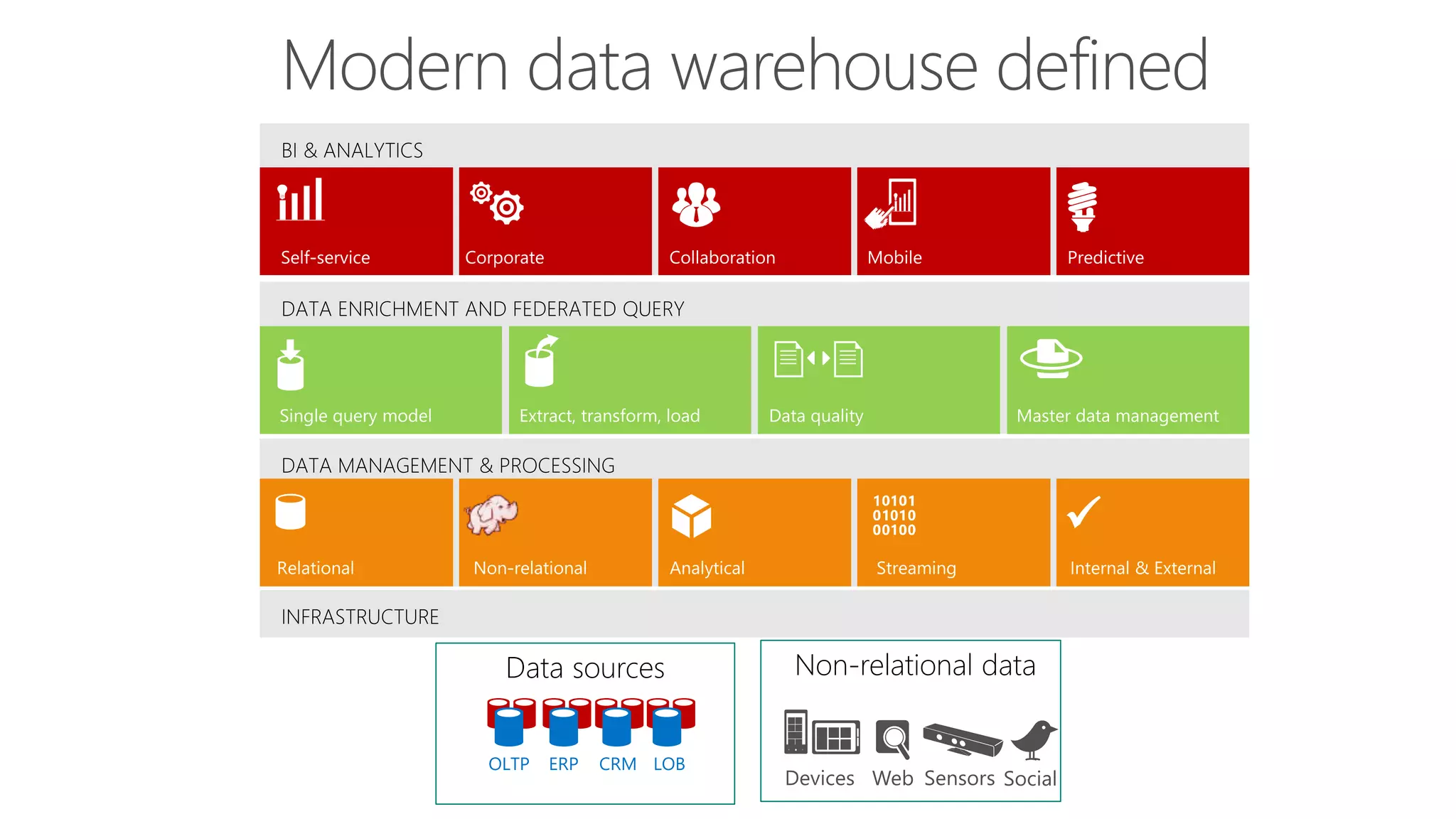
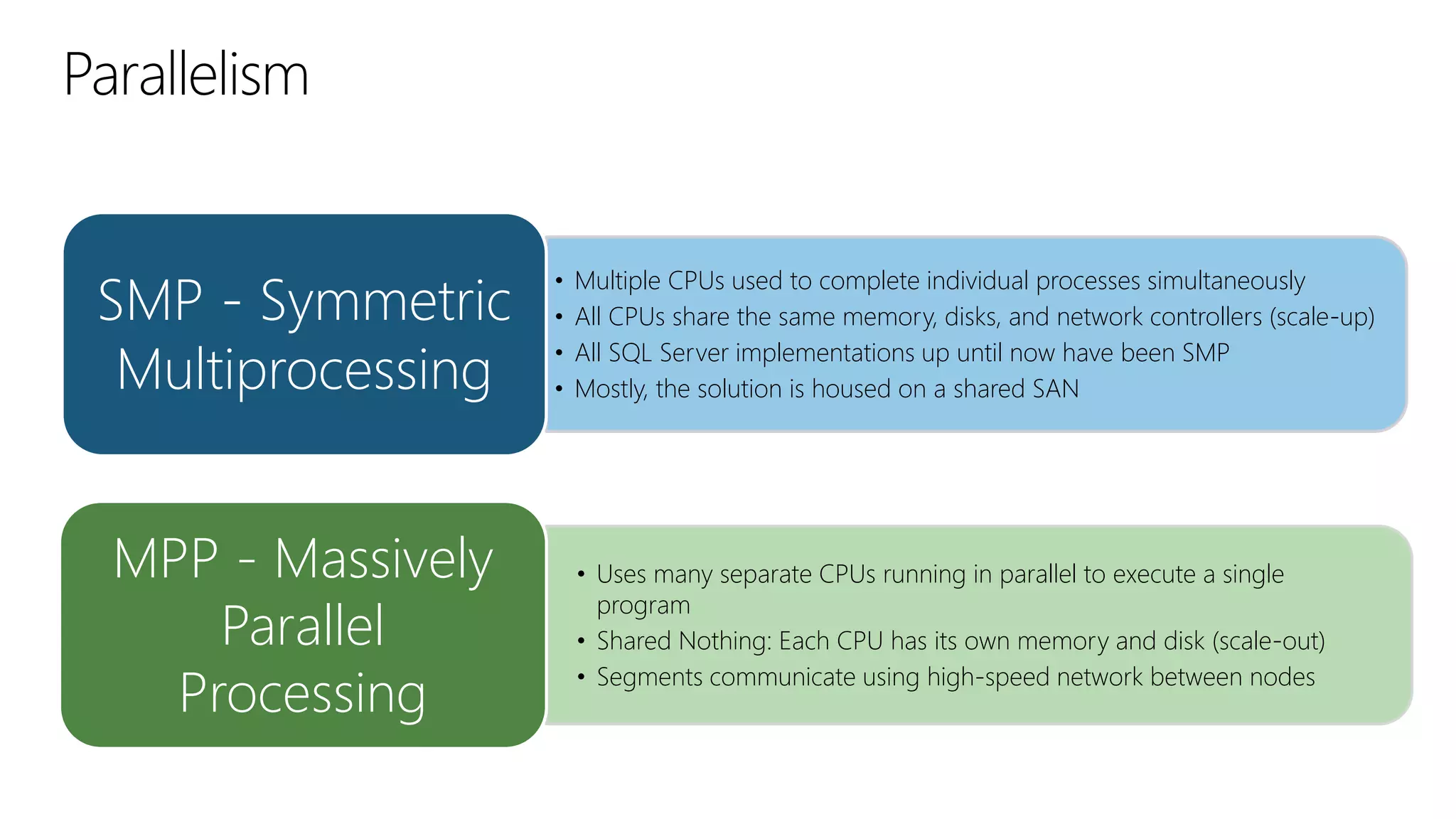
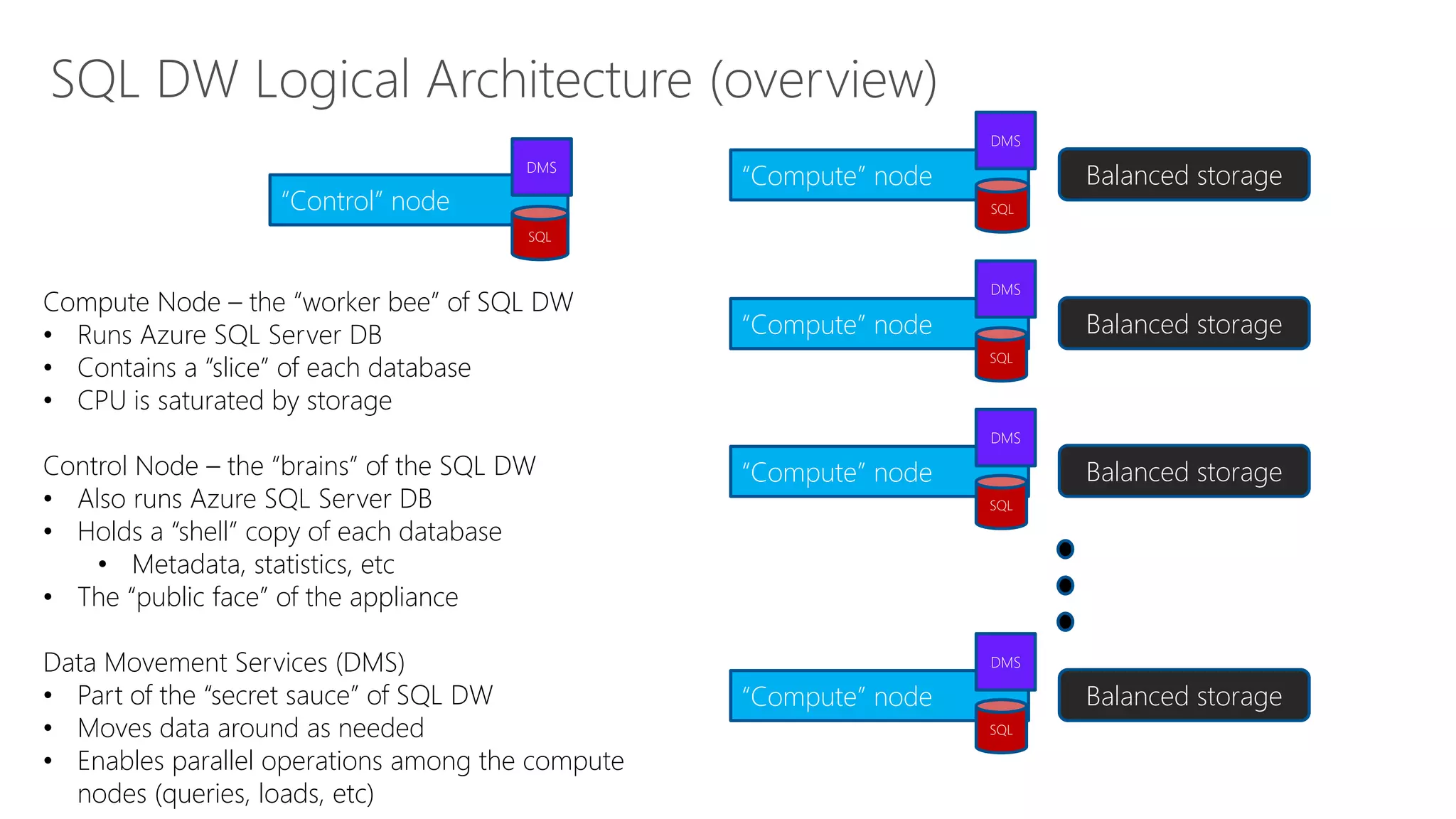
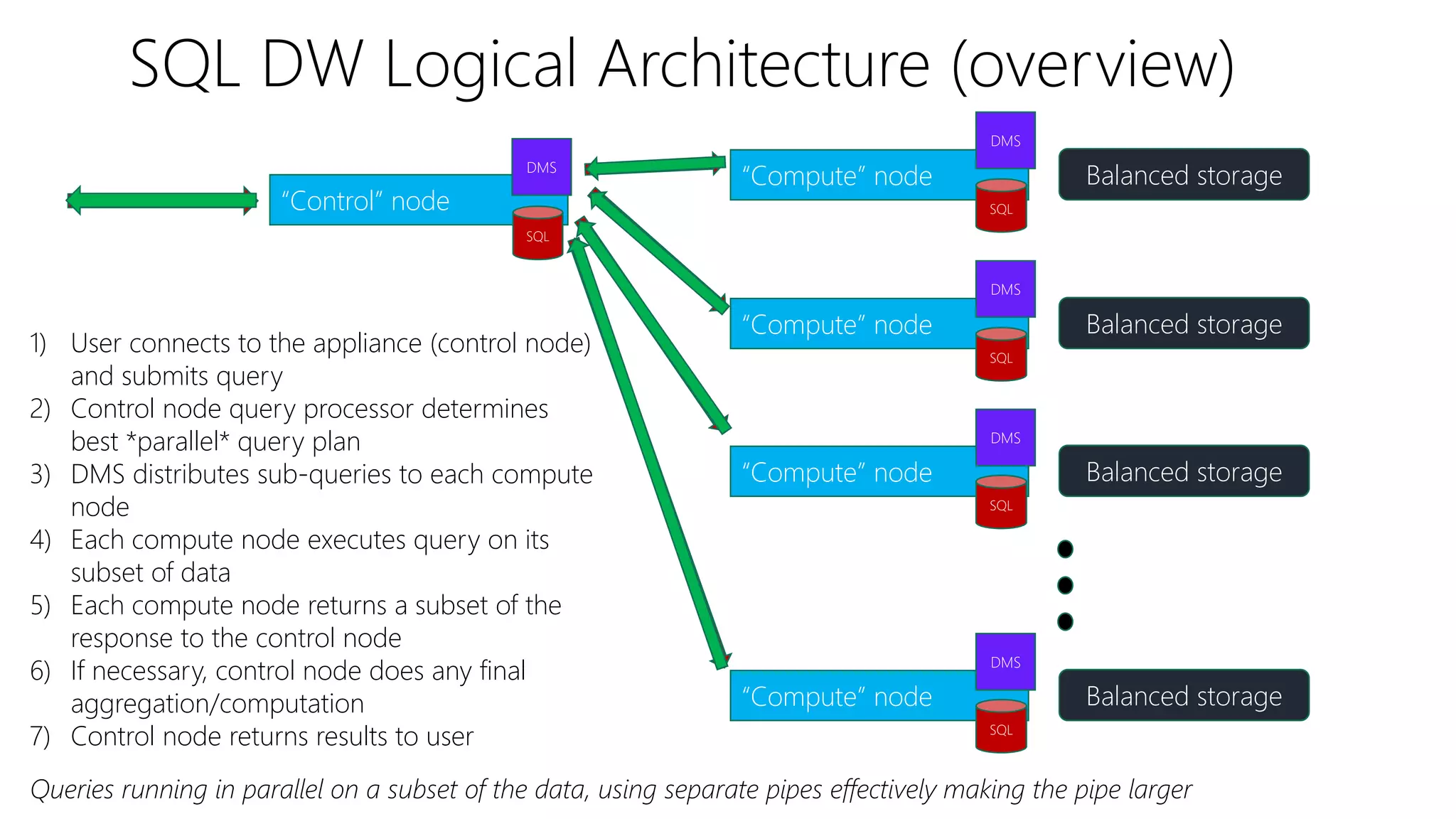
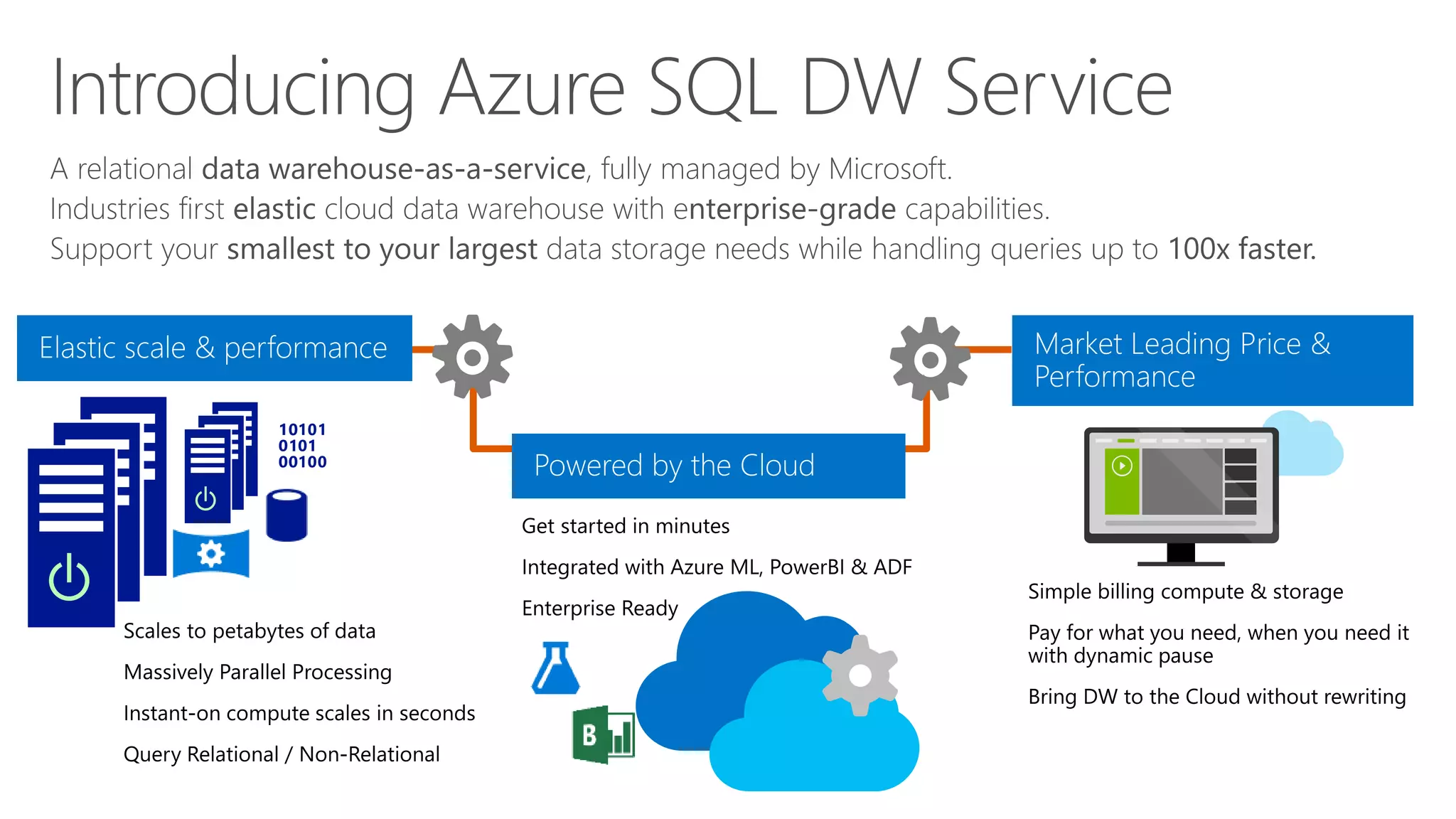
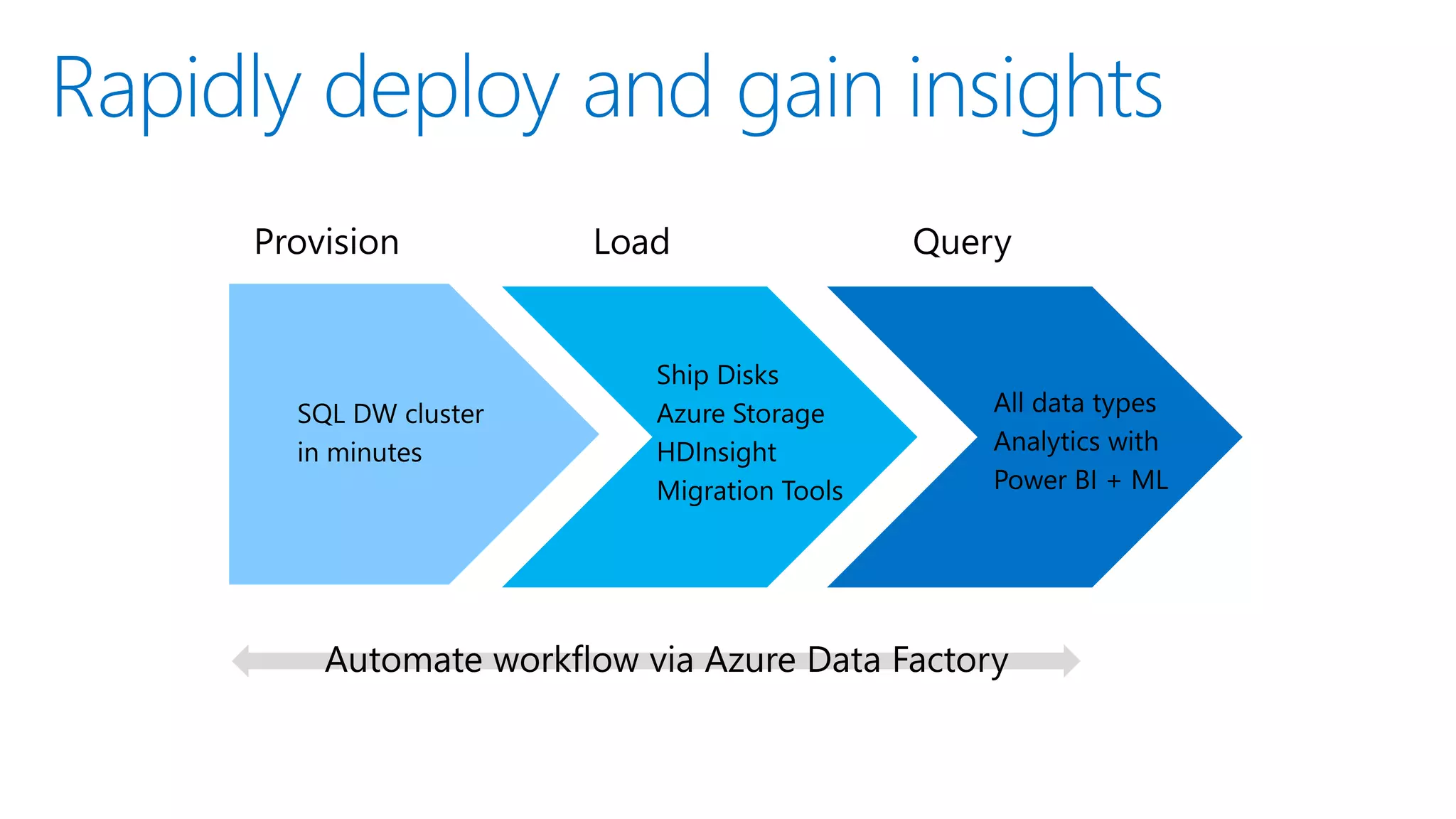
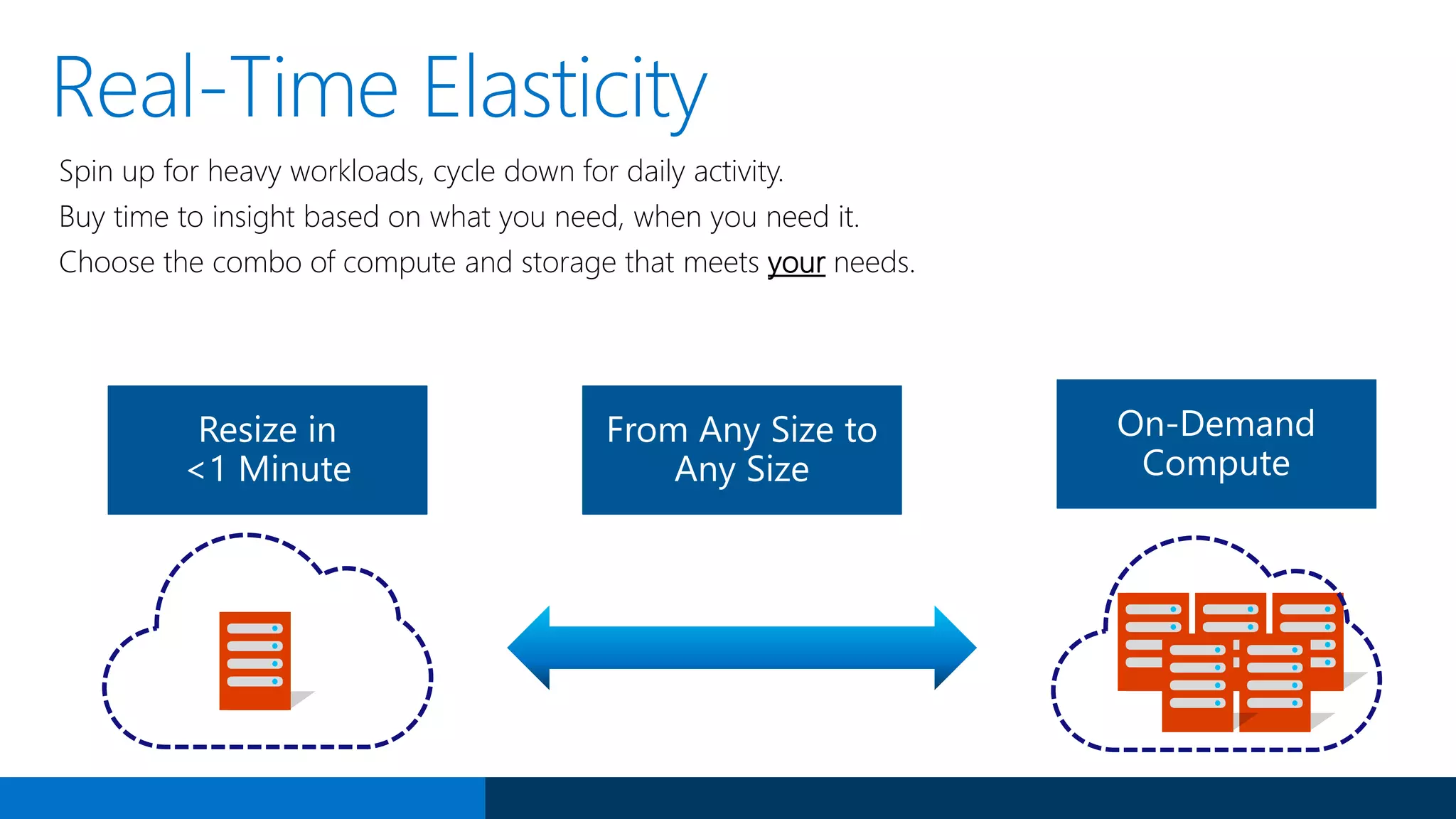
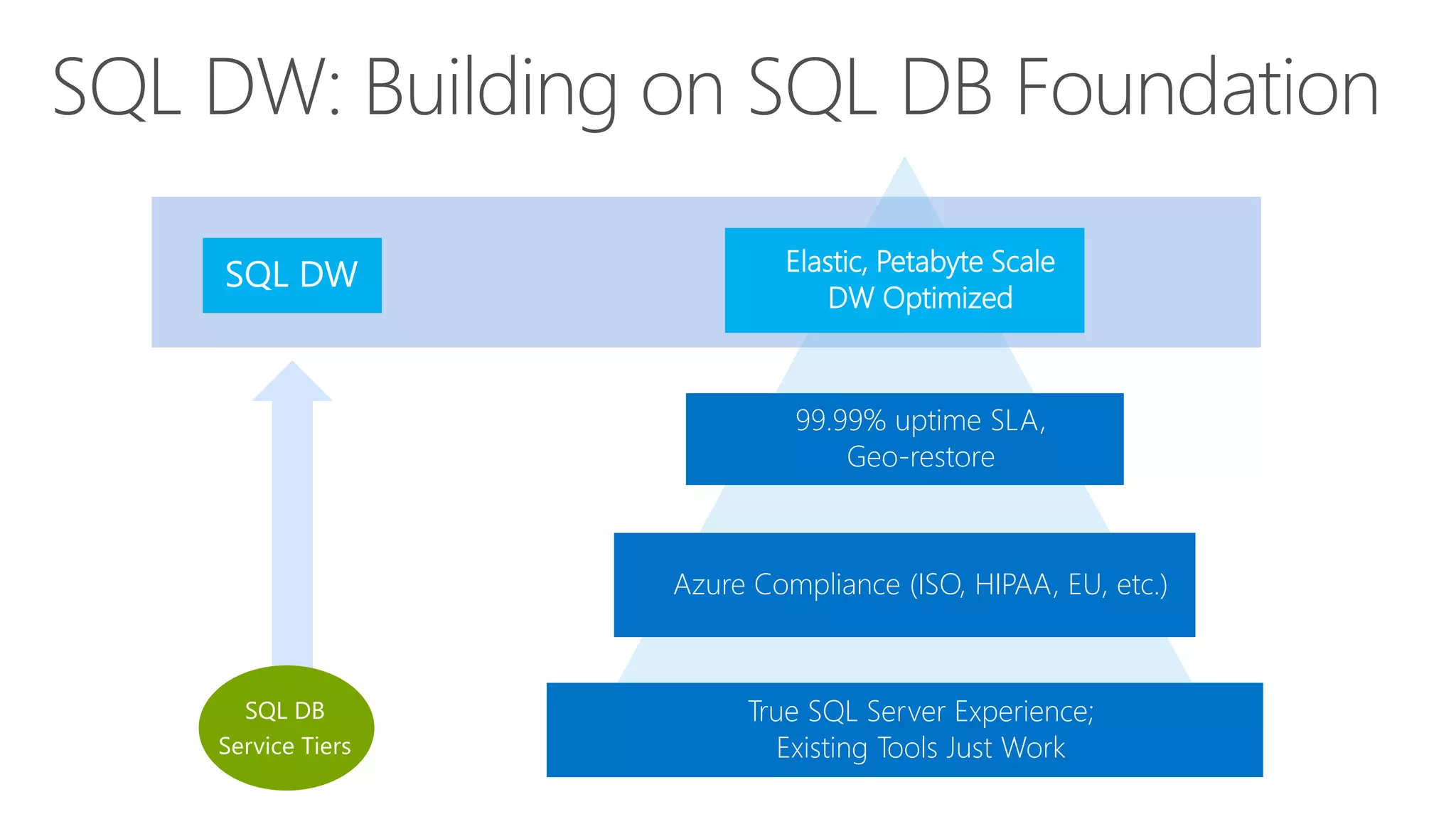
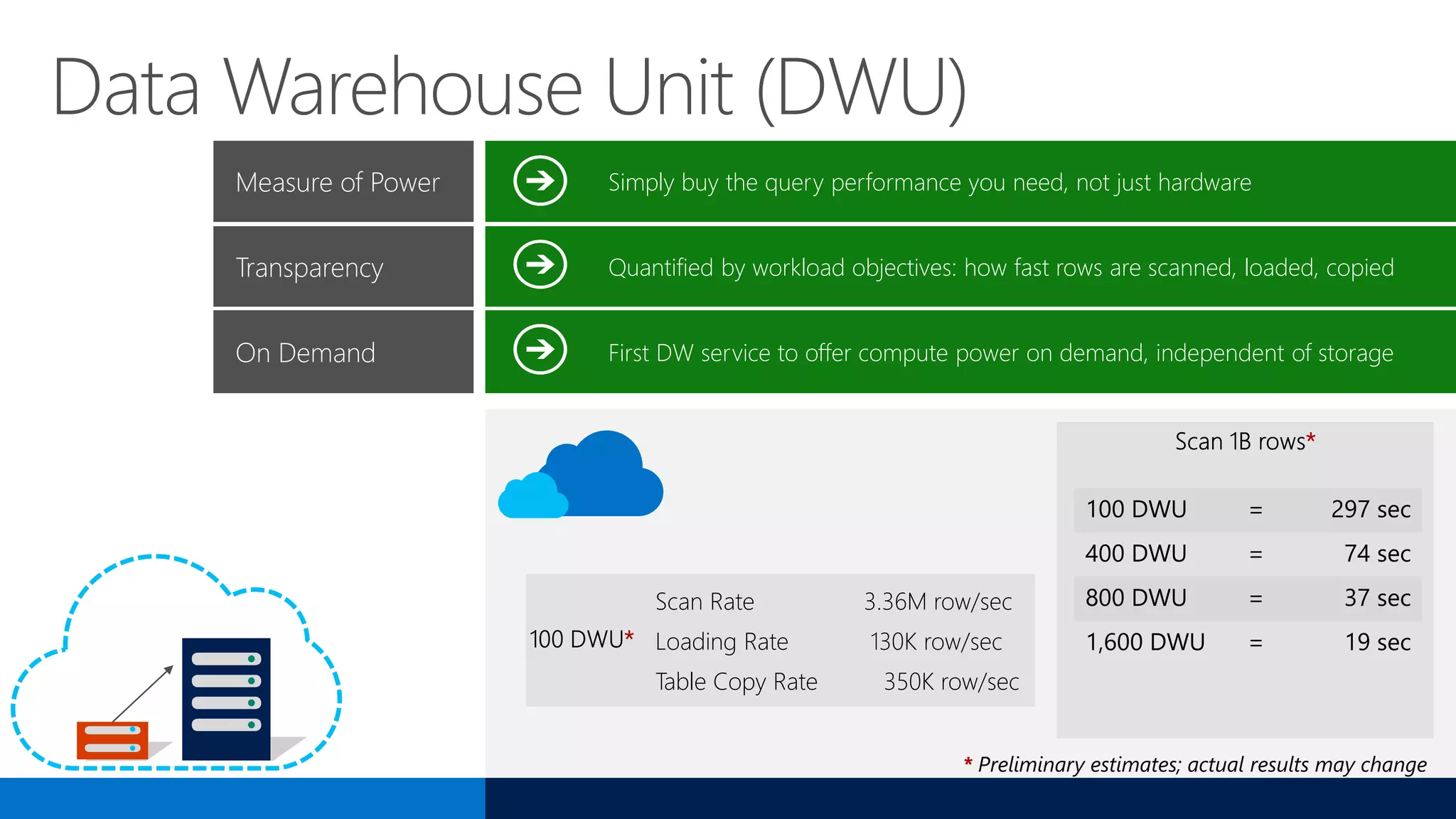
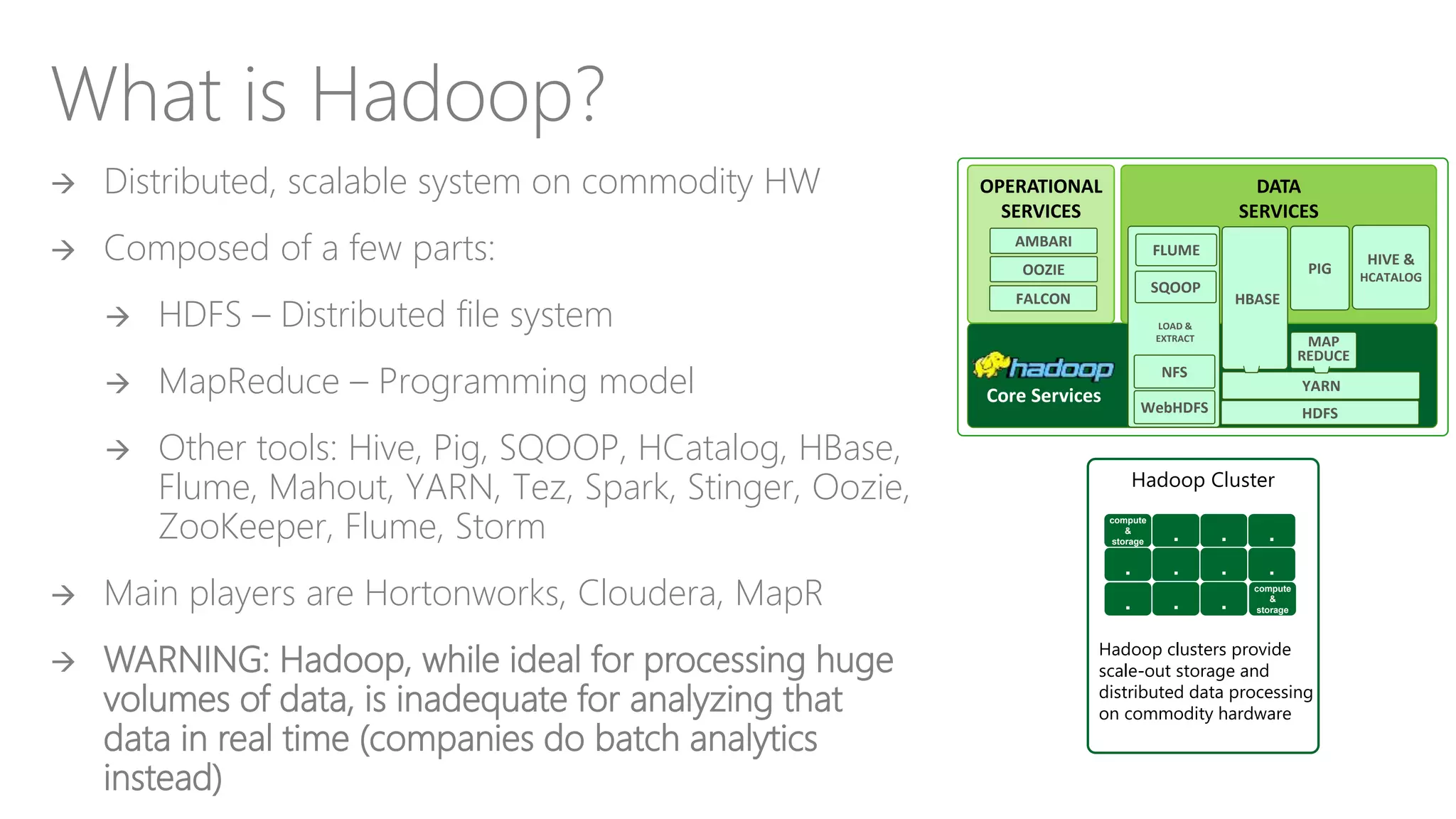
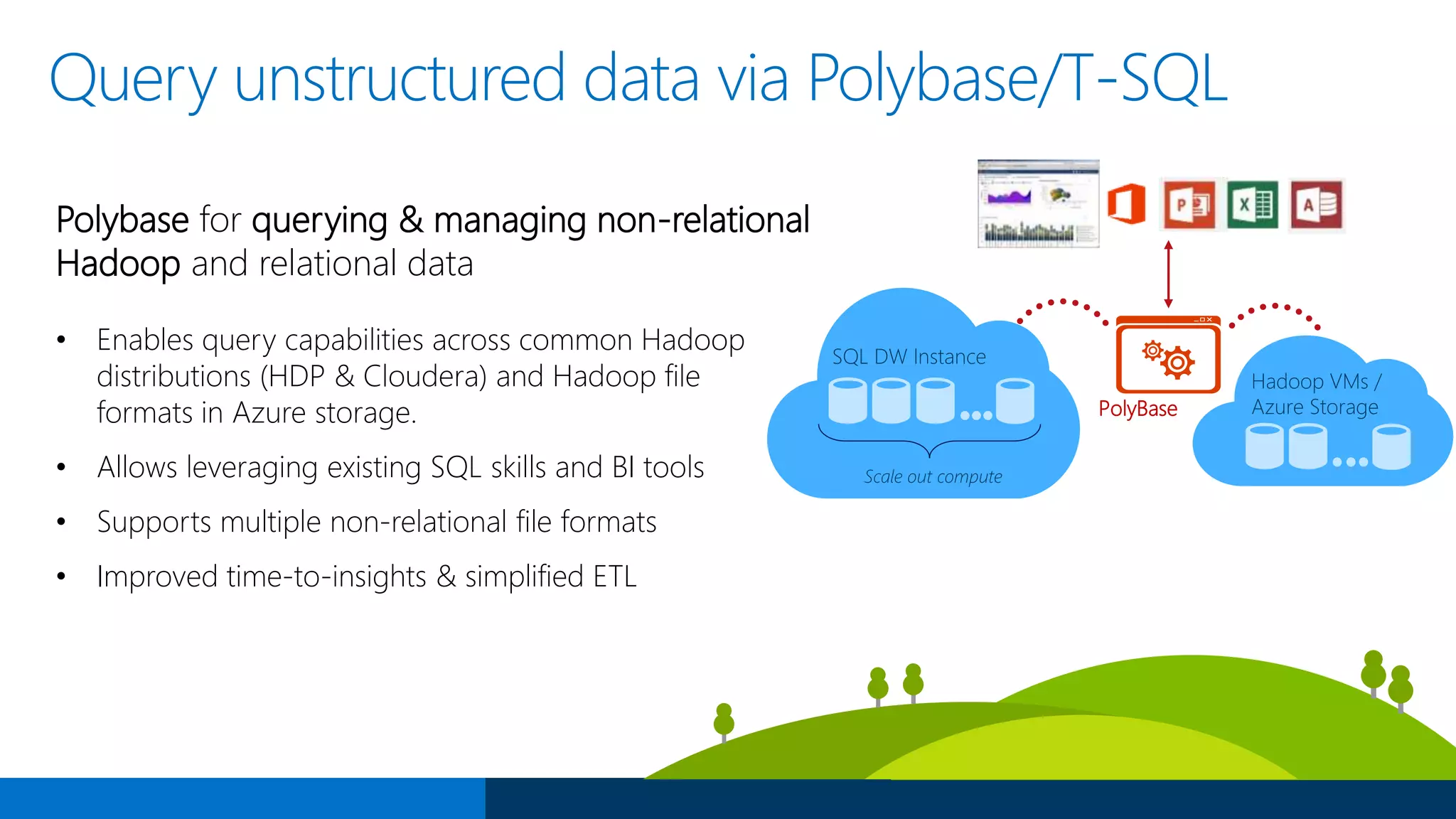
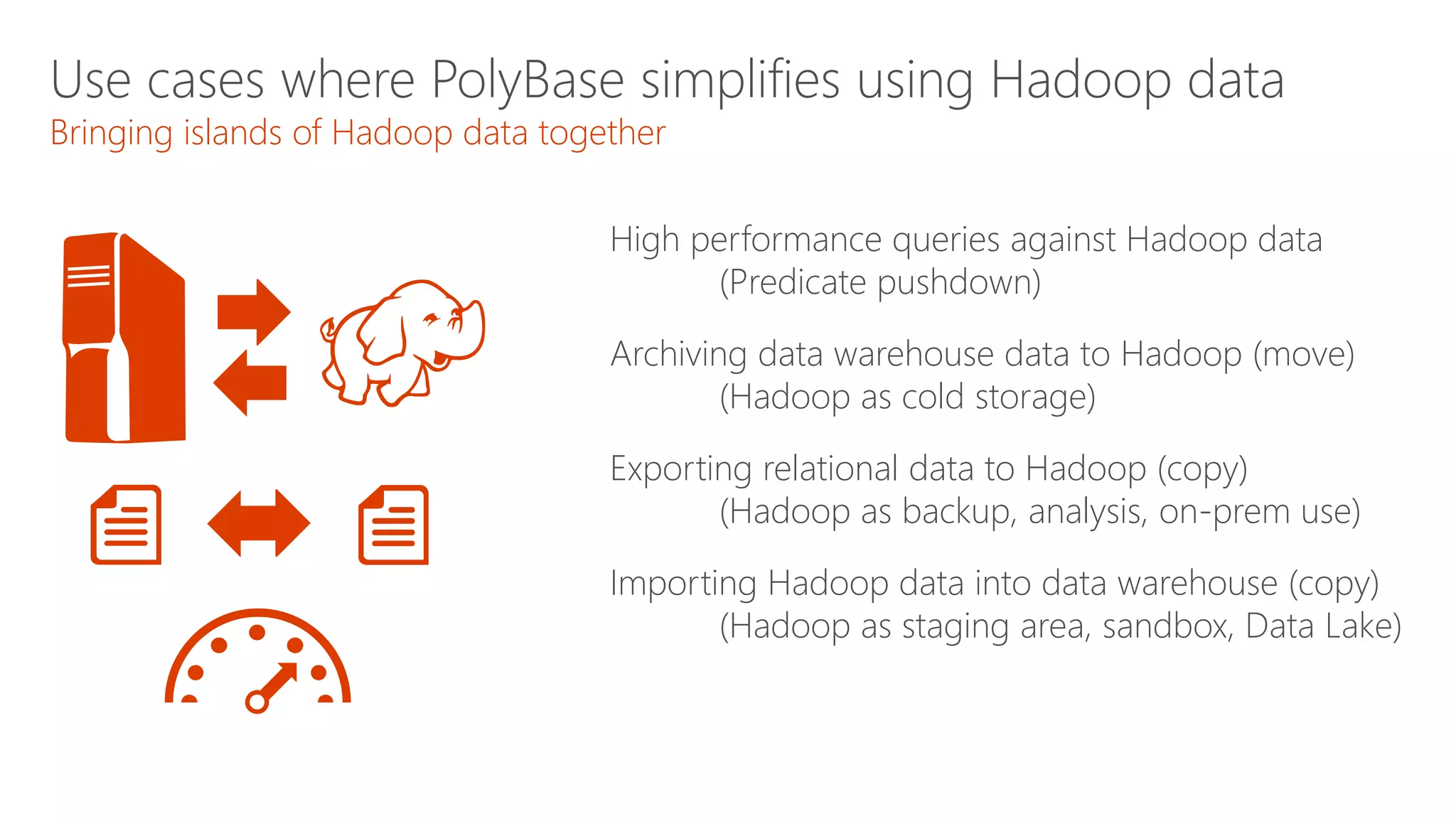
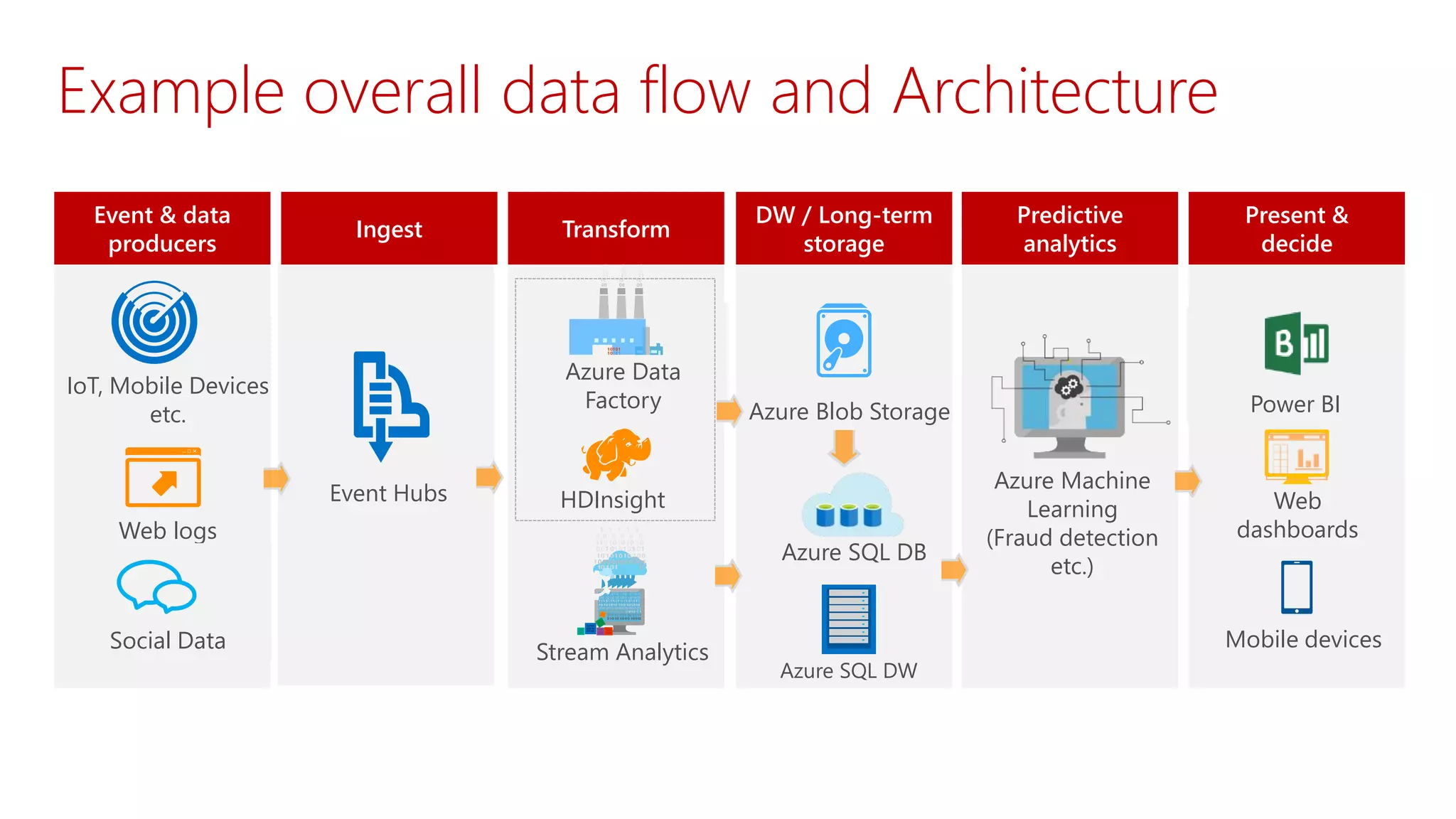
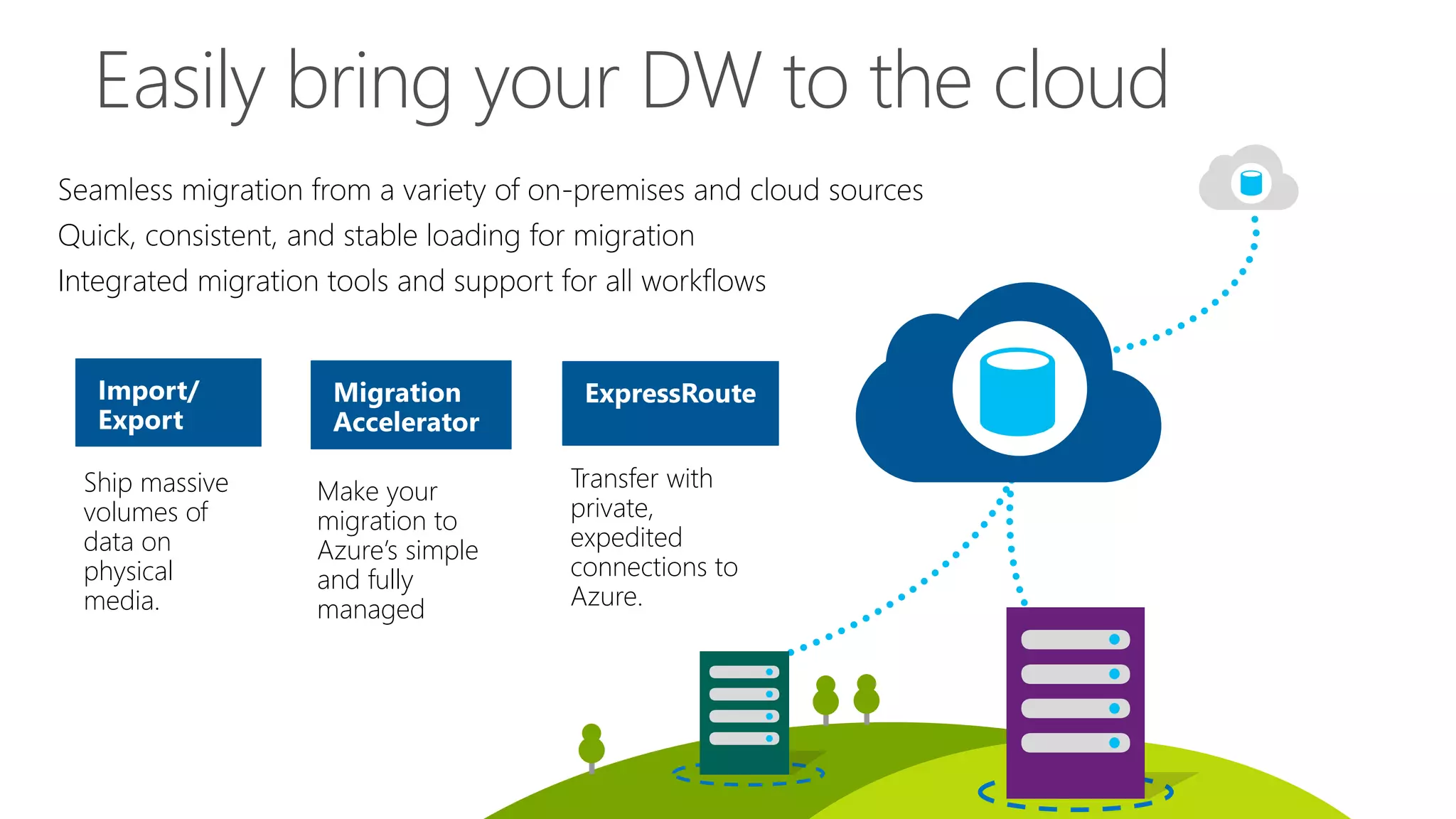
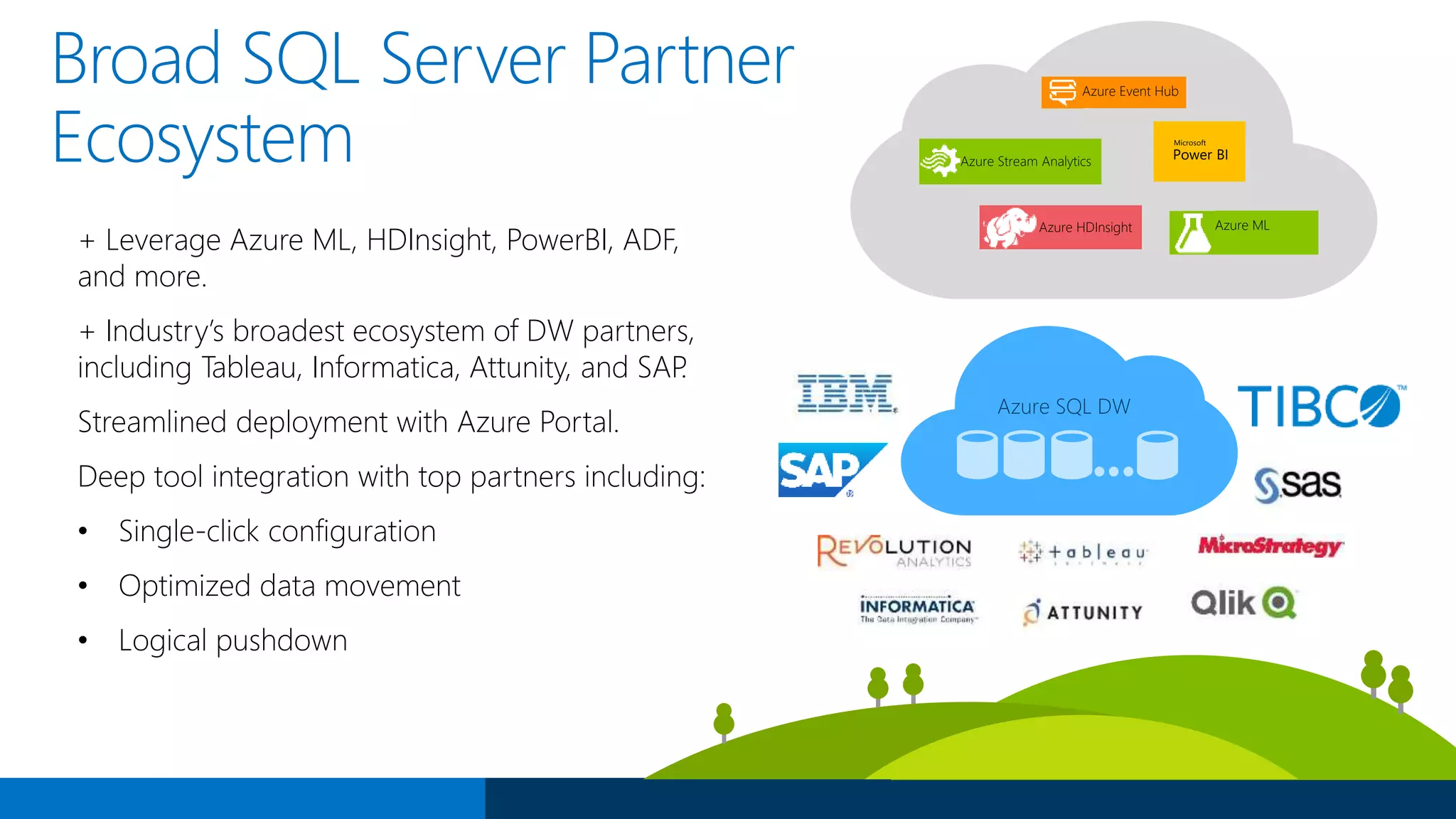
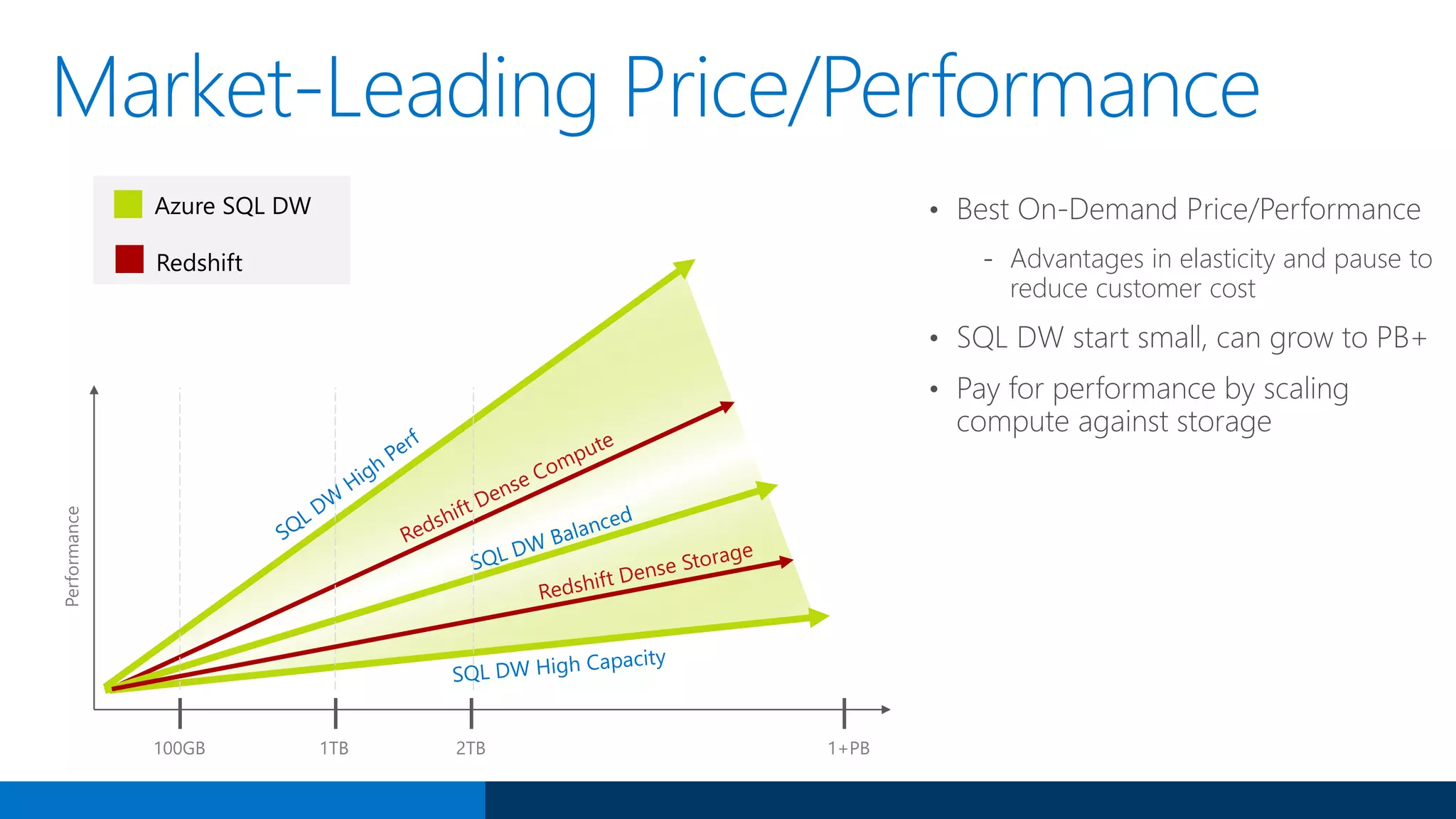
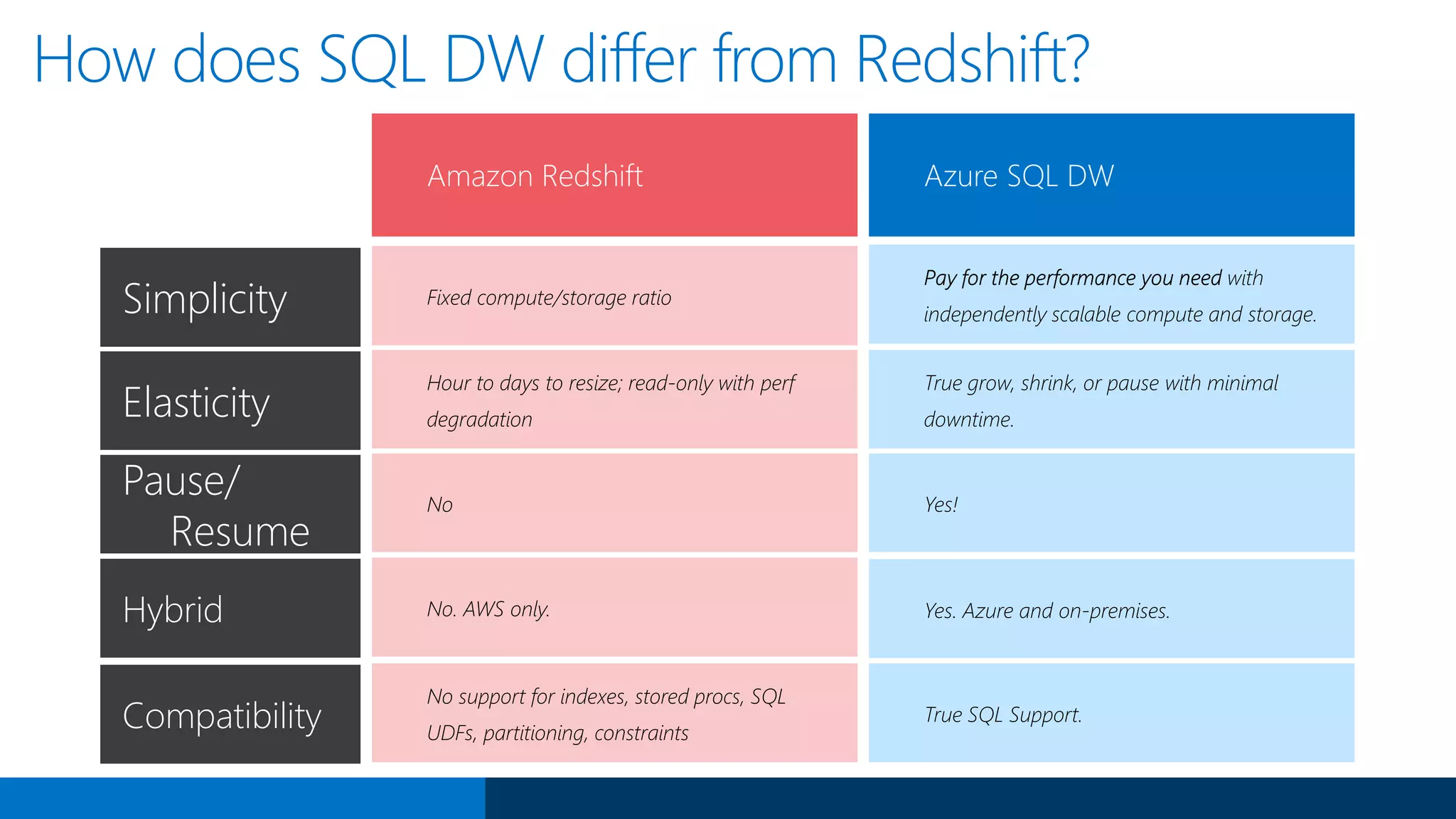
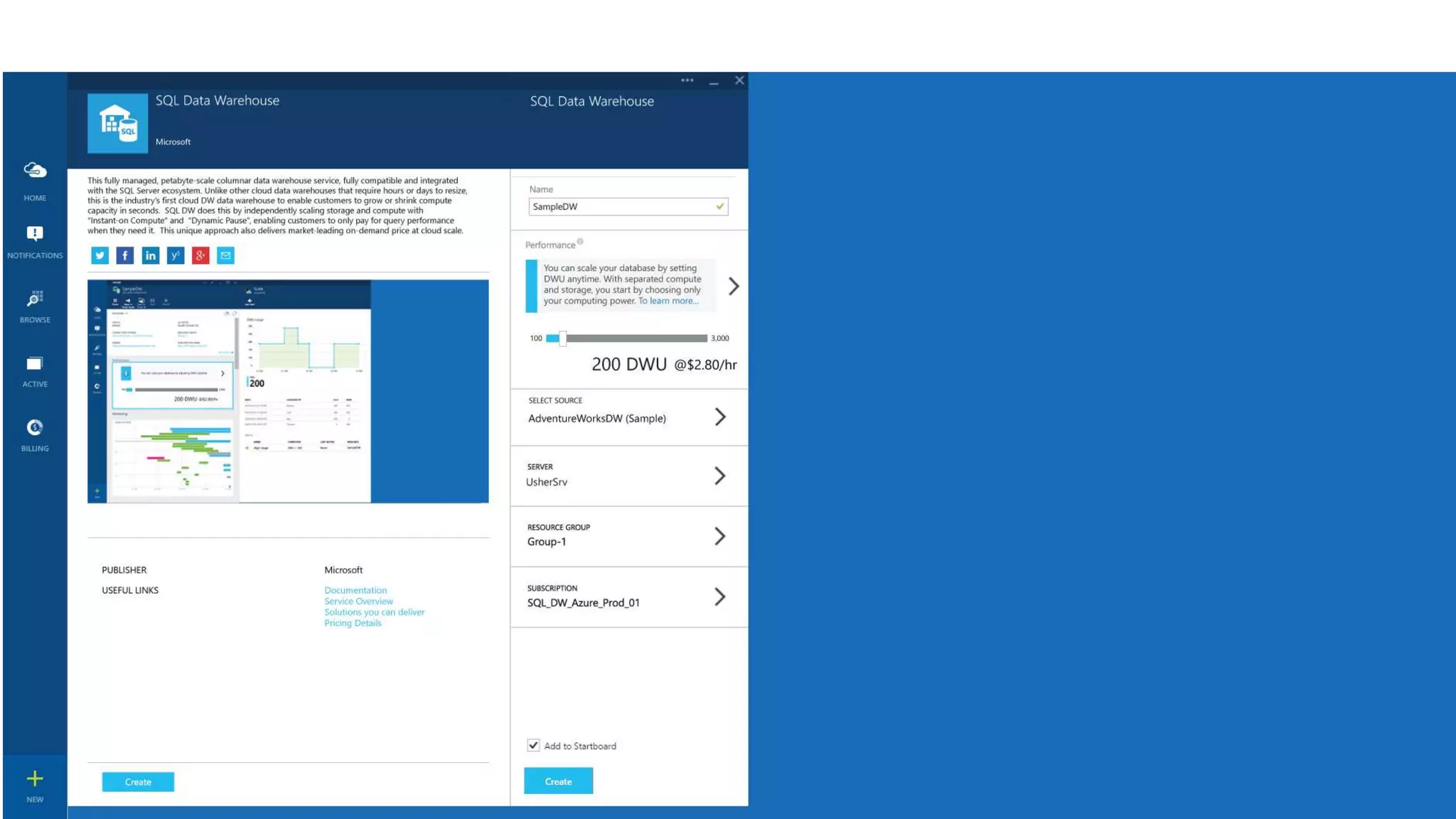
The document outlines Microsoft's evolution of data warehouse solutions, focusing on the Azure SQL Data Warehouse, which features Massively Parallel Processing (MPP) capabilities for enhanced scalability and performance. It emphasizes the integration of various services, such as Hadoop and Azure Machine Learning, to manage diverse data sources effectively while maintaining cost efficiency through elastic scaling. The document also highlights the competitive advantages of Azure SQL DW over other services like Amazon Redshift, particularly in terms of elasticity and operational ease.